4-REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH
CHAPTER NO.4 REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH
A30
INTRODUCTION
DEFINITION:
According to World health organisation (WHO),
reproductive health is defined as
TOTAL WELL-BEING IN PHYSICAL, EMOTIONAL, BEHAVIOURAL
AND SOCIAL ASPECTS OF REPRODUCTION.
PROBLEMS:
1. Explosion in population causes shortage of food,
space, employment essential goods and education. This affects well-being of
reproductive health.
2. Due to lack of sex education, people have little
knowledge of personal
hygiene and hygiene of reproductive organs. This
causes sexually transmitted diseases (STD's).
3. Early marriages lead to high maternal and infant
mortality rate.
4. Lack of knowledge leads to myths and
misconceptions about sex related
issues in young minds.
5. Illegal abortion of female foetuses.
6. Congenital or acquired infertility.
STRATEGIES OF REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH
1. India was the first country in the world to
initiate actions and plans to attain
total reproductive health as a social goal.
2. Family Planning programmes were started in 1951
in India.
3. Reproductive and Child Health Care (RCH)
programmes were launched on 15" October 1997.
RCH programmes have following aims:
i) Create awareness among people about various
reproduction related aspects.
ii) Provide facilities and support for building up a
reproductively healthy
society.
4. With the help of audio-visual aids and print
media, both government and
non-government agencies are creating awareness among
people about reproduction related aspects.
5. Introduction of sex education in schools to give
right information to young
minds about reproductive organs, dolescence and
related changes.Thus, save them from myths and misconceptions.
6. Impart knowledge about available birth control
options, care for pregnant
mothers, post-natal care of mother and child and
importance of breast feeding.
7. Compulsory ban on amniocentesis to legally check
increasing female
foeticides. This will give equal opportunities to
male and female child.
8. Consequences of problems due to uncontrolled
population growth and
social evils like sex abuse, drugs, etc.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE LEARNT!
PART-A VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
a) MCQ’s
1. Reproductive health is a total
well-being in:
a) Physical Aspects
b) Emotional Aspects
c) Social Aspects
d) All of Above
2. Marriageable age for females and males
is:
a) 18 & 21 Years
b) 21 & 18 Years
c) 15 & 21 Years
d) 19 & 21 Years
3. We can control population explosion by:
a) Raising age of marriage
b) Family planning
c) Amniocentesis
d) Botha &b.
4. Which was the first country in the world
to initiate family planning program?
a) India
b) China
c) Pakistan
d) Japan
5. Measures taken by an individual to
prevent STDs are :
a) Avoid sex with unknown partner
b) Use condoms
c) Knowledge of occurrence of STD's
d) All of the above
b) FILL UPS
1. RCH stands for .
2. technique has been banned in our country.
c) TRUE/FALSE
1. Creating awareness about sex related aspects is
an effective method to improve reproductive heaith of the people.
2. Rapid increase in infant mortality rate and
maternal mortality rate has caused population explosion.
3. Family planning programs were started in India in
1951.
ANSWER KEY: PART -A.
a) MCQ’s
1. (d). All of above-(because reproductive health
includes all the aspects of reproduction physical, emotional, social and
behavioral.)
2. (a). 18 & 21 Years— (This is done to control
population control)
3. (d). Both a & b. —( Raising age of marriage
and family planning helps to
control population growth.)
4. (a) . India. — (India was the first country in
the world to initiate actions
and plans to attain total reproductive health as a
social goal.)
5. (d). All of the above — (As STD's are transmitted
from infected person to
healthy person through sexual intercourse so use of
condoms,knowledge of occurrence of STD's and avoiding sex with unknown
partners helps to control these diseases. )
b) FILL UPS:
1. Reproductive and child healthcare.
2. Amniocentesis.
c) TRUE/FALSE:
1. True
2. False— (Rapid decline in infant mortality and
maternal mortality rate has
caused population explosion.)
3. True
PART B: SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. What is a reproductively healthy
society?
Ans : Society is said to be reproductively healthy
if the people have physically
and functionally normal reproductive organs. They
also have normal emotional
and behavioral interactions among them in all sex
related aspects.
2. List two measures to develop a
reproductively healthy society.
Ans : Measures to develop reproductively healthy
society are :
|. Create awareness about reproduction in people.
Il. Provide medical help and care during pregnancy,
delivery, STD's, etc.
Ill. Ban on amniocentesis legally check increasing
female foeticides.
3. Is sex education necessary in schools?
Why?
Ans. Yes, introduction of sex education is necessary
in schools. It gives right
information to young minds about reproductive
organs, adolescence and related changes, safe and hygienic sexual practices,
cause of occurrence of STD's, AIDS,etc. This Knowledge will save them from
myths and misconceptions about sex
related aspects. It will help them to lead a
reproductively healthy life later on.
PART-C: LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Suggest aspects of reproductive health which need
to be given special attention in present scenarios.
2. What are the problems associated with
reproductive health?
A31
POPULATION DEFINITION:Group
of individuals of the same species in a well defined geographical area which
share or compete for similar resources and can potentiallyinterbreed.
CHARACTERISITCS OF POPULATION :
BIRTH RATE(Natality):
It is expressed as increase in number because of births with
respect to the number of individuals in a
population.
DEATH RATE(Mortality):
It is expressed as decrease in number because of deaths
with respect to total number of individuals in the
population.
SEX RATIO:
An individual has sex male or female but a population has sex ratio.
Example — 60% of the population are females and 40%
aremales.
AGE DISTRIBUTION:
Various age groups in population determine its reproductive
status. Three stages are referred to as
pre-reproductive, reproductive and post-
reproductive.
POPULATION EXPLOSION:
Increased health facilities along with better living conditions had an
explosive impact on the growth of population. The world
population which was around 2 billion in 1900
rocketed to about 6 billion by 2000
and 7.2 billion in 2011. A similar trend was
observed in India to. Our population
which was approximately 350 million at the time of
our independence reached close to the billion mark by 2000 and crossed 1.2
billion in May 2011. That means every sixth person in the world is Indian.
REASONS FOR POPULATION EXPLOSION:
1. Rapid decline in death rate.
2. Decline in maternal mortality rate(MMR)
3. Decline in infant mortality rate(IMR)
4. Increase in number of people in reproductive age.
Through our RCH Programs we could bring down the
population growth rate,though it was only marginal. According to the 2001
census report the population growth rate was still around 1.7 percent i.e.
17/1000 per year a rate at which our population could double in 33 years. The
government was forced. To take up serious measures to check this population
growth rate. The most important of these is to motivate smaller families by
various contraceptive methods.
CONSEQUENCES OF OVERPOPULATION:
Overpopulation is associated with negative environmental and economic outcomes
ranging from the impacts of over-farming, deforestation, and water pollution to
eutrophication and global warming.
Emission of large quantities of green house gases
leading to global warming.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE LEARNT
PART A: VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS
(A) MCQs :-
1. The world Population was around 2
billionin:
(a) 1900
(b) 1905
(c) 1901
(d) 1908
2. At time of our Independence our
population was approximately:
(a) 340 million
(b) 350 million
(c) 280 million
(d) 150 million
3. MMR is:
(a) Mortality maternal rate
(b) Minimum Mortality rate
(c) Maternal Mortality rate
(d) Maximum Mortality rate
4. What is population explosion?
(a) Increase in Population.
(b) Small increase in Population
(c) Decrease in Population
(d) Large increase in Population
5. What is Global Warming?
(a) Temperature Change
(b) Rise in Temperature
(c) Decrease Temperature
(d) Low Pressure.
(B) True/False
1. Increase in number of people in reproductive age
leads to population
explosion.
2. Every sixth person in world is anIndian.
3. Contraceptive methods increase population.
(C) Fill ups
1. Our Population could in 33 years.
2. Graphic representation of different age groups is
called :
3. Number of births during a givenperiod is called :
ANSWER KEY :- PART-A
(A) MCQs -
1. (a)
2. (b)
3. (c)
4. (d)
5. (b)
(B) TRUE/FALSE --
1. True
2. True
3. False
(C) Fill Ups —
1. Double
2. Age Pyramid
3. Natality
PART B: SHORTANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1.What is population?
2.What is population explosion?
PART C: LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1.What are the consequences of overpopulation?
2.What is Global Warming and its causes?
A32
INTRODUCTION
As you all have known up till now that Fertilisation
is necessary for the formation of embryo and then young one. For fertilization
to take place there should be union of male gamete (sperm) and female gamete (egg).In
this assignment we will study about the different methods that
stop the meeting of sperm and egg, so as to stop
fertilization and hence to stop the birth.
BIRTH CONTROL METHODS:The
most important step to overcome the population explosion is to motivate smaller
families by using Contraceptive or Birth Control methods.
CHARACTERISTICS OF AN IDEAL
CONTRACEPTIVE:
It should be user friendly easily available,
effective with no or least side effects.
it should not interfere with sexual desire and act.
CONTRACEPTIVE METHODS:
A) NATURAL/TRADITIONAL METHODS:
1. Periodic abstinence--Avoid coitus during the
fertile period (day 10-17 )of
menstrual cycle.
2. Coitus interrupts--Withdraw penis from vagina
before ejaculation.
3. Lactation amenorrhea-lt is the absence of
menstrual cycle and ovulation due to intense lactation after parturition.
Natural methods have no side effects but chances of
failure are high.
B) BARRIERS:
1. Condoms-They are made of rubber or latex sheet
.Condoms for males cover the penis and condoms for females cover the vagina and
cervix. They prevent the entry of semen into the reproductive tract of females.
2. Diaphragms, cervical caps and vaults- Made of
rubber and are inserted into the female reproductive tract to cover the cervix.
3. Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)- These are inserted
by doctors or nurses in the uterus through vagina. They increase phagocytosis
of sperms.
Types of IUDs:
a. Non medicated IUDs:Retard sperm motilityE.g.-
Lippies loop.
b. Copper releasing Ds:CuT,Cu7,Multiload375 etc.,
suppress the motility of
sperms.
c. Hormone releasing |UDs: These IUDs make the
uterus unsuitable for implantation and cervix hostile for the
sperms.e.g.Progestasert,_LNG-20.
4. Oral contraceptives: Oral administration of
progestogens or progestogen-oestrogen combination in the form of tablets
(pills) inhibit ovulation and implantation and thicken cervical mucus to
prevent entry of
sperms. Pills are very effective with lesser side
effects.Saheliis a new oral contraceptive with very few side effects and high
contraceptive value.
5. Injectable and Implants:Progestogen or
progestogen-oestrogen combinations are used by females as injections or
implants under skin.Their effective periods are much longer than pills.
6. Surgical methods:(sterilisation) :lt helps to
block gamete transport and
thereby prevents conception .It is very effective
but reversibility is very poor.
Vasectomy is the sterilisation procedure in males
.In this a small part of the
vas deferens is removed or tied .Tubectomy is the sterilisation
procedure in females.in this ,a small part of
the fallopian tube is removed or tied up .
Nausea ,abdominal pain, breakthrough bleeding
,breast cancer etc. are
some of the side effects of anti-natural
contraceptives.
C) MEDICAL TERMINATION OF PREGNANCY
(MTP)
Voluntary termination of pregnancy before full term
is called MTP or induced abortion.Many countries have not legalised MTPs due to
some Ethical, Religious, and
Social issues.The Government of India has legalised
it with many restrictions to check Female foeticides. It is done to avoid any
major abnormality in future child.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE LEARNT!
A) MCQs:
1) An ideal contraceptive should be:
a) Costly
b) User friendly
c) With side effects
d) None of the above
2) The fertile period in the female is:
a) (5-10) day of menstrual cycle
b) (10-17) day of menstrual cycle
c) both a and b
d) none of the above
3) Oral contraceptives:
a) Inhibit ovulation
b) Inhibit implantation
c) Thicken cervical mucus
d) All of the above
4) Copper releasing IUDs include:
a) CuT
b) Multiload 375
c) Both a and b
d) None of the above
5) Side effects of anti-natural
contraceptives include:
a) Nausea
b) Breast cancer
c) Abdominal pain
d) all of the above
B) FILL UPS:
1. lUDs increase ............. of sperms.
2. Injectables and implants are combinations of
............ and ............. hormones.
3. The sterilisation procedure in males is called
.............
C) TRUE/FALSE:
1. Condoms are made up of rubber or latex
(True/False).
2. Cervical caps are inserted into the female
reproductive tracts (True/False).
3. Tubectomy is the sterilization procedure in males
(True/False)
ANSWER KEY: PART-A
A) MCQs:
1. b) user friendly
2. b) (10-17) day of menstrual cycle
3. d) All of the above(hormone combinations prevent
all activities leading to
pregnancy.
4.c) Bothaandb.
5. d) All of the above.
B) FILL UPs:
1. Phagocytosis
2. Progesterone and estrogen
3. Vasectomy
C) TRUE/FALSE:
1. True
2. True
3. False: It is the sterlisation process in females.
(“Tube” means fallopian tube or
Oviduct)
PART B: SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1 Mention few characteristics of a contraceptive.
Q.2 How natural contraceptives are different from
other contraceptives?
Q.3 Write a note on MTP.
PART C: LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS.
Q.1 Explain the method of sterilisation for
contraception in males and females.
Q.2 Explain Barrier methods of contraception.
A33
INTRODUCTION
Hello, dear students, we have discussed different
birth control methods in
previous assignment. Now today we will discuss about
different sexually
transmitted diseases i.e. the diseases that pass on
from an infected person to
his or her healthy partner at the time of sexual
intercourse or sexual contact.
SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES :
Diseases or infections which are transmitted through sexual intercourse are
collectively called sexually transmitted diseases
(STD) or venereal diseases
(VD) or reproductive tract infections (RTI).
Examples are: GONORRHOEA, SYPHILIS and AIDS.These
are generally acquired diseases and usually affect the reproductive
system of the person but may spread to other body
parts as well. Though these
can affect persons of all the age-groups, but their
incidence rate is found to be
very high among persons in the age group of 15-24
years.
STDs CAUSED BY BACTERIA CHLAMYDIASIS
PATHOGEN - Chlamydia trachomatis
Symptoms characterized by a thick pus like discharge
from the penis and painful
urination in males, while causes inflammation of
cervix, uterus and uterine tubes in females. If remain untreated then may
transform into pelvic inflammatory disease.
GONORRHOEA (CLAP)
PATHOGEN - Neisseria gonorrhoeae
SYMPTOMS - Characterized by inflammation of mucous
membrane of urinogenital tract. It may also cause arthritis, female sterility.
SYPHILIS
PATHOGEN - Treponema pallidum
SYMPTOMS - A hard dry and becteria filled sore,
called chancre, appears on the
genitalia or may appear on lips or fingers.
STDs CAUSED BY VIRUSES
(i) AlDS(Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome)
(ii) Hepatitis B(Serum Hepatitis) —
PATHOGEN - Double- stranded DNA virus, hepatitis B
virus(HBV) SYMPTOMS - Fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, arthritis and damage to
liver cells releasing bilirubin which causes jaundice(yellowing of skin and
eyes).
(iii) GENITAL WARTS —PATHOGEN — Human Papilloma
Virus(HPV) SYMPTOMS - Appearance of warts on the genital organs like penis,
labia, around anus, in vagina and on the cervix.
(iv) GENITAL HERPES — PATHOGEN - Herpes Simplex
Virus(HSV-2) SYMPTOMS - The primary symptoms of genital herpes are periodically
recurring watery blisters on the genitalia or buttocks, fever, painful
urination and swollen lymph nodes in the groin.
EARLY SYMPTOMS : Itching, fluid discharge, slight
pain and swellings in the genital region.
COMPLICATIONS DUE TO CHRONIC STDs :Pelvic
inflammatory diseases (PID) Abortions
Still births : is the death or loss of a baby before
or during delivery.Ectopic pregnancies : in which fertilized egg implants
outside the uterus.
Infertility
Even cancer of the reproductive tract.
PREVENTION :
Prevention is better than cure.
1. Avoid sex with unknown partners/ multiple
partners.
2. Always use condoms during coitus.
3. In case of doubt, one should go to a qualified
doctor for early detection
and get complete treatment if diagnosed with the
disease.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT
PART-A VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
(a) MCQs
Q.1. 1 December is celebrated as :-
a) World population day
b) World Environment day
c) World AIDS day
d) World Science & Technology day
Q.2. Which of the following is a STDs:-
a) Cancer
b) Malaria
c) Pneumonia
d) Trichomoniasis
Q.3. Chlamydiasis is caused by :-
a) Neisseria
b) Treponema
c) Chlamydia
d) HSV-2
Q.4. Which one of the following groups
includes all sexually-transmitted
diseases?
(a) AIDS, Syphilis, Cholera
(b) HIV, Malaria, Trichomoniasis
(c) Gonorrhoea, Hepatitis-B, Chlamydiasis (d)
Hepatitis-B, Haemophilia, AIDS
Q.5. Match the sexually-transmitted
diseases (column-) with their causative
agent(column-il) and select the correct
option: II
1.Gonorrhoea (i) HIV
2.Syphilis (ii) Neisseria
3.Genital warts (iif) Treponema
4.AIDS (iv) Human Papilloma Virus
Options :
1 2 3 4
(@) 6) =i) Sw)
(b) (iii) (Vv) (ii)
(c) (iv) (il) (iii) (IV)
(d) (i) (iii) (ii) (ili)
(b) TRUE/FALSE:
1. All reproductive tract infections (RTIs) are STDs
and all STDs are RTIs.
2. AIDS specifically affect sex organs.
3. All sexually transmitted diseases are completely
curable.
(c) Fill in the Blanks:
1. STDs are reported to be very high among persons
in the age group years.
2. Gonorrhoea is caused by .
3. STDs are also called .
ANSWER KEY: PART-A
a) MCQ:
1. (c) World AIDS day ; (World environment day is on
5" June. World population
day is on 11™ July. World science and technology day
is on 11™ May.)
2. (d) Trichomoniasis
3. (c) Chlamydia
4. (c) Gonorrhoea, Hepatitis-B, Chlamydiasis
5. (a)
b) TRUE/FALSE:
1. False. HINT: - STDs includes
sexually-transmittable diseases and include
Chlamydiasis, Syphilis, Gonorrhoea, Genital warts,
Genital herpes, Hepatitis-B,
and AIDS, etc. Out of these, Hepatitis-B and AIDS
are not RTls as these do not
cause infections in reproductive tracts but are also
transmitted through unprotected sexual intercourse so are also STDs. On the
other hand, other diseases are STDs as well as RTIs.
2.False. HINT :- HIV of AIDS attack and kills Helper
T-lymphocytes so causes
immunodeficiency. It spreads through sexual contact
with infected person.
3.False. HINT :- Hepatitis-B, Herpes, HIV and HPV
are not curable.
c) FILL IN THE BLANKS:
1.15-24 years.
2. Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
3. Venereal diseases.
PART-B SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1. What are sexually transmitted diseases in Human
beings? Name two sexually transmitted diseases. Name their causative agents.
Q.2 Mention early and chronic symptoms of STDs.
Q.3. What are the measures one has to take to
prevent from contracting STDs?
PART-C LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1 What are STDs? Explain Bacterial and Viral STDs.
How can these be
prevented?
A34
INTRODUCTION
When there is no fertilization even after
unprotected sexual intercourse and that is too during the days of ovulation,
then it
seems that there is some reason that renders the
formation of Zygote. This condition is called INFERTILITY.
Infertility may be because of physical, congenital, psychological
or
immunological disorder. Drugs may also cause
infertility.ARTs (Assisted Reproductive technologies) - ARTs are the techniques
by which an infertile couple is assisted to have children.
TYPES OF ARTs:
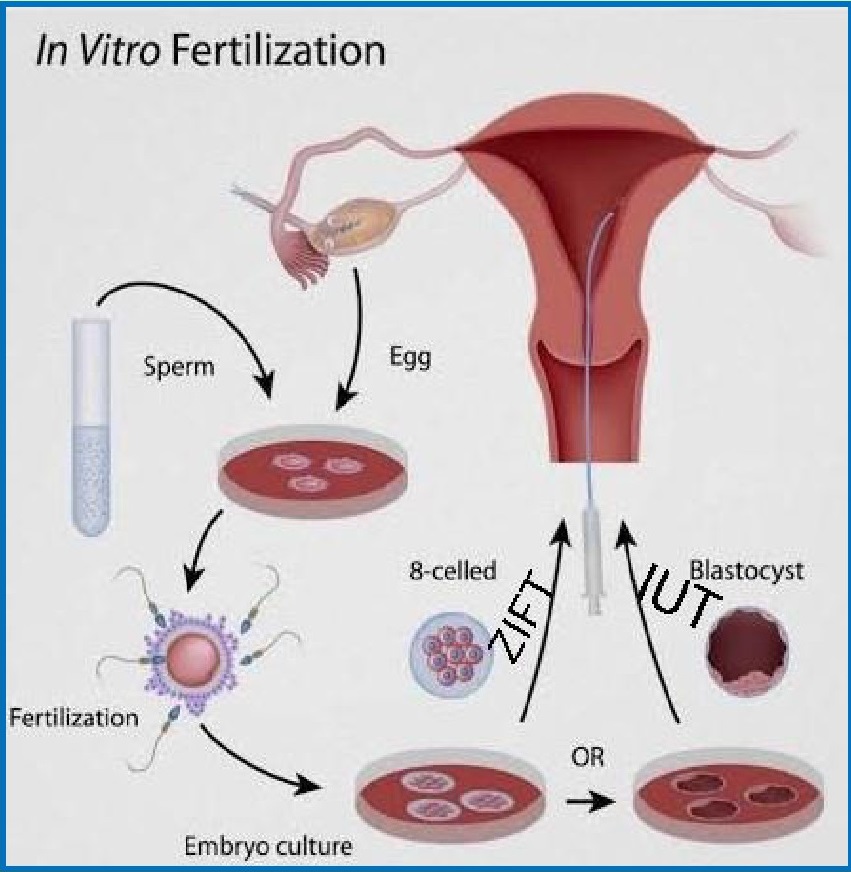
1. IVF- ET (In vitro fertilization - embryo
transfer) / Test Tube Baby — In this
technique, an ovum is collected from female ovary
and the sperms are collected from male which are then fertilized together in
glass container outside the body of the mother, in laboratory conditions to
produce a Zygote.Zygote is allowed to undergo mitosis and at some stage
transferred to the uterus of female for further development. The process
involves various steps.
It is of two types:
a) ZIFT (Zygote Intra Fallopian
Transfer) - In this technique, a zygote is developed,in
vitro, to an 8 celled stage, and it is then transferred to fallopian tube for
further development.
b) IUT (Intra uterine transfer)
- In this technique, the in vitro zygote is developed
to16 cell stage, and it is then transferred directly
to the uterus.
2. GIFT (Gamete Intra fallopian
transfer) - If in a female, ovum from ovary does
nottransfer because of defaulted functioning of fimbria or some other
obstacle , or female produces Antisperm antibodies,
gametes (may be ovum or
sperm or both) are transferred to fallopian tube
artificially. Further development
is in - vivo.
3. AIT (ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION
TECHNIQUE) If the male partner has low sperm count, thesperms
are collected from the male partner or donor and injected in the genital tract
of female, to ensure the fertilization.
4. INTRA CYTOPLASMIC SPERM INJECTION
(ICSI)-
The
sperm is injected directly in the cytoplasm of the ovum in laboratory
conditions.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
PART A - VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS
(a) MCQ’s
1. Which of the following is ART?
(a) |UDs
(b) GIFT
(c) ZIFT
(d) Both (b) & (c)
2. The technique called Gamete Intra
Fallopian Transfer (GIFT) is recommended for those females:
(a) who cannot produce an ovum.
(b) who cannot retain the foetus inside uterus
(c) who cannot provide suitable environment for
fertilisation
(d) all of these
3. Which of these can be used to cure
infertility in couples where male partner has very low sperm count?
(a) |UD
(b) GIFT
(c) IUI
(d) None of these
4. The method of directly injecting a sperm
into ovum in assisted reproductive technology is called
(a) GIFT
(b) ZIFT
(c) ICSI
(d) ET
5. The test-tube baby programme employs
which one of the following techniques?
(a) Zygote intra Fallopian transfer (ZIFT)
(b) Intra uterine insemination (IU1)
(c) Gamete intra Fallopian transfer
(d) All of these
b) FILL UPS
1. Infertility is the of a couple to produce child
inspite of unprotected sexual
cohabitation.
2. In vitro fertilisation is a technique that
involves transfer of into the
fallopian tube.
C) TRUE / FALSE
1. Test tube baby is an in - vivo technique.
2. It is never possible to have child from an
infertile couple.
3. In IUT technique, embryo at 16 cell stage is
transferred to uterus.
ANSWER KEY: PART-A
a) MCQ’S
1. (d) - Both (b) & (c) (IUD is a pregnancy
controlling device)
2. (a) - Who cannot produce an ovum (once ovum is
transferred, they can support
fertilization and embryo development)
3. (c) - UI (sperm being in low count, are directly
inserted in uterus to ensure
fertilization)
4. (c) - ICSI (The sperm is injected into cytoplasm
of ovum, directly in laboratory
conditions to ensure fertilization)
5. (a) Zygote intra Fallopian transfer (ZIFT) (GIFT
and IUI are practiced only when there is low sperm / ovum count)
b) FILL UPS
1. Incapability
2. Early zygote
c) TRUE/FALSE
1. False; it is an in- vitro or ex — vivo, i.e. out
side the body with minimum
alterations of natural conditions.
2. False : ARTs help in taking child from infertile
couple, dpending upon the
problem.
3. True: In GIFT or ZIFT itis of 8 — celled stage.
PART B SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. What is infertility?
2. What are reasons of infertility?
3. Name the various Assisted Reproductive
techniques.
4. Under what conditions, artificial insemination is
needed?
PART C -LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Explain ART’s applied under conditions of low
sperm or egg count.
2. Explain assisted reproductive techniques applied
to infertile couple, to have child.
A35
INTRODUCTION
Dear students, after fertilization, during the
formation of embryo, there are four extra embryonic membranes, formed around
the foetus. From outer to inner, these are;
Chorion, Amnion, Allantois and Yolk sac. Amnion is
the second layer that surrounds
the embryo. It encloses AMNIOTIC CAVITY that is
filled with a fluid, known as AMNIOTIC FLUID. Amniocentesis is a diagnostic
procedure, during pregnancy, in which the amniotic fluid is taken out from the
amniotic cavity with the help of fine and long needle to study the foetal cells
to know the genetic defects or infections if any.The foetus is surrounded by
the amniotic fluid that contains foetal cells and other substances such as
alpha foetoprotein. It also protects the foetus from any mechanical injury and
helps in regulating the temperature of the foetus. The cells and substances
present in the amniotic fluid provide important information about the baby’s
health
before birth.
Why is Amniocentesis performed?
Aim: The amniocentesis technique is performed to
check:
If the karyotype (the chromosomes) of the baby is
(are) normal;
If there is evidence of a neural tube defect (birth
defects of the brain, spine orspinal cord);
If there is evidence that the baby might have had an
infection;
If the lungs of the baby are ready to breathe;
Sex (male/ female)of the developing baby;
Genetically controlled congenital ( inborn)
diseases;
Metabolic disorders in the foetus (by abnormal
chemical reactions that alterthe
normal metabolic process).
1. LiThe patient is made to lie down on the table
and asked to place the
handsbehind the head.
2. The blood pressure, heart rate and breathing rate
are checked.
3. An ultrasound is performed to scan the heart rate
of the foetus, position of
the placenta, foetus, umbilical cord and locate the
pocket of amniotic fluid.
4. The abdomen is cleansed with an antiseptic and is
injected with anaesthesia.
5. A long, thin, hollow needle is inserted through
abdominal and uterine wall of
a pregnant female (about 14" to 15" week
after conception)into the amniotic
cavity of uterus to collect the amniotic fluid.
6. The collected fluid is placed in a light
protected container.
7. The heart rate of the foetus and the patient are
reassessed.
8. The collected fluid is sent to the laboratory for
examination.
SIGNIFICANCE OR USES:
a. SEX DETERMINATION :The
somatic cells of foetal skin drawn with amniotic fluid are stained to determine
the presence of sex chromatin (barr body).Presence of barr body indicates that
the developing foetus is female (as female is with 2X chromosome out of which
one X- chromosome is active while
other X-chromosome is heterochromatised into darkly
stained barrbody).
b. CONGENITAL DISEASES (INBORN
DISEASES): By _ karyotypic (the chromosomes) studies of
somatic cells abnormalities due to changes in chromosome number (Down's
syndrome: having additional copy of
chromosome number 21 or trisomy of chromosome 21),
(Turner's syndrome:
absence of one of the X chromosome resulting in the
karyotype 45+XO),
(klinefelter’s syndrome) having an additional copy
of X chromosome resulting
in karyotype 45+XXY) can be determined.
c. METABOLIC DISORDERS :By
the enzyme analysis of amniotic fluid ,different types of inborn metabolic
disorders like phenylketonuria (mental disorder due to lack of enzyme
phenylalanine hydroxylase), alcaptonuria (dark urine excreted due to lack of
enzyme level required to breakdown homogentisic acid in the body )etc. can be
detected.These inborn errors are caused by theabsence or inactivity of specific
enzymes due to gene mutations.So with the help of this, it is confirmed that
the child is likely to suffer from some
incurable, congenital defect, and the mother can go
for abortion.
DRAWBACKS:
1. MISUSE:
However, these days, the amniocentesis is being misused also.
Mothers even get their normal foetus aborted if it
is a female. This is just
equivalent to killing of normal child. So Government
of India enforced Pre-natal
Diagnostic Techniques (Regulation and Prevention of
Misuse) Act, 1994, since
January 1, 1994 under which all genetic counseling
centers and laboratories are
required to apply for registration. The violation of
this Act can bring a fine of Rs.50,000 and imprisonment for two years .The
doctor's registration is also
cancelled till the complaint is disposed of.
2. RISKS INVOLVED IN AMNIOCENTESIS
INCLUDE:
Risk of Miscarriages( loss of foetus)
Risk of Injuries.
Cramping(painful contraction of a muscle)
Leaking of amniotic fluid from the puncture site or
vagina
Preterm labour (labour after week 20 of pregnancy
and before week 37 of
pregnancy )
Occasionally a baby might also die after a normal
amniocentesis due to
unexplained reasons.
(a) determine any disease of heart performing the
Amniocentesis test is
(b) determine any disease of embryo
(c) know about the disease of brain
(d) grow cells on culture medium foetus
2. The fluid sample required for
(a) The amnion
(b) The placenta
(c) The liquid surrounding the immediate
(d) All of the above
3. How many days are required for the
Amniocentesis tests results?
conception.
(a) 1 day
(b) 1-2 days
(c) 1-2 weeks
(d) 3-4 weeks
4. The amniocentesis procedure is not done
before the ___ week after
(a) 4-5"
(b) era
(c) 10-12"
(d) 15-16"
5. Amniocentesis has helped
(a) The childless couples
(b) Anti female demographic snow ball set in motion
(c) Biological superiority of female eatablished
(d)waste of money
6. Amniocentesis is a prenatal diagnostic
test,which can also determine whether an unborn
child will have ______ or not.
(a) Obesity established.
(b) Diabetes
(c) Down's syndrome
(d) All of the above
TRUE /FALSE :
1. Amniocentesis technique used to determine
prenatal detection of many genetic and metabolic disorders in the embryo.
2. Location of foetus is determined by sonography.
3. A fine hollow needle is inserted into the
amniotic cavity of pregnant female (6 or 8" week after conception).
FILL UPS:
1. The amniotic fluid contains skin cells and a
number of enzymes.
2. Amniocentesis is a process to determine of the
embryo.
3. Amniocentesis technique is being for illegal
detection of sex of the
foetus.
ANSWER KEY: PART-A
MCQs
1. b
2.C
3. d
4.d
5. a
6.c
TRUE / FALSE :
1. True
2. True
3. False (Hint: 14 or 15" week after
conception).
FILL UPS:
1. Foetal
2. Sex
3. Misused
PART B. SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Name the act by which amniocentesis is banned in
our country?
2. Amniocentesis is misused in pregnancy
termination; is it true? Why?
3. Why has the Government imposed a statutory ban on
Amniocentesis, in
spite of its importance in the medical field?
PART C: LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. What is amniocentesis technique? Give its uses?
How has this technique
being misused?
Dear students, now let us Know what we
have learnt!
PART A: VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
MCQs