12- BIOTECHNOLOGY AND ITS APPLICATION
CHAPTER NO.12 BIOTECHNOLOGY AND ITS
APPLICATIONS
A133
WHAT IS TRANSGENIC ORGANISM?
A Transgenic organism is an animal, plant or microbe
whose DNA is manipulated to possess and express an extra (foreign) gene by
using genetic engineering techniques.
Gene that is artificially introduced into the genome
of another organism is called a transgene.
The production of transgenic organisms using these
transgenes is known as transgenesis .
A transgene will code for a protein, which
corresponds to a particular trait.
Transgenes are introduced into the recipient
organism's germ line. Because of the universality of genetic code, a transgene
will allow transgenic organisms to produce the same protein as the original
donor organisms.
The transfected organism gives birth to transgenic
offspring which can further be bred to form a transgenic line.
Transgenic animals can be made by transfer of whole
nuclei or transfer of whole individual chromosomes or fragments as well as by
transfer of DNA.
Transgenic animals are also called transgenics or
Genetically Modified
Organisms or GMOs.
Many bacteria, plants and animals are produced, which
express foreign genes
inside them.
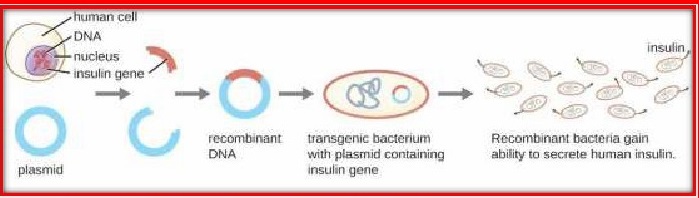
TRANSGENIC MICROORGANISMS:Transgenic bacteria produce many important substances for health and industry,because they reproduce quickly and are easy to grow.Bacterial cells can be genetically modified so that they have the gene for producing human insulin. As these modified bacteria grow, they produce human insulin. This
protein can be
purified and supplied to diabetics GM bacteria are used in the production of
enzymes such as milk-clotting enzymes for cheese production and food/feed
additives such as aspartame and I-lysine.
TRANSGENIC PLANTS
Transgenic plants are plants that have been
genetically engineered, using DNA
techniques to create plants with new
characteristics.Today, approximately 90 percent of the corn, soybeans, and
sugar beets on the market are GMOs. Genetically engineered crops produce higher
yields, have a longer shelf life, are resistant to diseases and pests, and even
taste better. These benefits are a plus for both farmers and consumers. For
example, higher yields
and longer shelf life may lead to lower prices for
consumers, and pest-resistant
crops means that farmers don't need to buy and use
as many pesticides to grow
quality crops. GMO crops can thus be friendly to the
environment than conventionally grown crops.
TRANSGENIC ANIMALS
A transgenic animal is one that has a foreign gene
that has been inserted into its genome .
Transgenic rats, rabbits, sheeps, pigs , cows, and
fish have been produced,although over 95 percent of all existing transgenic
animals are mice
Transgenesis involves a number of methods like:
1. Transfer of the whole nucleus from a somatic cell
into the enucleated egg of
the recipient animal.
2. Transfer of a part of dissected embryo into the
enucleated unfertilized egg.
3. Transfer of a chromosome or chromosomal fragments
4. DNA microinjection technique. The new gene is introduced directly into the
fertilized ovum.
5. Gene targeting using embryonic stem cells: The gene is introduced into the
Embryonic stem cell soon after fertilization and
then implanted into surrogate mothers.
1. TO STUDY NORMAL PHYSIOLOGY AND -
DEVELOPMENT PARTICULARLY OF DIFFERENT GENES AND THEIR BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS
Transgenic animals can be specifically designed to
allow the study of how
genes are regulated and how they affect the normal
functioning of the body and
its development e.g., study of complex factors
involved in growth such as an
insulin-like growth factor. By introducing genes
from other species that alter the
formation of this factor and studying the biological
effects that result,
information is obtained about the biological role of
the factor in the body.
2. STUDY OF DISEASE BY USING THEM AS
MODELS:
Many transgenic animals are designed to increase the
understanding of how
genes contribute to the development of diseases such
as cancer, cystic fibrosis,
rheumatoid arthritis and Alzheimer. These are
specially made to serve as models for human diseases, so that investigation of
new treatments for diseases is made possible. Transgenic mice and rats are also
being used as models for human diseases since they are easier to monitor, and
have a
physiology corresponding to many human diseases..
3. TO STUDY VACCINE SAFETY TESTING:Transgenic mice are first to be used as laboratory animals in testing the safety of vaccines before they are used in humans .Transgenic mice are being used to
test
safety of polio vaccine.
4. TO TEST CHEMICAL SAFETY:Transgenic
animals are also used for the toxicity or safety testing procedures. If found
reliable and successful they could replace the use of monkeys in order to test
the safety of batches of the vaccine. Transgenic animals are made to carry the
genes, which make them more sensitive to the toxic substances than the
non-transgenic ones. They are then exposed to toxic substances and effects
are studied. The time required to obtain the results
is less. This is known as
toxicity/safety testing.
6. TO OBTAIN INCREASED PRODUCTION OF
BIOLOGICAL PRODUCTS:
i. In 1997, the first transgenic cow, Rosie,
produced human protein enriched milk (2.4 grams per litre). The milk contained
the human gene alpha-lactalbumin and was nutritionally a more balanced product
for babies than that of natural cow milk.
ii. Transgenic sheep having different foreign genes
have been produced.In the transgenic sheep, wool production was found more than
non transgenic sheep.
iii. Sheep with the gene for growth hormone has also
been formed , they yield more mutton.
iv. Transgenic fishes of many species like carp,
catfish, salmon have been produced by microinjection of genes coding for human
growth hormone.Transgenic fish are twice in size then than non transgenic fish.
7. INMOLECULAR FARMING:The
method of manufacturing drugs in transgenic animals is called molecular
farming. The transgenic animals can revolutionize the pharmaceutical industry
by providing large quantities of valuabledrugs and proteins.
i) Transgenic goats have been used to produce tissue plasminogen activator which helps in dissolving blood clots and is useful for treating coronary
thrombosis.
ii)Female sheep having human anti haemophilic factor
IX gene in their genome have been produced.
iii)Transgenic sheep having human protein
(a-1-antitrypsin ) which is used to
treat emphysema.( using sheep), milk which can be
used to treat coronary thrombosis .Thus by transgenesis the animals are
genetically modified in such a way that they start acting bioreactors producing
useful products in abundance and continuously.
8. ORGAN TRANSPLANTATION:Transgenic
animals today are also being used in the field of organ transplantation.Pigs
and mice are being used to grow organs like the heart, ear and pancreas
ISSUES RELATED TO TRANSGENIC
TECHNOLOGY:
There may be health risks associated with
transgenics.
There may be long term effects on the environment
when transgenic animals are released into the field.
Various bioethics consider it is wrong to create
animals that would suffer as a
result of genetic alterations.
CONCLUSION:Many transgenic animals have been
successfully created for a variety of
purposes, and the prospects are enormous.
It holds great potential in many fields including
agriculture, medicine and
industry. With proper research and careful use,
transgenic animals can goa
long way in solving problems.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
PART-A VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
A) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
Q1. Maximum number of existing transgenic
animals is of:
a) Cow
b) Mice
c) Fish
d) Pig.
Q2.Organisms that has had a foreign gene
inserted into them is called:
a) Hermaphrodite
b) Transgenic Organisms
c) Transmuted Organisms
d) Transposon.
Q3.Today transgenic model exist for disease
like:
a) Cold
b) Fatigue
c) Cystic fibrosis
d) Fever
Q4. Which of the following methods should be used to increase crop production without use of chemicals and fertilizers?
a) Use of ancient technique of agriculture
b) Use of genetically modified crops
c) Use of organic fertilizers
d) Use of more water
Q5. Gene used to treat emphysema is:
a) Trypsin 1
b) Beta -1 anti-trypsin
c) Alpha-1
d) Alpha -1 antitrypsin
B) STATE TRUE OR FALSE:
1. Transgenic mice are being developed for use in
testing the safety of vaccines before they are used on humans.
2. Production of transgenic animals require
transfections of eggs or embryos
3. The gene transferred to another organism
artificially by technique of genetic
engineering is called wonder gene.
C) FILL IN THE BLANKS:
1. The first transgenic cow ,Rosie produced human
milk with protein measured
to be
2. The protein secreted in the milk of transgenic
goats can be used in treatment
of disease
A) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
1. (b) mice (approximately 95% of transgenic animals
are transgenic mice)
2 (b) Transgenic animals (Transgenic animals are
those who have a foreign gene within them.)
3.(c) Cystic fibrosis (Transgenic animals serve as a
model for human diseases. Cystic fibrosis is a genetic, hereditary disease that
affects the lungs and digestive system of humans.)
4. (b) use of genetically modified
crops.(Genetically modified crops may increase crop production many times
without use of chemicals and fertilizers. )
5. (d) alpha- 1 anti-trypsin.(alpha- 1 antitrypsin
is used to treat emphysema,
this disease causes breakdown of alveoli cells and
reduces surface area for
exchange of gases.)
B) TRUE /FALSE:
1 True
2 True
3 False (The gene transferred to another organism
artificially by technique of
genetic engineering is called transgene)
C) FILL IN THE BLANKS:
1. 2.4grams per litre
2. coronary thrombosis
PART B- SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS:
Q1. What are transgenes and trans genesis?
Q2.The protein secreted in the milk of transgenic
goats can be used in the
treatment of which disease?
Q3. Why transgenic mice are most preferred model of
human diseases?
PART- C LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
Q1.What is transgenic animals? What are the
categories of application of transgenic animals?
Q2. Write the role of transgenic animals in vaccine
safety.
A134
INTRODUCTION
BIOTECHNOLOGY is the integration of natural science
and organisms, cells,parts and molecular analogues for products and services
useful to mankind.
BIOTECHNOLOGY HAS A WIDE RANGE
APPLICATIONS:
a) Biopharmaceuticals
b) Therapeutics
c) Diagnostics
d) Genetically modified crops for agriculture
e) Processed food
f) Bioremediation
q) Waste treatment
h) Energy production
GREEN REVOLUTION succeeded in increasing the yield
of crops by the use of agrochemicals but these are often too expensive so
through genetic
engineering introduced GENETICALLY MODIFIED CROPS.
GENETICALLY MODIFIED PLANTS OR
TRANSGENIC PLANTS:The plants in which foreign genes have
been introduced through genetically engineering are called TRANSGENIC PLANTS.
METHOD FOR MAKING OF TRANSGENIC PLANTS:
Isolate DNA that codes for the protein you want to express.
Insert the DNA into a plasmid.
Insert the plasmid into bacteria. Grow a large
amount of bacteria containing this plasmid.
Dip the flowering plant into a large amount of
bacteria.
Give bacteria the opportunity to insert the DNA into
the plant cells.
Select for plants that have the insertion.
INSECT RESISTANCE IN TRANSGENIC PLANTS:
Soil bacterium Bt. Cotton (Bacillus thurengenesis)
produces proteins that
kill insects like lepidopteron (bud worm),
coleopteran’s (beetles) and dipterans (flies). These crystals contain a toxic
insecticidal protein. The Bt.
toxin form proteins exist as inactive PROTOXINS but
once insects ingests
the inactive toxin it is converted into an active
form of toxin that solubilizes
the crystals. The activated toxins bind to the
surface of midgut epithelial
cells and create pores which cause cell swelling and
lysis and finally cause
death of the insect.
Bt. toxins genes were isolated from Bacillus
thurengenesis and incorporated into crop plants such as cotton.
Most of Bt. toxins are insect-group specific. The
toxin is coded by a gene named Cry. For e.g. proteins encoded by the genes
crylAc and
cryll[Ab control the cotton bollworms. Similarly,
cry[Ab has been introduced in Bt.corn to protect the same from corn borer.
PEST RESISTANCE IN TRANSGENIC PLANTS:
(PROTECTION AGAINST NEMATODES):
A nematode Meloidogyne incognitia infects the roots
_of tobacco plants causing a reduction in yield. It can be prevented by RNA
interference (RNAi)strategy. RNAi is a method of cellular defence in all
eukaryotic organisms.
HERBICIDE RESISTANT TRANSGENIC PLANTS:
Weeds such as Striga decrease crop yields and
quality by competing with crop plants for light, water and nutrients. Weeds are
to be removed with the help of herbicides. For e.g. ROUNDUP READY transgenic
plant has been
produced and commercialised.it is tolerant to
herbicide ROUNDUP (trade name).
MOLECULAR FARMING:Production
of proteins encoded by transgenes in animals/crops; the
proteins recovered from milk, urine, seeds is called
MOLECULAR FARMING.
ADVANTAGES OF TRANSGENIC PLANTS:
Pest resistant crops
Tolerance against environment stress
Reduction in post- harvest losses
Herbicide resistance
Increasing nutritional value of food
DISADANTAGES OF TRANSGENIC PLANTS:
Environmental hazards
Human health risks like allergies
PART: A_ VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
(A) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
1. Bt cotton variety that was developed by
the introduction of toxin gene of
Bacillus thurengenesis (Bt) is resistant
to:
(a) Insect pests
(b) fungal diseases
(c)plantnematodes
(d) insect predators
2. Consumption of which one of the
following foods can prevent the kind of blindness associated with vitamin ‘A’
deficiency?
(a) ‘Flavr Savr tomato
(b) Canolla
(c) Golden rice
(d) Bt-Brinjal
3. The process of RNA interference (RNAi)
has been used in the development of plants resistant to:
(a) Nematodes
(b) fungi
(c) viruses
(d) insects
4. Golden rice is a transgenic crop of the
future with the following improved trait-
(a) Insect resistance
(b) high lysine (essential amino acid) content
(c) High protein content
(d) high vitamin-A content.
5. In RNAi, the genes are silenced using-
(a)ds-RNA
(b)ss-DNA
(c)ss-RNA
(d)ds-DNA
B. TRUE AND FALSE:
1. Meloidegyne incognitia infect stem of tobacco
plant
2. RNA interference is essential for the cell
defense.
C. FILLIN THE BLANKS:
1. The alkaline pH in the midgut of insect larvae
triggers the activation of .
2. Using Vectors, nematode-specific genes are
introduced into host plants.
3. The genes crylAb and cryllAb produce toxins
against and ,respectively.
ANSWERS KEY: PART -A
A. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
1. (a) Insect pests
2. (c) Golden rice
3. (a) Nematodes
4. (d) High vitamin-A content
5. (a) ds-RNA
B. TRUE OR FALSE:
1. FALSE, It infects roots of tobacco plant.
2. TRUE
C. FILL IN THE BLANKS:
1. Bt.toxin
2. Agrobacterium
3. Corn borer, cotton bollworm.
PART: B SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. What are Cry proteins? Name an organism that
produces it.
2. What are the problems associated with GMF.
3. Nematode resistant transgenic plants have been
produced. Explain diagrammatically.
PART: C LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. What is the importance of Biotechnology in
agriculture explain in detail.
A135
INTRODUCTION
Recombinant DNA Technology in Biotechnology plays a
very important role in large
scale productions of safe and more effective
recombinant therapeutics.
RECOMBINANT THERAPEUTICS-Recombinant
pharmaceuticals or therapeutics is created by inserting genes from one species
into a host species, often yeast or bacteria.For example, In case of insulin
production, genes coding for human insulin are inserted into bacteria. Bacteria
produce insulin, which is harvested and used for diabetic patients.
ADVANTAGES OF RECOMBINANT THERAPEUTICS:
Recombinant therapeutics never induce unwanted
immunological responses as is
common in case of similar products isolated from
non-human resources or other
animals which contain other proteins and generate
immune responses.Recombinant therapeutics is produced in very large amounts and
also very easy to produce.
These drugs are very effective with no any kind of
side effects.Production of these drugs are time and money saving.30 recombinant
therapeutics have been approved for human use on word level but in India 12 of
these are approved and presently being marketed.
NATURAL PRODUCTION OF INSULIN:Diabetes-
It is a type of disease when blood glucose is too high.Insulin- This is a
hormone produced by pancreas. It converts extra blood glucose
into glycogen which further stored in liver.
In humans insulin is synthesized as a prohormone
(inactive form) and consists of
three polypeptide chains: chain A, chain B and an
extra chain called C-peptide.
During its processing C-peptide is removed and chain
A and chain B joined by
disulfide bonds. Then hormones become fully mature and functional.
In diabetic patient enough insulin not produced which results in
high blood sugar level.In past insulin isolated from pancreas of slaughters
animal pig and cow. Sometimes it cause allergy.
BIOTECHNOLOGICAL PRODUCTION OF INSULIN:
In 1983 Eli Lilly an American company took
initiative. Company prepared two DNA
sequence correspond to A and B chain of insulin and
introduce them into plasmid
of Escherichia coli bacteria separately and produce
corresponding A and B chain
separately in separate culture medium or in separate
bioreactor.In next step chain A and B extracted and combined by creating
disulfide bond to form final product (Human insulin) or HUMULIN.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
PART: A VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
(A) MCQs:
1. Insulin hormone consist of of —
a. Polypeptide chain
b. Lipid molecules
c. Oligosaccharides
d. Nitrogen oxides molecules
2. Recombinant pharmaceutical insulin
produced by using-
a. Fungi
b. Eukaryotic cell
c. Bacteria
d. Virus
3. Which bond hold together amino acids
chain in insulin hormone?
a. Hydrogen bond
b. Peptide bond
c. Disulfide bond
d. Ester bond
4. How many recombinant pharmaceutical
product approved in India for
human use?
a. 30
b. 12
c. 22
d. 15
5. Which gland produces insulin hormone?
a. Pituitary gland
b. Thyroid gland
c. Pancreas gland
d. Liver
(B) TRUE/FALSE:
1. Insulin hormone consists of lipids and organic
acid.
2. Insulin isolated from other slaughtered animal
not cause any kind of
allergy in human being.
3. In 1983 Eli Lilly an American company took
initiative to produce
recombinant insulin.
(C) FILL UPS:
1. ____ Number of recombinant pharmaceutical
products approved for
human use on word level.
2. It is very easy to produce on a large scale with
the help of
biotechnology.
ANSWER KEY: PART -A
MCQs:
1. a Polypeptide chain
2. c Bacteria
3. c Disulfide bond
4. b12
5. c Pancreas gland
TRUE/FALSE:
1. false
2. false
3. true
FILL UPS:
1. 30
2. Recombinant therapeutics
PART:B SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. How is Prohormone different from hormones?
2. Why is recombinant therapeutics safe for human
use?
3. What is c-peptide?
PART: C LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. Describe the role of biotechnology in large scale
production of recombinant pharmaceuticals with the help of an example insulin.
A136
INTRODUCTION
GENE THERAPY is a collection of methods that allows
correction of a gene defect that has been diagnosed in a child/embryo.
Genes are inserted into a person’s cells to treat a
disease.
Correction of a genetic defect involves delivery of
a normal gene into the
individual or embryo to take over the function and
compensate for the non-
functional gene.
The first clinical gene therapy was given in 1990 to
a 4-year old girl with
Adenosine De Aminase (ADA) deficiency.
GENE THERAPY is therapeutic treatment of defective
heredity by introduction of normal healthy and functional genes to silence the
defective genes.
ADA DEFICIENCY:ADA
(adenosine deaminase) enzyme is crucial for the immune system to
function.
In some children ADA deficiency can be cured by bone
marrow transplantation or by enzyme replacement therapy.
STEPS OF GENE THERAPY:
Lymphocytes from the blood of the patient are grown
in a culture outside the body.
A Functional ADA cDNA (Complementary DNA produced by
reverse transcription using a retroviral vector) is introduced into these
lymphocytes which are returned to the patient.
Now these cells are not immortals, so the patient
requires periodic infusions of such genetically engineered lymphocytes.
For a permanent cure, the genes are isolated from
cells producing ADA & are introduced into cells at early embryonic stage.
This is
however not possible.
Therefore in 1990 midway approach is adopted to cure
a 4-year old girl,Ashanti.
MAJOR REQUIREMENT OF GENE THERAPY USING
RETROVIRUSIS:
The isolation of the desired gene
Amplification of the desired gene
Aretrovirus for removal of viral genes
Insertion of desired gene
Helper retrovirus lacking packing sequence.
PROCEDURE:
ADA gene was taken out from leucocytes of a healthy
person.
It is amplified in bacteria and inserted in
retrovirus, from which viral!genes had been taken out.
A helper retrovirus devoid of packing sequence was
also prepared.
Lymphocyte stem cells from bone marrow of patient
were taken out.
These lymphocytes are now injected with two types of
retroviruses,one carrying ADA gene and other helper.
The normal ADA gene begins to express in the
lymphocyte stem cells, now called transformed stem cells.
The transformed healthy stem cells, now introduced
into the bone marrow of the patient.
The immune system of the patient now becomes
functional.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!!
PART: A VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
A) MULTIPLE TYPE QUESTIONS:
Q1: A genetic disorder can be cured
through:
a) rDNA technology
b) embryo transfer
c) gene therapy
d) all of the above
Q2: Gene therapy in humans was first
practiced to cure:
a) Cystic fibrosis
b) Haemophilia
c) Thalassemia
d) ADA deficiency/severe combined immuno deficiency
disease
Q3: In gene therapy the genetic defect
is corrected by delivery of which gene?
a) Incorrect
b) Mutant
c) Normal
d) Jumping
Q4: ADA stands for:
a) Adenosine nucleotide amine
b) Vitamin A deficiency
c) Adenosine deaminase
d) A double bond amine
Q5: ADA deficiency can be permanently
cured by:
a) Bone marrow transplantation
b) Enzyme replacement therapy
c) Gene therapy at early embryonic stages
d) All of these
B) TRUE/FALSE:
1) Lymphocytes are immortal.
2) ADA enzyme is crucial for immune system to
function.
3) A functional ADA cDNA is introduced using
retroviral vector.
C) FILL UPS:
1) The first clinical gene therapy was givenin tt.
2) The patient requires periodic infusionof_ tt.
ANSWER KEY: PART-A
A) MULTIPLE TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. C) Gene Therapy
2. D) ADA deficiency/severe combined immuno
deficiency disease
3. C) Normal
4. C) Adenosine deaminase
5. C) Gene therapy at early embryonic stages
B) TRUE/FALSE:
1) False
2) True
3) True
C) FILL UPS:
1) 1990
2) Genetically engineered lymphocytes.
PART: B SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
Q1: What is meant by gene therapy?
Q2: What is ADA Deficiency?
Q3: How ADA Deficiency can be cured?
Q4: What is retroviral vector?
PART: C LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
Q1: Illustrate in detail gene therapy using ADA
deficiency?
A137
INTRODUCTION
ETHICAL ISSUES:Certain acts are regulated by
communities to consider their legitimacy.
Such regulations are called ETHICS.ETHICAL ISSUES
occur when a given decision, scenario or activity creates a conflict with a
society’s moral principles.
ETHICAL ISSUES:
I. Introduction of a transgene from one species into
another species violates the integrity of species.
ll. Biotechnology may lead to unforeseen risks to
the environment,including risk to biodiversity. It can disturb the existing
ecological balance.
Ill. Utilization of animals !In biotechnology causes
great suffering to them.
IV. There is another biological damage .it can
accidentally create new infectious agents.
V. When animals are used for production of
pharmaceutical proteins they are virtually reduced to the status of a factory.
BIO PIRACY:Pirates
in general terms were blood thirsty. They stole and killed other to enrich
themselves. The bio pirates are slightly different. They do not kill, they
patent. They are completely protected by law asthe result, no body hurts them.
EXAMPLES OF BIOPIRACY:For
thousands of years Neem is being used in India for killing pests and as
medicine. One of the American companies patented Neem.As a result anybody using
Neem will have to pay for it. This was called legalized theft.The free heritage
of seeds or knowledge can be protected by patent. The basic meaning of PATENT
is intellectual property right or IPRs. If the product is not patented, it may
be freely shared between everybody who required them, but after getting its
patent one will have to buy it to use it legally.
BIOPATENT help in economic
growth for individual involved and country concerned. Biopatents are being done
due to their ethical and political values also. Sometimes the unplanned Genetic
modification of organisms may produce unpredictable harmful results. So the
Indian government set up
genetic engineering approval committee (GEAC), which
keeps an eye on the validity of GM approach and the safety of GM organisms for
the public services like food and medicine services.
A nice example of bio patency of indigenous
biological resources by an influential corporate is that Basmati rice an
important food grains crop being grown in the Asian region even sent thousands
of years in 1977.
US patent and trade mark office granted its bio
patent to an American company though it was produced by crossing Indian basmati
rice variety with semi-dwarf variety.
BIOETHICS:Certain
acts are regulated by communities to consider their legitimacy. Such regulation
is called ethics. Bioethics includes standards followed by us to
regulate the activities linked with biological
activities.BIOETHICS concerns related to biotechnology are:
I. For the production of pharmaceutical products
like Protein many animals are
reduced to thestatus of factory.
ll. Animals undergo great physical sufferings while
performing experiments on them.
lll. There is violation of integrity of species due
to transferring of a transgene
from one speciesto another.
IV. Concept of humanness is diluted due to
introduction of human genes to various animals orvice versa.
V. Biotechnological studies have been considered as
mere exploitation.Biodiversity may be affected due to biotechnological
experiments, thus posing a threat to environment.
BIOPATENT:Government
grants the patent to certain inventors, a permission to use invention for
commercial purpose. Patent is given for:
a) Producing new product or invention.
b) Modified and improved earlier invention.
c) Technical know-how.
d) New designing concept.
BIOPATENT are being granted by the government for
biological entities and products derivedfrom them.BIOPATENT are given:
a) For discovery of new strains of microorganisms.
b) Transgenic (genetically modified) pants and
animals.
c) Discovery of cell lines.
d) New biotechnological methods.
e) Unearthing the DNA sequences.
f) Formation of new product.
g) New product techniques.
Some Interesting Aspects of Bio Piracy:
Mae-wan ho biologist from Open University, UK (1999)
is of the view that transgenic agriculture is needed to feed the world .The
tightening of corporate monopoly on food by patenting the seeds may cause famine.
It also diverts the various countries to successful
Implementation of sustainable, organic agriculture which can ensure food
security and better health for ail.
Adalberto Antonio, judge of state of Amazons points
out that Harry Wickham took about 70,000 seedson behalf of new gardens,
Britain. This only act plunged the state of Amazons in to starvation for year’s
altogether.
American countries are also opposing the new patents
on life and to commercialization of science.
Several scientists have called for various
governments to improve a moratorium on global releases oftransgenic crops and
to ban patents on living organisms.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!!
PART: A VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
A) Multiple choice questions:
1. bt cotton is not :
a) AGM plant
b) Insect resistant
c) Abacterial gene expressing system
d) Resistant to all pesticides
2. GEAC stands for:
a) Genome engineering action committee
b) Ground Environment Action committee
c) Genetic engineering approval committee
d) Genetic and environment approval committee
3. Golden rice is:
a) A variety of rice grown along the yellow river in
china
b) Long stored rice having gene for b-carotene
c) Wild variety of rice with yellow colored grains.
d) All the above
B) Fill in the blanks:
1. Plants , bacteria, fungi and animals whose genes
have been altered by
manipulation called
2. In GM plants, genetic modification enhances
3. Basmati rice is distinct for its unique aroma and
C) True/ False:
1. Genetic engineering approval committee is
expansion of GEAC.
2. First Genetically modified plant commercially
releases in India is Bt-cotton..
3. Golden rice is rich in vitamin A.
ANSWER KEY: PART -A
A) Multiple choice questions:
1. d) Resistant to all pesticides
2. c) Genetic engineering approval committee
3. c) Wild variety of rice with yellow colored
grains.
B) Fill in the blanks:
1. genetically modified organisms
2. nutritional
3. flavour
C) True/ False:
1. True
2. True
3. True
PART: B SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. Right a short note on Bio piracy.
2. What are transgenic organisms?
3. What are disadvantages of GM crops?
PART: C LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. What do you mean by bio-patent? Write its uses
and abuses?
A138
RECAPITULATION
Biotechnology has given to humans several useful
products by using microbes, plant, animals and their metabolic machinery.
Genetic engineering involves the isolation of
specific genes, making of copies of genes and their transfer to target genomes.
Genetically Modified organisms have been created by
using methods other than natural methods to transfer one or more genes from one
organism to another, generally using techniques such as recombinant DNA
technology.
Bacteria, yeast and cultured plant and animal cells
are commonly used as hosts for recombinant DNA experiments.
Agriculture has been a major focus of genetic
engineering activity.
GM plants have been useful in:
1. Increasing crop yields
2. Reduce pest harvest losses
3. Make crops more tolerant of stresses
4. Improve nutritional value of foods
5. Produce pest resistant crops
Transgenic animals are also used to understand how
genes contribute to the
development of a disease.
In gene therapy, a faulty gene is replaced with a
normal healthy gene, to treat disease where other medical approaches are not
effective like cancer,AIDS and Haemophilia.
Despite benefits, the ethical, social and legal
implications of these potent
gene technologies have led to considerable public
concem over the possibility of accidentally producing new pathogens or “Genetic
Monsters”
Q1. Crystals of Bt toxin produced by some
bacteria do not kill the bacteria themselves because:
a) bacteria are resistant to the toxin
b) toxin is immature;
c) toxin is inactive;
d) Bacteria encloses toxin in a special sac.
Ans.1 (C) toxin is inactive: In bacteria, the toxin
is present in an inactive form, called protoxin, which gets converted into
active form when it enters the body of an insect.
Q2. What are transgenic bacteria?
Illustrate using any one example.
Ans.2. Transgenic bacteria contain foreign gene that
is intentionally introduced into its genome. They are manipulated to express
the desirable gene for the production of various commercially important
products.
An example of transgenic bacteria is E.coli. In the
plasmid of E.coli, the two DNA sequences corresponding to A and B chain of
human insulin are inserted, so as to produce the respective human insulin
chains. Hence, after the insertion of insulin gene into the bacterium, it
becomes transgenic and
starts producing chains of human insulin .Later on,
these chains are extracted from E. coli and combined to form human insulin.
Q3. Compare and contrast the advantages and
disadvantages of production of genetically modified crops.
Ans. 3
Q. 4) What are cry proteins? Name an organism
that produces it. How has man exploited this protein to his benefit?
Ans.4 1. Cry proteins refer to the protein crystals
containing a toxic insecticide.
2. It is produced by soil bacterium, Bacillus
thuringiensis.
3. The genes encoding cry proteins called Bt toxic
genes were isolated from
B.thuringiensis and incorporated several crop plants
such as Bt cotton, Bt corn etc., to provide resistance against insect pests .
Q.5) What is gene therapy? Illustrate using
the example of adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency?
Ans.5 Gene therapy is a process of introduction of
DNA into an organism in
order to treat a disease. It is used to replace a
missing gene product or to
correct mutant alleles. e.g. - Human beings.
ADA (adenosine deaminase deficiency) is a rare
genetic disorder caused due to deletion of the gene for adenosine deaminase.
This enzyme is critical for the normal functioning of the immune system. This
disorder can be
treated by gene therapy wherein the gene is
transferred into early embryonic cells of the bone marrow for permanent
utilization.
Q.6) Diagrammatically represent the experimental steps in cloning and
expressing a human gene ( say the gene for
growth hormone ) into a bacterium like E. coli?
Ans.6 DNA cloning is a method of producing multiple
identical copies of specific template DNA. It involves the use of a vector to
carry the specific foreign DNA fragment into the host cell. The mechanism of
cloning and transfer of gene for growth hormone into E. Coli is represented
below:-
Q.7) Can you suggest a method to remove oil
(hydrocarbon) from seeds based on your understanding of r DNA technology and
chemistry of oil?
Ans.7 Recombinant DNA technology or rDNA is a
technique which is used for the manipulation of the genetic material of an
entity in order to obtain desired results. The genes for the formation of oil
in the seed should be
identified. The appropriate genes should be removed
with the help of restriction endonucleases. Such DNA should then be treated
with DNA ligases to make seal DNA at the broken ends. These cells when grown
aseptically on nutrient medium will differentiate
into a new plant whose seeds
will not have oil in them.
Q.8) Find out from internet what is golden
rice.
Ans. 8 Golden Rice, a variety of rice, Oryza sativa
is a genetically modified crop, which is developed as a fortified food to
supply them to areas where there is scarcity of dietary vitamin A, as Golden
Rice is richly supplied with vitamin A.Golden Rice consists of a precursor of
pro vitamin A, known as the beta carotene, inserted into the rice through the
process of genetic engineering.This is a simpler and low priced alternative. It
was developed at Swiss Federal Institute of Technology by professor Ingo
potrykus and Peter Beyer.
Q.9) Does our blood have proteases and
nucleases?
Ans.9 No, blood does not have proteases and
nucleases. But some proteases do exist in its inactive form. If it would have
been found in blood and cells, it would have been digested.
Q.10) Consult internet and find out how to
make orally active protein pharmaceutical. What is the major problem to be
encountered?
Ans.10 Orally active protein pharmaceuticals contain
biologically active material such as proteins, antibodies and polymeric beads.
It is administrated orally into the body through various formulations.These
proteins are used for treatment of various diseases such as Hepatitis B,
Herpes, and Influenza etc. and are also used as vaccines.However the oral
administration of these proteins has some problems related to it. Once these
proteins are ingested, the proteases present in the stomach juices denature the
protein. As a result, there effect will be nullified.
Hence it is necessary to protect the therapeutic
protein from digestive enzymes, if taken orally. This is the reason for the
proteins to be injected directly into the target site.
A139
RECAPITULATION
Dear students we have discussed the chapter no. 12
“Biotechnology and its applications” and its NCERT questions in previous daily
dose assignments. Now let us revise important concepts of this chapter.
Biotechnology is the process of using living
organisms or their enzymes or their molecules to produce products and processes
for the welfare of mankind.
Application of DNA manipulation ranges from cloning
genes to cloning organisms including transgenic microbes, agriculturally
important crops and farm animals. Humans have used biotechnology in the
improvement of the
quality of life, in the field of health and food
production.
APPLICATIONS IN MEDICINES:
1. GENETICALLLY ENGINEERED INSULIN: -Insulin
is produced in 8 cells of islets of Langerhans synthesised as proinsulin which
is inactive form of insulin. Insulin is made up of two short polypeptide chains
Chain A (having 21 amino acids) and Chain B (having
30 amino acids) linked by disulphide bonds. But
proinsulin contains one more polypeptide chain called C chain which acts as
linker chain, helps to bind sulphur molecules on both A and B chain. As soon as
disulphide
bond is formed C chain disappear and active insulin
molecule is formed.
Earlier insulin used by diabetics were extracted out
of pancreas of slaughtered animals. In some patients, due to insulin received
by animals,other types of reaction against allergies or external proteins could
be started.
To avoid these situations, in 1983, a US company
named Eli Lily designed two DNA sequences coding for A chain and B chain and
introduced them into the plasmid of E. Coli. Chains
A and B were produced separately extracted and combined by creating disulphide
bonds of form human insulins.
Insulin (Humulin) was the first hormone which is
produced artificially by culturing bacteria by employing recombinant DNA
technology.
GENE THERAPY:Gene
therapy in humans is to replace “a faulty gene” by a normal
healthy functional gene.
The first clinical gene therapy was given in 1990 to
a 4-year-old girl with Adenosine De Aminase (ADA) deficiency. The enzyme is
crucial for the immune system to function.
As a first step towards gene therapy: Lymphocytes
from the blood of the patient are grown in a culture outside the body.
A functional ADA (using a retroviral vector) is then
introduced into these lymphocytes which were then returned to patient. But life
of lymphocytes is short so such patients are
required to give infusion at the short intervals
regularly.
However, if this treatment is done at early
embryonic stage, is could be a permanent cure.
MOLECULAR DIAGNOSIS:DNA
technology has provided a broad range of tools to diagnose
various diseases like food poisoning Salmonella, pus
forming Staphylococcus, hepatitis virus, HIV and so on.
By testing the DNA of prospective genetic disorder
in carrier parents, their
genotype can be determined and their chances of
producing an afflicted child can be predicted.
ELISA, PCR are some of the techniques by which early
detection of disease
can be done. ELISA (Enzyme Linked Immuno-Sorbent
Assay) is based on the principle of antigen antibody interaction.
In suspected AIDS patients, PCR for the
identification of HIV is being used routinely now a day.
It is also used to detect the mutations occurring in
the genes of suspected
cancer patients.
TB can also be detected by the antigen antibody
reaction.
APPLICATIONS IN AGRICULTURE:Though
Green Revolution succeeded in tripling the food supply but it is not possible
to fill the growing needs of human population. For this, use of Genetically
Modified Crops is the only solution.
GENETICALLY MODIFIED ORGANISMS:Plants,
bacteria, fungi and animals, whose genes have been converted by manipulation,
are called Genetically Modified Organisms.
The use of GM plants is beneficial in
many ways:
i. GM crops are more tolerant to abiotic stresses
(cold, drought, salinity,heat).
ii. Less dependency on chemical pesticides.
iii. Helped to reduce post-harvest losses.
iv. Increased efficiency of mineral usage by plants.
v. Increase in nutritional level of food e.g.,
Vitamin A enriched rice.
Vi In the use of biotechnology in agriculture it is
the production of pest resistant crops that reduced the use in the amount of
pesticide.
Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) toxin genes are cloned
by bacteria and introduced in plants to produce pest resistant crops e.g., Bt
cotton, Bt rice, Bt tomatoes, Bt potatoes and Bt soyabean etc.
A. Bt cotton: -
Some strains of Bacillus thuringiensis produce proteins that can kill certain
insects. But these proteins are active only when they come in contact with
alkaline pH. As plants do not have alkaline pH, the specific protein remains
inactive. But when any insect or larva feed on
such plants, it will die.
B. PEST RESISTANT PLANTS: -
To obtain pest resistant plants by RNAi (RNA interference techniques) e.g., the
nematode Meloidegyme
incognitia reduces the yield of tobacco plant.
In tobacco plant dsRNA is formed by using Nematode
gene which acts as defence mechanism.
When nematode enters the plant or feed on such
plant, MRNA formed by its own gene binds with dsRNA formed from same gene in
the plant. As they bind mRNA cannot produce proteins
required for the growth of nematode.
C. OBTAINING HIRUDIN from the seeds
of Brassica napus by introducing hirudin producing gene in the plant.
D. FLAVR SAVR TOMATOES : -Complimentary
DNA of enzyme Poly Galact Uronase is introduced in plant which silenced the
production
of Pectin Protein and delayed the ripening of fruit.
E. GOLDEN RICE
is the transgenic variety of basmati rice which gives high yield and rich in
Vitamin A. It is used to cure the deficiency of Vitamin A.
TRANSGENIC ANIMALS:Animals
that had their DNA manipulated to possess and express an extra gene are called
transgenic animals. Transgenic rats, rabbits,pigs, sheep, cows and fish have
been produced.
USES OF TRANSGENIC ANIMALS:
1. To study normal physiology and development
controlled by various genes.
2. To study how genes contribute to the development
of diseases.
3. Transgenic that produce useful biological
products can be created by introduction of DNA (gene) which codes for a
particular product.
In 1997, the first transgenic cow Rosie produced
human protein enriched milk, which was more beneficial for human infants than
ordinary cow milk.
4. Transgenic mice are developed for use in testing
the safety of vaccines before they are used on humans.
5. Transgenic help in chemical safety testing.
ETHICAL ISSUES:Genetic
modification of organisms can have unpredictable results when
such organisms are introduced into the ecosystem.
GEAC (Genetic Engineering Approval
Committee):set up by Indian Government make
decision regarding the validity and safety of GM research.
BIOPIRACY
BIOPIRACY: is the term related to using biological
resources without proper authorisation and compensatory payments from
multinational companies and other organisations to a nation or its people.
The Indian Parliament has recently cleared the
second amendment of the Indian Patients Bill that takes such issues into
consideration.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!!
(A) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
1. Insulin consists of two short
polypeptide chains; chain A and chain B, that are linked together by:
a.) Hydrogen bridges
b.) Ester bridges
c.) Peptide bridges
d.) Disulphide bridges
2. The Bt toxin is produced by a bacterium
called:
a.) Bacillus termegiensis
b.) Bacillus thermogiensis
c.) Bacillus thuringiensis
d.) Bacillus trichonegiensis
3. Golden colour of Rice is due to occurrence
of:
a.)Vitamin A
b.)Vitamin C
c.) Vitamin K
d.)Vitamin Be
4. Transgenic animals are used in:
a.)Normal physiology and development
b.)Study of disease
c.) Vaccine & Chemical safety testing
d.)All of the above.
5. In RNAi, genes are silenced using:
a.)ss RNA
b.)ds DNA
c.)ds RNA
d.)ss DNA
(B) FILL IN THE BLANKS:
1. Flavr savr is the variety of tomato.
2. Transgenic hirudin is obtained from .
3. was the first hormone which is produced
artificially by using recombinant DNA technology.
4. A transgenic plant having high storage protein is
.
5. part of tobacco plant is infected by incognita.
(C) TRUE/ FALSE:
1. SCID is caused by the defect in the gene for the
enzyme Adenosine deaminase.
2. The growth of nematodes is controlled by using
RNA interference technique.
3. Bt toxin in coded by a gene named Sad.
4. ELISA is the test for HIV.
5. Salt tolerant transgenic has been developed for
tomato.
ANSWER KEY: PART - A
1.) (d) Disulphide bridges
2.) (c) Bacillus thuringiensis
3.) (b) Vitamin C
4.) (d) All of the above
5.) (c) ds RNA
1.)transgenic
2.)Brassica napus
3.)Insulin (Humulin)
4.)Potato
5.)Root
1.)True
2.) True
3.)False: Bt toxin is coded by a gene named cry.
4.)True
5.) True
PART B: SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. What is GMO? How does it differ from a hybrid?
2. What is ELISA?
3. What is Biopiracy?
4. What is GEAC? What are its main objectives?
5. How are ‘cry’ and ‘CRY’ different from each
other?
PART C: LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. Explain five areas where biotechnology has
influenced human lives?
2. What are transgenic animals? Enlist any four
areas where they can be
used?
A216
RECAPITULATION
The use of biology to develop technologies and
products for the welfare of human being is known as biotechnology.e
Biotechnology has a wide spread applications in the welfare of human beings.
Biotechnology Application in Agriculture:
Biotechnology has different application in agriculture. It can be used in
agro-chemicals, organic agriculture, and genetically engineered crop-based
agriculture. It can be used to produce genetically modified organisms.
Genetically modified organisms can be obtained by alternation in their genetic
materials.
Genetic medication has: Production of crops which
are resistant to abiotic factors such as heat, cold etc., Pest-resistant crops,
Help to reduce post-harvest losses, Minerals can be used efficiently by the
plants, Food with enhanced nutritional values, eg. Golden rice i.e. Vitamin
‘A’.
The most important application in the field of
biotechnology is the formation of pest resistant plants.
Bt Cotton: Bt toxin is produced by a bacterium
called Bacillus thuringiensis. Bt toxin gene has been cloned from the bacteria
and been expressed in plants to provide resistance to insects without the need
for
insecticides. The toxin is coded by a gene crylAc
name cry. There are a number of them, for example, the proteins encoded by the
genes crylAc and cryllAb control the cotton bollworms.
Another Pest Resistant Plants: Various pests affect
the plants which causes loss as well as decrease in the yield of the plants. A
nematode meloidegyme incognitia infects the roots of tobacco plants and cuases
s
decrease in the yield of the plants. To prevent
this, RNA interference technology was used.
Biotechnology Applications in Medicine: Biotechnology
has contributed a lot in medicine industry. Tne use of biotechnology in
medicine is known as medicinal biotechnology. They provide methods for
the formation of genetically modified insulin known
as humulin. This helps in treatment of large number of diabetes patients.
Gene Therapy: To correct the heredity disease, gene
therapy is used.The correction of gene defects is known as gene therapy. A
normal gene is inserted into the individual or in an embryo to replace the
abnormal
gene.
Molecular Diagnosis: It helps in disease diagnosis
by various techniques such as ELISA, PCR and recombinant DNA technology.
Ethical Issues: GEAC: Genetic engineering Approval
Committee is a committee set of by the Indian Government of oversee all
decisions regarding GM research and the safely of GMOS for public use.
Biopiracy: Use of bio-resources by commercial and
multinational companies and other organizations without the appropriate
authorization and permission from the countries and people concerned without
making
the compensatory payment.
1 MARKS Que/Ans (MCQ AND DEFINITION
TYPE)
Q. 1 Which of the following technique can
serve the purpose of early diagnosis of a disease: (a) Recombinant DNA
technology
(b) PCR
(c) ELISA
(d) All of these
Ans.(d) All of these
Q.2 First hormone produced artificially by
culturing bacteria is:
(a) Insulin
(b) Thyroxine
(c) Testosterone
(d) Adrenaline
Ans.(a) Insulin
Q.3 A transgenic animal has:
(a) Foreign DNA in its cells
(b) Foreign DNA in some of its cells
(c) Foreign RNA in its cells
(d) Both B and C
Ans.(a) Foreign DNA in its cells
Q.4 Which of the following peptide chain is
not present in mature insulin:
(a)A
(b)B
(c)C
(d) None of these
Ans.(c)C
Q.5 ELISA is used to detect viruses where:
(a) DNA probes are required
(b) Southern blotting
(c) Alkaline phosphatase is key reagent
(d)Catalase is the key reagent
Ans.(c) Alkaline phosphatase is key reagent
Q.6 Golden rice is a transgenic crop of the
future with the following improved trait:
(a) High lysine (essential amino acid) content
(b) Insect resistance
(c) High protein content
(d) High vitamin A content
Ans.(d) High vitamin A content
Q. 7 Bt cotton is not:
(a) a GM plant
(b) Insect resistant
(c) A bacterial gene expressing
(d) Resistant to pesticides
Ans.(d) Resistant to pesticides
Q.8 Antitrypsin is:
(a) An antacid
(b) An enzyme
(c) Used to treat arthritis
(d) Use to treat emphysema
Ans.(d) Use to treat emphysema
Q.9 What is biotechnology?
Ans.The use of biology to develop technologies and
products for the welfare of
human being is known as biotechnology.
Q.10 What is transgenic bacteria?
Ans.Those bacteria whose genes are treated by
genetic engineering, are called transgenic bacteria e.g. E. coli bacteria
having human insulin gene.
Q.11 Write a short note on biopiracy.
Ans.It is the use of bioresources, such as
genetically engineered viruses,bacteria, plants and animals by multinational
companies and _ other organisations without proper authorisation from concerned
authorities and
people.
Q.12 Why is proinsulin so called? How is
insulin different from its?
Ans.It is the prohormone which needs to be processed
before it becomes a fully
mature and functional hormone/insulin. Proinsulin
has three polypeptide chains (A, B and C), whereas insulin has only two (A and
B) polypeptide chains.
Q.13 What is gene therapy? Name the first
clinical case where it was used.
Ans.Gene therapy is a collection of methods that
allows the correction of a defective gene. The first clinical gene therapy for
adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency.
Q.14 What are cry genes? In which organism
are they present?
Ans.1. The genes which code for the Bt toxin
proteins, are called cry genes.
2. They are present in the bacterium,Bacillus
thuringiensis.
Q.15 What is Ti-plasmid?
Ans.The Ti-plasmid, which stands for tumor inducing,
is a piece of DNA that
occurs in soil inhabiting plant pathogenic
bacterium.
Q.16 What are transgenic plants?
Ans.These plants whose genes have been altered by
genetic engineering are called transgenic plants. E.g. Bt. Cotton, Bt-tomato,
Flavr-saver variety of tomato.
Q.17 What are transgenic animals?
Ans.Animals that have had their DNA manipulated to
possess and express an
extra (foreign) gene are known as transgenic
animals. Transgenic rats,rabbits, pigs, sheep, cows and fish.
Q.18 What are cry genes?
Ans.These are the genes found in bacteria Bacillus
thuringienis which produce an
insecticidal crystal protein called as cry protein.
Q.19 Mention two objectives of setting up
GEAC by our government?
Ans.1. To make decisions regarding the validity of
GM research.
2. To ensure the safety of introducing GM organisms
for public services.
Q.20 State the role of C-peptide in human
insulin.
Ans.The C-peptide is a short 31-amino acid polypeptide
that connects insulin's A-
chain to its B-chain in the proinsulin molecule. It
is also called as connecting
peptide. It also play important role in the
synthesis of insulin.
A217
RECAPITULATION
INTRODUCTION
BIOTECHNOLOGY-The term Biotechnology was coined in
year 1919 by an agricultural engineer Karoly Ereky, hence he is called as
father of biotechnology.Principles of biotechnology
According to modern biotechnology the main principles of biotechnology are:
1. Genetic Engineering
2. Bioprocess Engineering
3. Recombinant DNA Technology
4.DNA Cloning
BIOTECHNOLOGICAL APPLICATION IN
AGRICULTURE:
Production of GMO (Genetically modified organisms)
Transgenics plants are produced
Bt cotton- Tne genetically modified crop is called
bt cotton as it contain Bt toxin
genes. Bt toxin produced certain proteins that kill
insect
Formation of pest resistant plants using
Agrobacterium vectors
Golden rice is transgenic variety which contain good
quantity of vitamin A
BIOTECHNOLOGICAL APPLICATION IN MEDICINE:
In case of insulin production genes coding for human
insulin are inserted into
bacteria produce insulin which is used for diabetic
patient.Role of biotechnology in molecular diagnosis:
ELISA is based on principle of antigen and antibody
interaction.
Gene therapy is technique of genetic engineering to
replace faulty gene by normal healthy functional gene
PCR is done to amplify the content of DNA
Ethical issues:Introduction of trans genes from one
species into another species violates the integrity of the species there is
another biological damage it can accidently create new infectious agents
2-MARKS QUESTIONS ANSWER
Q1. Name the genetically engineered human
insulin.
Ans. Humulin is the genetically engineered human
insulin
Q2. What do you mean by Golden Rice?
Ans. Golden rice is a variety of rice produced
through genetic engineering
to Bio synthesizes the precursors of beta-carotene.
Golden rice has 23 times
Provitamin - A. The colour of golden rice is golden
due to synthesis of Provitamin - A in entire grains.
Q3. Write brief account on recombinant
Insulin.
Ans. In 1983 ELI LILLY an American company prepared
two DNA Sequences corresponding to A and B chains of insulin such DNA Sequences
were introduced in E-coli plasmid when these
bacteria produced chains than these chains were extracted and combined by
disulphide bonds to form human insulin called Humulin.
Q4. Write the full form of the terms PCR
and ELISA.
Ans. PCR- Polymerase Chain reaction. It is used to
amplify the gene of interest.
ELISA- Enzyme Linked Immuno Sorbent Assay. It is
used for early diagnosis of the disease and results can be obtained at very low
concentration of Pathogen in the body.
Q5. What is Green Revolution? Write the
basic elements.
Ans. Many times increase in yield of food crops due
to improved crop varieties, use of better management practices and use of
agrochemicals.Green revolution had succeeded in tripling the yield of crops due
to
(i)Improved crop varieties.
(ii) Use of better management practices.
(ii) Use of agrochemicals i.e. fertilizers,
insecticides & pesticides.
Q6. What is Ti plasmid? Name the organism
where it is found?
Ans. The Ti plasmid, which stands for tumor
inducing, is a piece of DNA that occurs in soil inhabiting plant pathogenic
bacterium Agrobacterium tumefactions which induces formation of cancerous
Growth called crown gall tumour in several dicot plants.
Q7. What is a Gene Therapy? What is the
cause of Adenosine De Aminase deficiency.
Ans. It is a technique of genetic engineering to
replace a faulty gene by a normal healthy functional gene in humans. The cause
of ADA deficiency is the defective autosomal gene. Thus, this particular gene
does not synthesis
the enzyme adenosine deaminase.
Q8.What are transgenic plants? Give two
examples of these plants.
Ans. These plants whose genes have been altered by
genetic engineering are called transgenic plants.e.g. Bt.cotton,Bt-tomato
Flavr- Saur variety of tomato.
Nemotoda resistant tabacoo plants.
Q9. What are transgenic animajs? Give two
examples of these animals.
Ans. Animals whose genes have been altered by
genetic engineering are called transgenic animals e.g. rosie cow, transgenic
mice, etc.
Q10. What is bio-technology? Name two
important products of bio-technology.
Ans. Branch of microbiology concerned with the use
of microbes, plants,animal cells and their components to generate useful
products & services in industrial processes is called biotechnology
important products.
(i) Biopharmaceuticals, anti-biotics, vaccines
(ii) Fermented beverage
Q11. What are Cry Proteins? Name an
organism that produces it.
Ans. Cry proteins are encoded by genes named cry.
They are produced in Bacillus Thuringienis. Cry proteins are toxic to insects
and act as Insecticides.
Q12. Write note on Biopatent.
Ans. The patent being given to the Biological agents
and their products are called biopatent. Biopatents are awarded for the
following;
(i)Genetically modified microbes
(ii) Gene Sequence
(iii) GM plants & animals
(iv) Biotechnological procedures
Q13. How did the first transgenic cows
Rosie differ from other cows with
respect to quality of milk?
Ans. Rosie produced human protein alpha-lactaalbumin
enriched milk which is nutritionally a more balanced product for human babies.
Q14. What do you mean by Biopiracy?
Ans. Biopiracy refers to the use of bioresources lay
multinational companies & other organizations without proper authorization
from countries & people concerned.
Q15. Name two pest resistant plants
produced bu using DNA recombinant Technology?
Ans. Bt Cotton, Bt Corn, Bt Brinjal are pest
-resistant plants produced by DNA Recombinant technology.
Q16. Name any disease against which vaccine
is developed by DNA Recombinant technology ?
Ans. Hepatitis B the disease against which vaccines
are developed by DNA recombinant technology.
Q17. What is the full form of ADA in ADA
deficiency?
Ans. Adenosine De Aminase Q18. Can you suggest a
method to remove oil from seeds based on DNA Technology and chemistry of oil?
Ans. The oil in seed is composed of glycerol or
fatty cids. Production of these
molecules is governed by particular gene. Such genes
can be removed by using DNA technology. This will help in production of oil
less seeds.
Q19. What are antigens?
Ans. Antigens are the substance that stimulates the
immune system to
produce antibodies. Antigen can be bacteria, virus,
or fungi that can cause infection and disease.
Q.20 Write note on GEAC.
Ans. GEAC stands for Genetic engineering approval
committee. The Indian
Government has set up it for making decisions
regarding the validity of modifications and safety of introducing genetically
modified organisms for public services.
A218
RECAPITULATION
The applications of biotechnology include
therapeutics, diagnostics, and
genetically modified crops for agriculture, processed
food, bioremediation,waste treatment and energy production.
BIOTECHNOLOGICAL APPLICATIONS IN
AGRICULTURE
Production of GMO (Genetically modified organisms).
Formation of pest resistant plants using
Agrobacterium vectors
Transgenic plants are produced Bt cotton- The
genetically modified crop is called Bt cotton as it contains Bt toxin genes. Bt
toxin genes isolated from Bacillus thuringiensis which produces certain
proteins that kill insects such as lepidopterans, coleopterans, and dipterans.
Golden rice is a transgenic variety of which
contains good quantities of beta carotene.
BIOTECHNOLOGICAL APPLICATIONS IN
MEDICINE
Formation of genetically modified insulin Known as
humulin. In the treatment of a large number of Diabetes patients , humulin helps
a lot.
ROLE OF BIOTECHNOLOGY IN MOLECULAR
DIAGNOSIS
Gene therapy is the technique of genetic engineering
to replace a faulty gene by a normal healthy functional gene.
ELISA is based on the principle of antigen-antibody
interaction.Infection by pathogens can be detected by the presence of antigens
or by detecting the antibodies synthesized against the pathogen.
PCR is done to amplify the content of DNA.
ETHICAL ISSUES:The
Indian government has set up organisations such as GEAC (Genetic Engineering Approval
Committee) which are authorised to make decisions regarding the validity of
genetic modifications and safety of introducing genetically modified organisms
for public services.
Biopiracy is use of bio resources by multinational
companies and other
organization without proper authorization from the
countries and people concerned without compensatory payment.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q 1.What is transgenic organism?
Ans: An organism which carries a foreign functional
gene in its genome is termed
as transgenic organism.
Q2. Expand the following terms and mention
one application of each a. PCR b. ELISA
Ans: a) PCR- Polymerase Chain Reaction. It is used
to amplify the gene of interest.
b) ELISA- Enzyme Linked Immuno-Sorbent Assay. It is
used for early diagnosis of disease and results can be obtained at very low
concentration of pathogen in the body.
Q3: What are vaccines?
Ans- Vaccines are either dead or attenuated agents
of disease which when injected into healthy person provide immunity to that particular
disease.
Q4. What do you mean by Golden Rice?
Ans: Golden rice is a variety of rice produced
through genetic engineering to
biosynthesize the precursors of beta- carotene.
Golden rice has 23 times more
provitamin A. The colour of golden rice is golden
yellow due to synthesis of
provitamin A in entire grains.
Q5. Write a note on Bt cotton.
Ans- It is genetically engineered plant. Bacillus
thuringiensis is a naturally
occurring soil bacterium that produces a crystal
protein that is toxic to insect
larvae. Crystal protein genes have been transferred
into cotton plant, enabling the
cotton plant to produce its own pesticides against
insects such as bollworm.
Q6: What are transgenic bacteria?
Ans- The bacteria whose genes have been treated by
genetic engineering is called
transgenic bacteria. E.g. E.coli bacteria having
human insulin gene.
Q7. Define antibiotic.
Ans- An antibiotic is an organic compound produced
by a microorganism that
inhibits the growth of or kills another
microorganism.
Q8: What are Cry proteins? Name an organism
that produces it.
Ans- Cry proteins are encoded by genes named cry
They are produced in
Bacillus thrugiensis. Cry proteins are toxic to
insects and act as insecticides.
Q9: What is Ti-plasmid ? Name the organism
where it is found?
Ans: The Ti-plasmid , which stands for tumour
inducing , is a piece of DNA that
occurs in soil inhabiting plant pathogenic bacterium
Agrobacterium tumefaciens
which induces formation of cancerous growth called
in several dicot plants.
Q10: What are transgenic plants? Give two
examples of these plants.
Ans- The plants whose genes have been altered by
genetic engineering are called
transgenic plants.e.g. Bt cotton, Nematode resistant
tobacco plants.
Q11: Name the genetically engineered human insulin.
Ans- Humulin is the genetically engineered human
insulin.
Q12: Why did bacterial toxins not kill the
bacteria but only the insects?
Ans- Bacillus thuringiensis is not killed by the
bacterial toxins because toxic protein
exists as an inactive protoxin but if it is consumed
by an insect it gets transformed into an active form of toxin due to alkaline
pH of the alimentary canal of insect.
Q13: Name the technique based on the
principle of antigen-antibody interaction used in the detection of a virus (HIV).
Ans- The technique based on the principle of
antigen-antibody interaction used in the detection of a virus is ELISA (Enzyme
linked Immuno-sorbent assay).
Q14: write short on GEAC.
Ans: GEAC stands for Genetic engineering approval
committee. The Indian government has set up it for making decisions regarding
the validity of genetic modifications and the safety of introducing genetically
modified organisms for public services.
Q15: Write any two advantages of production
of genetically modified crops.
Ans: Advantages of genetically modified crops:
1.Genetically modified crops have improved agronomic
and other features such as
resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses.
2. Over ripening losses can be reduced. e.g.flavr
savr tomato.
Q16: Write two applications of
biotechnology?
Ans- 1. Treatment of diseases
2. Preparation of processed fortified food.
Q17: What do you mean by term Biopatent?
Ans- A patent is a right granted by a government to
an inventor to prevent others
to make commercial use of such an invention. Patents
granted for biological entities and the various products obtained from these
organisms termed Biopatent.
Q18: What are transgenic animals? Give two
examples of these.
Ans- Animals whose gene has been altered by genetic
engineering are called transgenic animals.e.g. Rosie cow, transgenic mice.
Q19: What is biopiracy?
Ans- Biopiracy is use of bio resources by commercial
and multinational companies and other organization without the appropriate
authorization and permission from the countries and people concerned.
Q20. Distinguish between Cry and cry.
Ans- Cry stands for crystal of toxic protein whereas
cry is the gene responsible for synthesis of toxin.
A219
INTRODUCTION
Students, in previous sheet you have learnt about
various 2 marks questions but in
this revision sheet you will discuss important
topics in the form of 3 marks framed question from chapter Biotechnology and
its application. These questions will
help you in preparing for your Borad exams.
3- MARKS QUESTIONS:
Q.1 What do you mean by Genetically
Modified Crops? Write any 4
advantagesof Genetically Modified Crops.
Ans: Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs) are
plants, animals, bacteria and
fungi whose genes have been altered by
manipulation.Advantages of GMOs are as follows:
(1) Higher yield- Crop plants can be made to grow
fast and produce very high yield
through genetic modification, example, Super wheat.
(2) Nutritional value- Vitamin A rich Rice and
protein rich potato have been
developed through genetic engineering.
(3) Stresses tolerant- Genetically engineered plants
can tolerate drought, frost,salinity, heavy metal toxicity.
(4) Disease resistance- Resistance to viral disease
has been introduced in tobacco,
potato, tomato and rice. Cry gene from Bacillus
thuringiensis has been introduced in
Bt cotton and Bt corn. Nematode infection has been
overcome in some plants through RNA interference.
Q.2 List the disadvantages of production of
genetically modified crops.
Ans: (1) Genetic pollution- Transgenes can be
transferred from one plant to another plant, microbes and even animals. It
shall disturb the genetic setup of organism and
cause ecological imbalance.
(2) Superweeds- Weedicide’s genes are being
introduced into crop plants. Any of these crop plants can itself become a super
weed.
(3) Super insecticide- Cry gene being introduced in
crop plants can pass into wild
vegetation. Insects feeding on pollen and other
parts will be killed resulting in the
destruction of pollinators and disseminators.
(4) Damage to environment- Harvesting leaves a lot
of plant residue in the farm land
that would damage the biotic environment.
(5) Allergies: The products of transgenes are
foreign to human body and animals feeding on transgenic. This may cause allergy
and toxicity.
(6) Antibiotic resistance: Antibiotic resistance
gene present in transgenic food
canbe picked up by bacteria present in human gut and
transfer the same to pathogens.
Q.3 With an example, explain how
biotechnology has been applied in each
ofthe following:
(i) in curing diabetes mellitus
(ii) in raising pest resistant plants
(iii) in producing more nutritionally balanced milk
Ans:(i) Diabetes mellitus- By producinginsulin or
Humulin§ from transgenic
Escherichia coli.
(ii) Pest resistant plants- By m RNA silencing
through the technique of RNA
interference which produces both sense and antisense
RNAs
(iii) Transgenic cattle- Cattle have genes for milk
proteins, growth hormones and
casein given high yield of nutritionally balanced
milk with high protein content.
Q.4 What is RNA silencing? How is this
strategy used to create pest
resistanceplants?
Ans: RNA silencing is a technique which involves
silencing or disabling of specific mRNA due to complimentary ds RNA molecule
that binds to and prevent translation
of MRNA.This strategy is used to prevent infection
of roots of tobacco plants by nematode
Meloidegyne incognita. In this strategy,
complementary ds RNA are produced
against specific mRNA. The source of this
complementary RNA could be from an infection by viruses having RNA genome.
Using Agrobacterium vector nematode
specific genes were introduced into host plants. The
introduction of DNAwas such that it produced both sense and anti-sense RNA in
the host cell. These two RNAs
being complementary to each other formed a double
stranded RNA that initiated
RNAi and thus silenced specific mRNA of the
nematode. The consequencewas that parasite could not survive in transgenic
host.
Q.5 What are cry proteins? Name an organism
that produces them. How
manhas exploited proteins to his benefit?
Ans: Cry proteins are a group of toxic proteins
which are highly poisonous to
different types of insects, example, tobacco bud
worm, army worm, beetles, flies and
mosquitoes.The organism producing Cry proteins is
Bacillus thuringiensis. The genes controlling their formation were called cry
genes. The bacterium produces the protein as
endotoxin in protoxin crystalline state.
Two cry genes have been incorporated in cotton (Bt
cotton) while one has been
introduced in corn. As a result, Bt cotton has
become resistant to boll worms while
Bt corn has developed resistance to corn borer.
Q.6 (i) Name the pest that destroys the
cotton bolls.
(ii) Explain the role of Bacillus thuringiensis in
protecting the cotton crop
against the pest to increase the yield.
Ans: (i) The pest that destroys the cotton balls are
cotton boll worms and cotton
borer.
(ii) Bt cotton is created by using some strains of a
bacterium, Bacillus
thuringiensis. This bacterium produces protein, that
kill certain insects such as
lepidopterans (tobacco budworm and armyworm),
coleopterans (beetles) and
dipterans (flies and mosquitoes). Bacillus
thuringiensis forms protein crystals
during a particular phase of their growth. These
crystals contain a toxic insecticidal
protein. Bt toxin protein exist as inactive
protoxin, but once an insect ingests the
inactive toxin, it is converted into an active form
due to the alkaline pH of the gut
which solubilize the crystals. The activated toxin
binds to the surface of midgut
epithelial cells and create pores that cause cell
swelling and lysis leading to death
of insect. Specific Bt toxin genes were isolated
from Bacillus thuringiensis and
incorporated into several crop plants. Most Bt
toxins are insect-group specific.
Hence, the toxin is coded by a gene named cry. For
example, the proteins encoded by the genes cry | Ac and cry | Ab control the
cotton boll worms and cry |Ab controls corn borer.
Q.7 (i) Explain the effect of deletion of
the gene for ADA in an individual.
(ii) How does the gene therapy help in this
case?
Ans. (i) Deletion of the gene for ADA in an
individual leads to ADA deficiency
disorder. Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) enzyme is
crucial for immune system to function.
(ii) Gene therapy is helpful in case of ADA
deficiency.Hereditary disease can be corrected by gene therapy. It is a
collection of methods that allows correction or replacement of defective
gene.The first gene therapy was given in 1990 to a 4 years old girl with
Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) deficiency. It is caused due to the deletion of gene
for adenosine deaminase.The treatment involves following steps:
(a) Lymphocytes from the blood of patient are grown
on culture outside the body. A functional ADA, c DNA (using a Retro viral
vector) is then introduced into teelymphocytes.
(b) Such genetically engineered lymphocytes are
returned to the blood of patient.
(c) Periodic infusion of such genetically engineered
lymphocyte is required by the patient.
Q.8 What is molecular diagnosis? Explain.
Ans: Molecular diagnosis: Effective treatment of
diseases require early diagnosis
and understanding of their pathophysiology.
Early diagnosis of diseases is not possible by
conventional techniques like serum
and urine analysis, sputum and stool analysis
etc.Modem techniques like rDNA, PCR, ELISA and RIA are used for early
diagnosis.
Infection of pathogens (viruses, bacteria etc.) is
suspected only when they produce disease symptoms.
By this time the pathogens have multiplied in the
body.
But by PCR, amplification of nucleotide is possible
and thus it is possible to
detect bacteria, virus even ats very low
concentrations. e.g.:HIV detection, genetic disorders.Modem techniques can also
help in the identification of mutated genes in humans
A single stranded DNA or RNA, tagged with a
radioactive probe is allowed to hybridize with its complementary DNA in a clone
of cells, followed by detection by using autoradiography.
The clone having mutated gene will not appear in the
photographic film because the probe will not have complementary nitrogen base
with the mutated gene.
In ELISA test the infection of pathogen (viruses,
bacteria, fungi, mycoplasma
like organism) can detect the antibodies synthesized
against the pathogen.
Q.9 (i) Name the host plant and its part
that Meloidogyne incognita infects.
(ii) Explain the role of Agrobacterium in the
production of dsRNA in the host plant.
Ans. (i) The nematode Meloidogyne incognita infects
the roots of tobacco plants.
(ii) The Agrobacterium are used as vectors carrying
nematode specific genes
to be introduced in host plant. These genes when
expressed inside host plant
produces sense and anti-sense RNA strands,
complementary to nematode’s functional MRNA. This binding result in formation
of double stranded RNA and inhibiting or silencing the translation of RNA
specified. This process is called RNA interference.
Q.10 In the given figure, Form (A) and Form
(B) represent different forms of aproteinaceous hormone secreted by pancreas in
mammals.
(a) What type of bonding is present between chains
of this hormone?
(b) What are these form (A) and form (B). How these
forms differ from each
other?
(c) Explain how was this hormone produced by Eli
Lilly, an American company, using rDNA technology.
Ans. (a) Disulphide bonds
(b) Form (A) — Proinsulin
Form (B) — Mature insulin. Proinsulin contains an
extra stretch called C- peptide
which is absent in mature insulin.
(c) Eli Lilly Company prepared two DNA sequences
corresponding to A and
B peptide chains of human insulin and introduced
them in plasmid E. coli
to produce insulin chains. Chains A and B were
produced separately,extracted and combinedby creating disulphide bonds to form
insulin.
Q.11 What are the steps involved in
synthesis of genetically engineeredinsulin.
Ans. Steps involved in Insulin production are:-
1. For the synthesis of Insulin, RNA is extracted
from B- cells of islets of
Langerhans of pancreas.
2. With the help of enzyme Reverse transcriptase,
single stranded DNA
complementary to mRNA is synthesized. Second strand
of DNA complementary to first is synthesized with enzyme DNA polymerase.
3. The two strands of copy DNA is joined to plasmid
by using an enzyme called
terminal transferase.
4. The two ends of DNA get annealed by enzyme called
ligase thus ends of inserted DNA & plasmid are sealed & a new circular
plasmid is formed. This is a molecule of recombinant DNA.
5. This recombinant DNA is then inoculated in a new
bacterial cell of E-coli & inserted in a bacterial gene after having cut by
restriction enzyme.
6. After proper expression of genes the bacterial
cells of both cultures are lysed
with appropriate chemicals. The fragments of insulin
are then separated from enzyme by Cyanogen Bromide.
Q.12 Some multinational companies and other
organizations are using bioresources for commercial benefits, without proper authentication
andcompensation to concerned authorities.
(a) Give the term for this unauthorized act.
(b) Suggest any two ways to get rid of this.
Ans. (a) Biopiracy
(b) (i) Benefits of bioresources should be shared
between developed and developing nations.
(ii) Laws should be developed to prevent
unauthorsied exploitation of them bioresources.
Q.13 Describe with example, why transgenic
animals are produced?
Ans. Transgenic animals are produced for following
purposes: -
1. To allow the study of how genes are regulated
& how they affect normal function of body & its development e.g.
Information obtained about biological role of insulin like growth factor.
2. To increase our understanding on how genes
contribute to development of diseases.
3. To produce useful biological compounds by
introducing a portion of DNA that codes for that product from other organisms,
e.g. aa-1 antitrypsin, a protein used to treat emphysema.
4. For testing the safety of vaccine eg. Polio
vaccine in transgenic mice.
5. To test the toxicity of drugs.
Q.14 (i) Some crop plants are modified
genetically by manipulating their
genes.How are they made beneficial?
(ii) What is Golden rice? What is its advantage?
Ans: (i) More tolerant to abiotic stresses; pest
resistant; reduction in post harvest
losses; increased nutritional value of food.
(ii) Golden rice is a transgenic variety of rice
which contains a gene which codes for Vitamin A precursor. This variety has
green yellow colored grains and is rich in Vitamin A & thus nutritionally
very advantageous.
Q.15(i) Human insulin when synthesized in
the body needs to be processed before it can act. Explain giving reasons.
(ii) How is the insulin produced from recombinant
DNA technology different from that produced by the functional human insulin gene?
Ans: (i) Human insulin when initially synthesised in
human body consists of three
peptide chains- A, B and C. The C-peptide is an
extra stretch of amino acids joining
the A and B-chains. This is called Proinsulin or
Prohormone.It undergoes processingor splicing to release the functional mature
insulin that can carry out its normal functions. During processing, the
C-peptide is removed. Only A and B-chainscontribute to form the functional
insulin.
Q.16 (i) Why is Bacillus thuringiensis
considered suitable for developing GM plants?
(ii) Explain how it has been used to develop GM
crops.
Ans. (ii) Bacillus thuringiensis produces a protein,
which is toxic to the larvae of
insects like boll worm, budworm, flies, beetle, etc.
Bt toxin gene is cloned from the
bacteria and has been expressed in plants to provide
resistance against insects
without the need for chemical insecticides.
(ii) The method for developing GM plants involve:
cry gene coding for proteins has been isolated using
restriction enzymes. They are
cloned in the vectors and then introduced into
desired crop plants. The different
types of cry genes that code for insect-specific cry
proteins are cry l|Ac and cry IlAb that control cotton bollworm. crylAb
controls corn borer.
(iii) The transgenic plants, i.e., Bt cotton, Bt
corn, Bt rice, produce the protein in their cells and express insect pest
resistance.
Q.17 What are transgenic bacteria?
Illustrate using any one example.
Ans: Transgenic bacteria are microbes carrying
clones of foreign genes.Transgenic bacteria are being employed for a variety of
functions.
(1) Biochemical factories- Microbes are used for
producing important biochemicals. It is an old use of microbes. Traditionally
microbes have been synthesizing alcohol, enzymes, steroids, organic acids and
antibiotics. Transgenic bacteria have added anumber of biochemicals to this
list, example, human insulin,growth hormone, tissue plasminogen factor,
erythropoietin, fertility hormone, lung surfactant protein, blood clotting
factors, interferons, interleukin etc. Some genetically modified bacteria have
been made to augment traditional functions,
example, Pseudomonas putida for alcoholic
fermentation.
(2) Environmental protection- Microbes have been
genetically changed to help in
cleaning the polluted environment, example,
Pseudomonas putida for cleaning oil
spills, Pseudomonas for removing heavy metal
pollutants, Acetobacter aerogens for
decomposition of DDT and Flavobacterium for
decomposition of 2,4-D.
Q.18 Mention the advantages & disadvantage
of production of Genetically modified organisms?
Ans. ADVANTAGES OF PRODUCING GMOs:
1. GM crops produce desired phenotypic traits in
crop plants. The genes responsible for production of specific proteins are
inserted into GMcrops.These crops then produce that specific protein.
2. Transgenic crops synthesizes new end product of
specific biochemical pathway.
3. These crops also help in preventing expression of
existing native Gene.
DISADVANTAGES OF PRODUCING GMOS:
1. Transgenic crops may endanger wild & native
species.
2. GM crops may cause health problems by supplying
allergens.
3. GM crops may damage to the natural environment.
Q.19 (i) List the three molecular
diagnostic techniques that help to detect pathogens from suspected patients.
(ii) Expand ELISA. On what principle is ELISA test
based? List two ways by which an infection can be detected by this test.
Ans: (i) Molecular diagnostic techniques to
pathogens are as follow:
(a) Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR).
(b) Recombinant DNA technology.
(c) Enzyme Linked Immuno Sorbent Assay (ELISA).
(ii) ELISA — Enzyme Linked Immuno Sorbent Assay.
ELISA is based on antigen-antibody interaction.The two ways to detect the
presence of infection or disease by ELISA are as follow:
(a) The presence of antigens (proteins,
glycoproteins, etc) is detected.
(b) Antibodies produced against the pathogen are
detected.
Q.20 Diagrammatically represent the
experimental steps in cloning and
expressing a human gene (say the gene for
growth hormone) into a bacterium like E. coli?
Ans: A technique of producing multiple identical
copies of a particular template DNA
is known as DNA cloning which involves the usage of
a vector that carries the
particular foreign DNA fragment into the host
cell.The working of cloning and transfer of gene for growth hormone into E.coli
can bedepicted as given below:
A220
RECAPITULATION
Biotechnology is a broad area of biology, involving
the use of living systems and
organisms to develop or make products. Biotechnology
has given to humans
several useful products by using microbes, plant,
animals and their metabolic
machinery.
APPLICATION OF BIOTECHNOLOGY
The applications of biotechnology include
therapeutics, diagnostics, and
genetically modified crops for agriculture,
processed food, bioremediation, waste
treatment, and energy production.Recombinant DNA
technology has made it possible to engineer microbes, plants and animals such
that they have novel capabilities. Genetically Modified Organisms have been
created by using methods other than natural methods to transfer one or more
genes from one organism to another, generally using
techniques such as recombinant DNA technology.
BIOTECHNOLOGICAL APPLICATION IN
AGRICULTURE
The plants in which foreign genes have been
introduced trough genetically engineering are called transgenic
plants.Advantages of transgenic plants GM plants have been useful in
increasing crop yields
pest resistant crops
reduce post-harvest losses and make crops more
tolerant of stresses.Disadvantages of transgenic plants
Environmental hazards
Human health risks like allergies
BIOTECHNOLOGICAL APPLICATIONS IN
MEDICINE
Recombinant DNA technological processes have made
immense impact in the area of healthcare by enabling mass production of safe
and more effective therapeutics. Recombinant pharmaceuticals or therapeutics is
created by inserting genes from one species into a host species, often yeast or
bacteria. For example,In case of insulin production, genes coding for human
insulin are inserted into
bacteria. Bacteria produce insulin, which is
harvested and used for diabetic patients. Human insulin is made in bacteria yet
its structure is absolutely identical to that of the natural molecule.
ADVANTAGES OF RECOMBINANT THERAPEUTICS:
*Recombinant therapeutics never induce unwanted
immunological responses as is
common in case of similar products isolated from
non-human resources or other
animals which contain other proteins and generate
immune responses.
Recombinant therapeutics is produced in very large
amounts and also very easy to produce. *These drugs are very effective with no
any kind of side effects.
Production of these drugs are time and money
saving.30 recombinant therapeutics have been approved for human use on word
level but in India 12 of these are approved and presently being marketed.
TRANSGENIC ANIMALS
Transgenic animals are also used to understand how
genes contribute to the
development of a disease by serving as models for
human diseases, such as cancer, cystic fibrosis, rheumatoid arthritis and
Alzheimer's.
GENE THERAPY
GENE THERAPY is a collection of methods that allows
correction of a gene defect
that has been diagnosed in a child/embryo. Genes are
inserted into a person's
cells to treat a disease. Correction of a genetic
defect involves delivery of a normal
gene into the individual or embryo to take over the
function and compensate for the
non-functional gene. The first clinical gene therapy
was given in 1990 to a 4-year
old girl with Adenosine De Aminase (ADA) deficiency.
ETHICAL ISSUES IN BIOTECHNOLOGY
I. Introduction of a transgene from one species into
another species violates
the integrity of species.
Il. | Biotechnology may lead to unforeseen risks to
the environment, including
risk to biodiversity. it can disturb the existing
ecological balance.
Ill. Utilization of animals In biotechnology causes
great suffering to them.
IV. There is another biological damage .it can
accidentally create new infectious agents.
V. | When animals are used for production of
pharmaceutical proteins they are virtually reduced to the status of a factory.
Revision test sheet Time allowed: 2hrs. Max. Marks:
35
Important Instructions:
1. There are a total of 17 questions and four
sections in the question paper.All questions are compulsory.
2. Section A contains question numbers 1 to 5 very
short answer type questions of one mark each.
3. Section B contains question numbers 6 to 13,
short answer type questions of two marks each.
4. Section C contains question numbers 14 to 16,
short answer type II questions of three marks each.
5. Section D contains question number 17, long
answer type question of five
marks. There will be internal choice in this
question.
6. There is no overall choice in the question paper
Section-A
Each question carries 1 mark
Q1. What are DNA vaccines?
Q2. Name the bacterium that is first used as bio
pesticide?
Q3. What are the transgenic animals?
Q4. Name the genetically engineered insulin.
Q5. What is the full form of ADA in ADA deficiency?
Section-B
Each question carries 2 marks
Q6. Name two pest-resistant plants produced by using
recombinant DNA technology.
Q7. Which vaccine was being tested on mice?
Q8. Name any disease against which vaccine is
developed by Recombinant DNA technology.
Q9. What is the difference between ‘cry’ &
‘CRY’?
Q10. What are the two methods for correcting ADA
deficiency in a child?
Q11. What is Golden rice? What is its advantage?
Q12. The first transgenic cow produced human
protein-enriched milk. Name the cow and the protein found in milk.
Q13. What do you mean by “Biopiracy” Give an
example?
Section-C
Each question carries 3 marks
Q14. What do you understand by Molecular farming?
Q15. Describe some transgenic plants and their
useful characters.
Q16. What are the advantages and disadvantages of
transgenic plants?
Section-D
Each question carries 5 marks
17. Describe the biotechnical applications in
agriculture.
OR
18. How biotechnology is helpful in the field of
medicine.
ANSWERS
Section-A
A1. Genetically engineered vaccines are called DNA
vaccines.
A2. Bacillus thuringiensis.
A3. These are the animals, whose genome has been
altered by introduction of an extra (foreign) gene by manipulation.
A4. Humulin.
Ad. Adenosine De Aminase (ADA) deficiency.
Section-B
A6. Bt Cotton, Bt Corn, BtBrinjal are pest-resistant
plants produced by using
recombinant DNA technology.AT. Polio vaccine was
being tested on mice.
A8. Hepatitis B is the disease against which
vaccines are developed by Recombinant DNA technology.
AQ. cry is the gene that codes for Bt-toxin which is
an insecticidal protein while CRY is the protein coded by cry genes.
A10. Enzyme replacement therapy and bone marrow
transplantation with a functional ADA enzyme.
A11. Golden rice is a genetically modified type of
rice rich in Vitamin A. This
type has green-yellow grains and is high in Vitamin
A, making it nutritionally
beneficial.
A12. Rosie, is the first transgenic cow, it produced
human protein-enriched milk. Alpha-lactalbumin is the protein found in milk.
A13. Biopiracy is defined as the use of
bio-resources by multinational corporations and other organizations without
proper authorization from the countries and people concerned. For example,
Basmati rice grown in India is known for its distinct flavor and aroma, but
Basmati rice was patented by an
American company under a US patent.
Section-C
A14. Molecular farming :The method of manufacturing
drugs in transgenic
animals is called molecular farming or molecular
pharming. The transgenic
animals can revolutionize the pharmaceutical
industry by providing large quantities of valuable drugs.
A16. The plants in which foreign genes have been
introduced trough genetically
engineering are called transgenic plants.
Advantages of transgenic plants:
GM plants have been useful in
increasing crop yields
pest resistant crops
reduce post-harvest losses and make crops more
tolerant of stresses.
Disadvantages of transgenic plants:
Environmental hazards
Human health risks like allergies
Section-D
A17. Agriculture is a major sector for the
production of food materials and
development of the nation also. But, now a day we
are facing a huge problem with
food production for the need of growing human
population. There are three possible options for enhancement of crop
production.
1. Agro-chemical based agriculture, by using
chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
2. Organic agriculture, by using organic or bio
fertilizers and bio pesticides.
3. Genetically engineered crop based agriculture, in
which the crops are
genetically modified to enhance the food production
and to make them insect, pest
resistant.The first two options bring green
revolution, but yet it was not enough to feed the growing human population.
Then scientists have decided that use of genetically
modified crops is a possible solution.
The latest Recombinant DNA technology or Genetic
Engineering plays an important role in agriculture. This technology involved
transfer of one or more genes (i.e. DNA fragment) from one plant to another.
The plant in which foreign genes has been introduced is called transgenic
plant. Now these transgenic plants are used in agriculture for the following
reasons:
1. Improvement In Photosynthesis - RUBISCO Is an
important enzyme of photosynthesis which can act both on carbon dioxide and
oxygen. When this enzyme combine with CO2 it performs C3 cycle in which carbon
dioxide is
fixed into glucose. The property of any enzyme
Combining with COz is called
carboxylase and combining with oxygen is called
oxygenase. Whenever RUBISCO combines with oxygen, it performs C2 cycle also known
as photorespiration. C2 cycle is a wasteful cycle for plants because in this
cycle
plants starts losing their fixed carbon. The RUBISCO
can act as carboxylase as well as oxygenase also. When it is acting as
carboxylase, it is performing C3 cycle and when it is acting as oxygenase, it
is performing C2 cycle. It is now possible to isolate the RUBISCO gene, modify
it accordingly and reinsert into plants to minimise the loss due to
photorespiration. The scientists removes the oxygenase property of RUBISCO with
the help of genetic engineering and retains its carboxylase property. With
this, scientists
are successful to minimise the loss of fixed carbon.
2. Insect - Pest Resistant In Transgenic Plants -
The day is not far off wnen
our crop plants will resist all kind of pests.
Several such transgenic plants
have been developed. Bacillus thuringiensis is a
bacteria which produces a toxin protein which is a crystal protein which can
kill a number of insects.This protein is also known as cry protein. Bt, toxin genes
were isolated from
B. thuringiensis and added to several crop plants.
Such plants can resist many kind of pests. One such plant is Bt. cotton in
which Bt. Toxin has been used as a biological insecticide. This type of cotton
is resistant to the boliworm. Tomatoes with Bt. Gene are completely protected
from an attack of caterpillars. Similarly GM tobacco with Bt gene is protected
from hornworms.
3. Herbicide tolerance - Herbicides are the
chemicals which kill the weeds.When these Chemicals are sprayed in the field,
they not only kill the weeds but also damage the crop plants. In recent years,
genetic engineering has helped to develop such transgenic crop plants which are
resistant to herbicides, so that they are not damaged when farmers Spray herbicides
in the fields. Some herbicide resistant crops produced by genetic engineering
are - tomato, potato, tobacco, soyabean, cotton, corn, oilseed, sugar beet,
etc.
OR
A118. Viodern biotechnology is making a great
contribution to medicine, both in the diagnosis of diseases and in the
development of Pharmaceutical products for disease therapy. One purpose of DNA
technology is to identify the gene that's mutation, causes genetic diseases.
Discovery can help to
find ways for diagnosing, treating and preventing mutation.
So this technology is very helpful in diagnosing, treating and preventing the
mutation for helping the future generations to avoid the particular genetic
disorders.
1. Polymerase chain reaction(PCR):PCR is a technique
by which any piece of DNA can be quickly amplified(copied many times) Without
using cells. The DNA is incubated in a
test tube with a special kind of a DNA polymerase
enzyme, a mixture of deoxyribonucleotide for use as raw material, and short
piece of synthetic single stranded DNA to serve as primers for DNA synthesis.
PCR can make billions of copies of a DNA segment in a few hours. DNA technology
can help identify individuals with genetic disorders before the appearance of
symptoms, even before birth.
2. Pharmaceutical products:Many Pharmaceutical
products have been produced by using DNA technology. these products are mostly
proteins. The gene for a desired
protein is transferred into a bacterium, yeast or
other kind of cell which is
easy to grow in a culture. Such host cells produce
large quantities of protein
in a short time.
a. Hormones - Human insulin and human growth hormone
are earliest example.
(i) Insulin — Insulin is a hormone, produced by
human body. Insulin converts glucose into glycogen which is stored in our
liver. In the deficiency of insulin,glucose will not be converted into glycogen
and glucose level of blood will increase and it will develop the disease
diabetes. When human body is not
producing insulin then external insulin was given.
Insulin is an important lifesaving drug for diabetic patients. Earlier, the
insulin was obtained from the pancreas of cattle and pigs, and this is not
sufficient as per the need of growing number of diabetic patients. Injections
of this insulin have some side effects also. Scientists were looking for some
alternative source of human
insulin. The search for new source was soon
fulfilled by Recombinant DNA technology. The insulin was prepared with the help
of bacteria using this technology.
Production of genetically engineered insulin:
Insulin is made up of two short polypeptide chains;
A and B which are linked together by disulphide bridges. Insulin is synthesised
as Pro hormone. It needs processing to become mature and functional.
It contains an extra stretch called C — peptide.
This is removed during
maturation of insulin.
Genetic engineers took out the human gene
responsible for synthesis of insulin and inserted it into the DNA chain of
suitable vector, E. coli bacterial cell.
Chain A and B were produced separately, extracted
and combined by creating disulphide bonds to form human insulin called Humulin.
It was the first genetically engineered human insulin.
(ii) Human_growth hormone - Human Growth Hormones
(HGH) has proved highly useful to numerous children born with HYPOPITUITARISM,
a form of dwarfism caused by under secretion of the HGH by the anterior
pituitary. The HGH
may also have other uses, such as healing of
injuries.Milch cows are injected with Bovine Growth Hormone (BGH), formed in
which
Genetically Engineered Microorganisms (E. coli), to
raise milk production. BGH
also improve beef yield in cattle.
3. Gene Therapy — It is a collection of methods that
allows correction of a gene
defect that has been diagnosed in a child/embryo.
The disorders can be due to the
absence of a gene or due to non-functional gene
which not able to work properly.
With the help of gene therapy, the correct gene is
added into the body of patient or
embryo.