16- ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES
CHAPTER NO.16 ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES
A183
INTRODUCTION
Pollution is defined as an undesirable change in
physical, chemical or biological or Characteristics of air, water and land that
may or will adversely affect human life, Industrial progress, and living
conditions.
Word pollution has been derived from Latin Word
“pollutionem” which means defilement.
Pollutant is a substance, chemical or factor that on
release into the environment has an adverse effect on human interest.
TYPES OF POLLUTANTS:(On
the basis of degradation)
1. Biodegradable pollutants capable of being removed
or degraded by biological Actions e.g. domestic sewage, livestock wastes,
municipal sewage etc.
2. Non-biodegradable: The substances which are
normally not acted upon by microbes or acted upon very slowly. E.g. glass,
plastic, DDT, pesticides,polyethylene bags, heavy metals etc. (On the basis of
occurrence in nature)
Primary Pollutants: These are present in the same
form in which these are added by man e.g. SPM, CO, DDT, Hydrocarbons,
pesticides, fertilizers etc.
Secondary pollutants: These occur in different forms
and are formed by
Reaction between primary pollutants in the presence
of sunlight e.g. HNO3
H2SQO,, PAN etc.
(On the basis of existence in nature)
Quantitative pollutants: These are naturally present
in nature and are also added by man. These become pollutants when their
concentration reaches beyond a threshold value e.g.CO2, Nitrogen oxide
etc.Qualitative pollutants: These are not present in nature but are added by
due to hu- man activities e.g. pesticides, fungicides, herbicides.
TYPES OF POLLUTION:
On the basis of origin:
1. Natural Pollution: This type of pollution is
caused by natural phenomenon like volcanic eruptions, dust storms, pollens etc.
2. Anthropogenic Pollution: This type of pollution
is caused by man e.g. waste
of industries, farm runoff, power plants, etc.
On the basis of medium:On the basis of medium in
which it occurs, pollution is of three types:Air Pollution, Water Pollution and
Soil pollution.On the basis of physical nature:
Pollution is named after the physical nature of
pollutant like;Gaseous Pollution, Dust Pollution, Therma! Pollution, and Noise
Pollution.
LET’S KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
PART-A VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
A. MCQs:
1. Which of the following is not a
pollutant?
(A)CO2
(B) CO
(C) NO2z
(D) SO2
2. Pollutants
which are present in same form in which these are added by manare:
(A)Secondary pollutant
(B) Quantitative Pollutant
(C) Primary Pollutant
(D) Qualitative Pollutant
3. The pollutants which are naturally
present in nature and are also added by man are:
(A) Secondary Pollutant
(B) Quantitative Pollutant
(C) Qualitative Pollutant
(D) Primary Pollutant
4. The pollutants which are not present in
nature but are added by human activities are:
(A) Non-Biodegradable
(B) Qualitative Pollutant
(C)Secondary Pollutants
(D) Both A and B
5. Non-Biodegradable pollutants from the
following are:
(A) NOz, CO2, SO2
(B) Sewage, livestock Waste
(C) DDT, pesticides, polythene bags
(D) All of these
B. TRUE/FALSE:
1. Secondary pollutants are formed by reaction
between primary pollutants.
2. PAN is a secondary pollutant.
3. DDT is
biodegradable.
C. FILL IN BLANKS:
1. —-------- is a substance, chemical or factor that
on release in environment has
an adverse effect on human health.
2. Word Pollution has been derived from Latin word
---—---.
A.MCQs:
(A)CO2
(C) Primary Pollutant
(B) Quantitative Pollutant
(D) Both A and B
(C) DDT, pesticides, polythene bags
B. TRUE/FALSE:
1. TRUE
2. TRUE
3. FALSE: DDT is non-biodegradable.
C.FILL IN BLANKS:
1. Pollutant
2. Pollutionem
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. What is pollution?
2. What is a pollutant?
3. Name some primary pollutants?
4. List the types of pollution on the basis of
origin?
5. Expand the term SPM.
PART: C LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. What is pollution? Explain its types.
2. What is a pollutant? Explain its types with
examples.
A184
INTRODUCTION
POLLUTION:Occurrence of foreign particles or gases
in atmosphere which are harmful to man, vegetation, animals and buildings.
Clean and pure air is essential survival and good health.
POLLUTANTS:A pollutant is substance or energy
introduced in air that has undesired and
adverse effects over its quality and usefulness.
Pollutants are divided into several categories:
(a) Biodegradable (b) Non-biodegradable
(a) Primary pollutants (b) Secondary pollutants
(a) Quantitative pollutants (b) Qualitative
pollutant
(a) Natural pollution (b) Anthropogenic pollution
(a) air pollution (b) water pollution (c) soil
pollution
CAUSES OF AIR POLLUTION:
SOURCES OF AIR POLUTION:
1. INDUSTRIAL AIR POLLUTANTS
(i) Metallurgical processes: Release of dust and
fumes loaded lead with nickel etc.
(ii) Chemical industry: Hydrochloric acid, chlorine
gas, zinc, lead, arsenic
and many oxides CO,CO2,SOz pesticide, fungicide,
weedicides and fertilizer industry releases lot of chemicals.
(iii) Thermal power plant: Release particulate
matter and gaseous air pollutants.
2. MOBILE COMBUSTION SOURCES:
Locomotives, Air crafts and automobiles.
[Arecord :- In Dehli Automobiles release CO
(77.2%),NO (7.7%) tons are pumped out from automobiles only.]A record hitting
data of metro cities show a considerable amount of lead let out from auto
mobiles threatens lead poisoning among residents of cities.
3. BURNING OF FOSSIL FUEL:
Coal - It produces COz, incomplete burning releases CO, variety of
hydrocarbons, methane and soot.
4. AGRICULTURAL WASTE:
CO, methane are produced from paddy, guts of Livestock, burning of biomass,
crop spraying.
Dusting of pest and weed control emits organic
phosphates,chlorinated hydrocarbons arsenic and lead into air.
5 IONIZING RADIATIONS:
Alpha, beta particles and gamma rays produced during xperimentation nuclear
explosion, and in nuclear power plants.
6. SUSPENDED PARTICULATE MATTER: Major air pollutant
generated from coal (oil refineries ,power plants) cement dust,silica
dust(stone crushing ,welding) and lot of dust is blown by transport
vehicles.Fly ash and smoke from
burning coal .
7. SOLID WASTE DEPOSITION IN LANDFILLS:
Generate methane.
8. NATURAL AIR POLLUTANTS:
Pollen spores, marsh gas ,volcanic gases from natural phenomenon in nature.
MAJOR AIR POLLUTANTS
1. Oxides of Carbon:-(a) CO2 released by human
activities such as burning fossil fuel as well as natural processes respiration
and volcanic eruptions. It is a greenhouse gas, as it traps heat.
(b) Carbon monoxide: it accounts for 50% of total
air pollution . 50% of CO is
emitted from automobiles.Over 15 million tonnes of CO is added to
environment
every year.Produced due to use of coal and oil for
energyproduction,manufacturing and transport.respiration process. About 15%
increase in last 100 yearsis recorded due to
Deforestation and burning of fuel, biomass, forests,
savannah grass lands for
pasture and cropland.
3. Sulphur dioxide; and nitrogen dioxide: Acid rain
is 60-70%due to SO2 and
30-40% due to NO2. Dry deposition formed from acidic
gases and particles in wind.Wet deposition formed of acidic water received
through rain, fog and snow.pH of rain fall estimated 4.0 to 6.5. Produced from
ore smelting, coal burning, industrial
processes,municipal incineration.Sources of oxides
of nitrogen ; petrol and diesel
vehicles,burning biomass,nitrogen fertilizers.
Lichens are sensitive to SO2.
4 .Aerosols: These are chemicals present in the form
of vapours or fine mist ;contain chlorofluorocarbons. CFC are emitted from jet
planes,refrigerators, air conditioners etc.Burning of plastics releases poly
chlorinated biphenyls (PCB)
5. Benzpyrene. :It is a carcinogen produced by
tobacco smoke, industrial affluence and automobile exhausts.
6.Photochemical oxidants: Unburnt hydrocarbons react
with nitrogen oxides to
form Os, peroxy-acyl nitrates (PAN), aldehydes. Some
form peroxy - propional
nitrate (PPN), peroxy -buteryi nitrate.
7. SMOG: Formed by combination of smoke and fog.
Term smog was coined by scientist Dr. Henry Antoine. It contains SO2, NO: etc.
It is of two types: —--- London smog (sulphurous
smog), Photochemical smog
(Los Angeles smog).Photochemical smog is produced
due to reaction between nitrogen oxides and unsaturated hydro carbons.
7. Hydrocarbons: Volatile organic carbons (VOCs)
e.g. unsaturated ethylene, CH. Most of hydrocarbons are added by burning of
petroleum and methane by decay of organic matter ,from paddy fields (about
40%). Methane is also a greenhouse gas.
8.Particulate matter:--It is of two types: —
(a) settable (more than10 um)
(b) Suspended
Suspended particulate matter is of three types: ——
(i) Aerosol (less than 1pm) (ii/Dust solid (more
than 1 pm) (iii) Mist liquid (more
than 1 ym) Anthropogenic aerosols (made by human
activity) account for about 10% of
our atomosphere.Due to pollution, average age of
person decreasing by 3.2 years.[A report 2016] most polluted cities of India
are: Ghaziabad, Noida, Delhi,Mumbai and Lucknow. Famous monuments are affected
by air pollution.
Let us know What we have Learnt!!
1.MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
1.Who was first scientist to coin the term
smog and describe layers of smog?
(a) Nikolas Tesla
(b) Stephen Hawking
(c) Dr. Henry Antoine
(d) Nicolas Copernicus
2. Which of following particles is called
particulate pollutants?
(a) Ozone
(b)radon
(c)Fly Ash
(d) Ethylene
3. The major photochemical smog is:
(a) Hydrogen peroxide
(b) Chlorofluorocarbon
(c) per oxy acetyl nitrate
(d) all of above
4. Smoke ,fumes, ash, nitric acid, sulphur
dioxide are the main sources of:
(a) Primary pollutant
(b) Secondary pollutant
(c) Biodegradable pollutant
(d) None of above
5. Carcinogen produced in tobacco smoke and
auto mobile exhausts is:
(a) H2SOz,
(b) chloroflourocarbons
(c) Benzpyrene
(d) all of above
2. TRUE / FALSE:
1. Peroxy-acyl Nitrate and ozone are primary
pollutants.
2. Wet deposition of acid rain is received through
rain, fog and snow.
3. Indoor pollution is caused by tobacco smoking,
air conditioning.
3. FILL IN THE BLANKS:
1. Automobiles are largest source of-- pollution in
cities.
2 -----is major pollutant which decreases oxygen
carrying capacity of haemoglobin of blood.
ANSWER KEY: PART-A
1. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
1.(C ) Dr. Henry Antoine
2.(C ) Fly ash
3. (B) Chlorofluorocarbon
4. (A) Primary pollutant
5. (C ) Benzpyrene
2 TRUE/ FALSE:
1. False
2. True
3. True
3. FILL IN THE BLANKS:
1. Air
2. CO (carbon monoxide)
1.Name two pollution indicator plants?
2. Write major effect caused on human health by
mobile combustion sources? 3What are secondary pollutants?
1. Define air pollution. Name two sources of air
pollution. Describe four primary air pollutants and their sources.
A185
INTRODUCTION
Air pollution control is control of pollutants
through different methods
to get pure air.
Many methods are adopted to purify air, are:Chemical
methods, ESP, Plantation etc.
SEPARATION OF POLLUTANTS: Separation of
pollutants can be done by different methods.
(a) Sulphur free lead free fuel should be used.
(b) Pollutants from automobiles can be decreased by
(i) By using more efficient fuel engines.
(ii) Multipoint fluid injection engines to reduce
un-burnt hydrocarbon emission.
(iii) Catalytic converters: —- Platinum, palladium
and rhodium act as catalysts.
Vehicles fitted with catalytic converters should use
unleaded (lead free)petrol ;as
lead inactivates the catalytic converters. Catalytic
converters can slash carbon
monoxide emission from 90 grams to 3-4 grams.
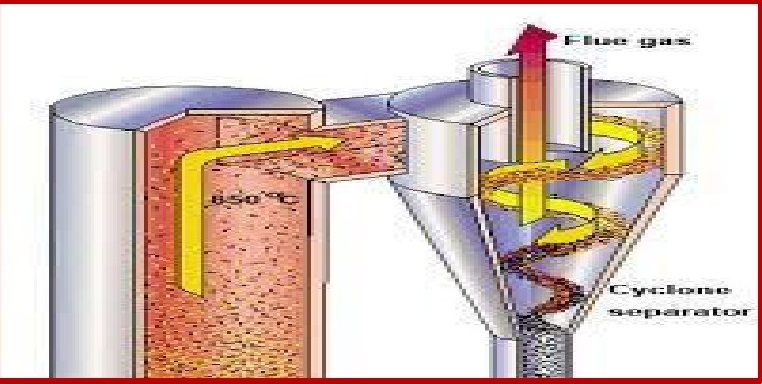
DEVICES TO CONTROL PARTICULATE MATTER:
ARRESTERS:
Arresters are of many types:
(i) ESP : Electrostatic Precipitators
(ii) CYCLONE SEPARATORS
(iii) TRAJECTORY SEPARATORS
(iv) GRAVITY SETTELING CHAMBERS
(V) FILTERS
It is most effective device to remove particulate
pollutants. It can be employed to
separate hot as well as dry charged particles. These
can remove size range of 5-
20 mm and to an extent of 99% but velocity of air
must be low. Particle collecting plates ESP’s are shaken or vibrated and
particles are shed to receiver basket. ESP’s are employed in thermal plants,
industries of power generation,paper mills and sludge incineration.
CYCLONE SEPARATOR:Dust laden gas stream is
transformed into combined vortex from centrifugal forces tend to derive the
suspended particles to wall of body of separator.
BAG HOUSE FILTERS:In this device dust laden fumes
are passed through the filtering devices.Filtering devices are made of porous
mats of polyester, Teflon, wool or
cellulose etc. Particles are held by filters and
clean gases pass through them.
SCRUBBERS:Scrubbers are formed from dry or wet
packing material. These are used to
separate dust particles and toxic gases (especially
SO2) from air.
Polluted air is forced in,simultaneously a counter
current of water or lime moves in by spray nozzle . Water drops remove
articulates as well as toxic gases while lime removes SO: as calcium sulphate
or sulphite.Wet scrubbers are used in metallurgical industries.
USE OF CNG:CNG is called a cleaner fuel because it
is mainly formed of methane with
smail percentage of other hydrocarbons. Its
combustion releases fewer pollutants. WORLD'S largest fleet of CNG buses is in
Delhi.
EURO NORMS:It refers to permissible emission level
of both petrol and diesel vehicles It
was first implemented in European countries.
Similar norms were instituted by government of India
are called Bharat stage emission standards (BSEB); to reduce vehicular
pollution in indian cities. The Government of India announced a new auto fuel
policy which includes stringent pollution - level norms e.g. Since 1 April,2000
Eurotnorms were introduced nationwide.Government of India announced to
implement BS VI emission norms for four wheelers from 2023.December 2, is
recalled as National Pollution prevention Day remembering Bhopal tragedy
occured on 2" December, 1984 due to leakage of MIC (Methyl
isocynate) from fertilizer plant (union carbide) in
atmosphere.In december1997 KYOTO SUMMIT was held in JAPAN where it was decided
to reduce the emission of greenhouse gases to a level. COP Ill Kyoto protocol stated:
The European union will reduce its greenhouse
emission by 8 pacet below the 1990 levels,the United states by 7 percent and
Japan by 6
percent.
Twenty oneotherindustrialized countries will meet
similar binding target and reductions would be achieved between 2008 and 2012
A.D.
Copenhagen Climate Summit was held in December 2009
(commonly callled
COP -9 at copenhagen Danish capital. Afair deal on
climate change,alegally non binding agreement was adopted by world’s 17 most
powerful nations thatthey won't allow the global temprature to rise by more
than 2° C. But it was rejected by most of poor countries who wanted a maximum
temperature rise to be fixed at 1.5°C.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT
1. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
(1) Montreal protocol which calls for
appropriate action to protect the Ozone Layer from human activities was passed
in year:
(a)1985
(b) 1986
(c) 1987
(d) 1988
2. Biodiesel is obtained from:
(a) Jatropa biloba
(b)cedrus
(c) Jatropa curcus
(d) None of these
3. Gaseous pollutants can be controlled by:
(a) Prolysis
(b) Arresters
(c) Incineration
(d) Adsorption
4. KYOTO PROTOCOL was endrosed at:
(a) COP III
(b)COP V
(c) COP VI
(d) COP IV
2. TRUE / FALSE
1. First earth summit was held in New Delhi.
2. In October 2019 government of India announced to
implement BSVI emission
norms for vehicles across the country from 2023.
3. CNG is called cleaner fuel as its combustion
releases fewer pollutants.
3. FILL IN THE BLANKS
1.Bhopal gas tragedy is associated with-—-—--—- --.
2.Device which separates the particulate matter on
the basis of their charges
and due to development of corona effect is
termed-—-- -.
ANSWER KEY: PART-A
1. (c)
2. (a)
3. (a)
4. (d)
1. FALSE
2. TRUE
3. TRUE
1. MIC (Methyl isocyanate)
2. ESP (Electrostatic precipitators)
Q 1. How does plantation helps to control air
pollution? Name two plants that can
use nitrogen oxides?
Q2. Name materials used as filtering mats in Bag
house filters.
Q3. Discuss steps taken in India to control air
pollution.
Q.1 How can particulate matter be controlled?
Explain role of Scrubbers?
A186
INTRODUCTION
All pollutants either affect vegetation or living
beings. Adverse effects are increasing day by day. Climate is changing
continuously.
Environmentalists are recording effects day by day.
causes mutations. Lethal in low doses, in low doses causes cancerous
growth.
EFFECTS OF RADIOACTIVE POLUTANTS:
1. ER Bone cancer
2 MR. Damages WBC's, bone marrow, lymph nodes, skin
cancer, sterility and defective eye sight. These may cause ionization of
various body fluids, chromosomal aberrations, and
gene mutations.
3. EERE brings about nervous muscular and genetic
changes
4 [EG Skin cancers and tumours to miners.
Apart from above effects many radioactive pollutants
cause:Snow blindness, Inactivation of biomolecules, leukemia, Brain tumors,
Eye cataract, Suppression in immune system.
BAD EFFECTS OF ACID RAIN:
1. Acid rain caused by polluted air
2. Damages a number of heritage monuments e.g Taj
Mahal in Agra
3. Below pH 5 rain causes death of planktons.
4. Kills soil microbial community.
EFFECT OF AIR POLLUTION ON CLIMATE:CFC’S
brings depletion of ozone layer column; which allows high energy UV radiations
in earth's atmosphere, a big damage to plants and animals.A vertical influence
Temperature profile of atmosphere; leads to greenhouse
effect.Reduction in Rainfall; aerosols change
physics of cloud formation.
GLOBAL WARMING:Greenhouse gases COz2, CHa, Oz, NO,
NO2 absorb infrared radiations
from earth and re radiate them towards earth.
Increase in temperature caused by CO2 60%, CFCs 14%
and oxides of nitrogen 6% recorded.
NEGATIVE IMPACTS OF GLOBAL WARMING;
1. ICE CAPS will melt and coastal areas round the
globe will be in undated under increased level of oceans.
2. Grain production will be reduced.
3. Many areas will be warmer and drier (e.g.
America)
4. One third of global forest will swept away.
5. Deserts will be increased.
6. Chances of flood, cyclones, and hurricanes will
be increased.
7. Oceans acidification will be caused.
8. Extinction of more than one million species of
animals and plants is expected upto 2050.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT !!
PART:A VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
Q1. Lead concentration in blood is
considered alarming ig it is:
(a)20 yg/100ml
(b) 30~ug/100ml
(c ) 4-6 ug/ 100ml
(d)10 yg/100ml
Q2. Anthracosis is caused by:
(a) Coal dust
(b) lron
(c) Cane fibre
(d) Silica
Q3. Freon gas causing stratospheric O3
depletion mainly released from:
(a) Refrigerators
(b) Automobiles
(c) Thermal Power Plants
(d) Steel Plants
Q4. Greenhouse gases cause global warming
resulting into:
(a)lncrease of deserts
(b) Acidification of oceans
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Q5. Thickness of ozone layer in a column of
air from ground to top of atmosphere is measured in terms of:
(a)Decibel units
(b)Pascal units
(c) Svedberg units
(d) Dobson units
1. The CO2 causes asphyxial death due to oxygen
starvation.
2. Photo chemical smog causes silvering, glazing and
necrosis of leaf.
3. According to CPCB (central pollution control
board) particulate pollutants of
4.5u m or more are harmful for human.
1. —---—---— breaks O3 enzymatically.
2. ---------- damages a number of heritage
monuments.
1.(b)
2.(a)
3.(a)
4.(d)
1.False
2.True
3.False
1. Active chlorine
2. Acid rain
PARTC SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
Q 1.What is snow blindness?
Q 2. What are brown clouds?
Q 3 Write a note on ozone layer depletion.
PART: G LONG ANSWER TVPE QUESTIONS:
Q1. Define global warming? Write its effects?
A187
INTRODUCTION
WATER POLLUTION occurs when harmful substances -
often chemicals or
microorganisms - contaminate a stream, river, lake,
ocean, aquifer, or other body of water, degrading water quality and making it
toxic to humans or the environment.
TYPES OF WATER POLLUTANTS:Water
used for household, agricultural and industrial purposes when discharged after
use is polluted with soluble, insoluble matter and even pathogens. Water
pollutants can be classified as follows:
1. Biological: It includes pathogens like bacteria,
viruses, worms and protozoa.
Most of these are added by excreta of animals.
2. Chemical: (a) Inorganic e.g. — phosphates,
nitrates, fluorides and chlorides.
(b) Organic e.g. — phenols, plastics, dyes,
pesticides and chloro compounds.
(c) Heavy Metals e.g. — cadmium, mercury, copper,
zinc and their organometallic compounds.
3. Physical: Waste heats from industrial plants.
SOURCES OF WATER POLLUTION:
1. Urbanization: Anytime there are massive numbers
of people conglomerated in one dense area, a physical disturbance of the land
follows. The building of new roads, houses, and industries affect the
cleanliness of the water through the use of detergents, chemicals, and exhaust
emissions. When it rains, these chemicals are washed into the rivers and
streams, and eventually into the
drinking water supply.
2. Industrial waste: Every day, industries produce
large amounts of waste. This
waste contains pollutants and toxic chemicals such
as mercury, lead,asbestos, sulphur and nitrates among other harmful chemicals.
Most
industries lack a proper waste management system.
This causes the waste to drain into water bodies such as rivers and the sea
through waste disposal canals. These waste chemical change the color of the
water, cause
eutrophication (excessive plant and algae growth)
and change the water temperature and pose a serious hazard to humans, animals,
and plants.
3. Domestic waste and sewage: Wastewater and sewage
from household are also common causes of water pollution. Sewer water carried
chemicals and harmful bacteria which pose serious health issues. Sewers from
houses carry pathogens which cause diseases. Wastewater and sewer carry
microorganisms which carry deadly diseases and are also breeding ground for
disease carriers.
4. Marine Dumping: Every household produces garbage.
It can be in the form of
papers, plastic bottles, glass, rubber, aluminium
and also waste food. This
garbage is sometimes dumped in water bodies, and
this causes water pollution. Some of these waste deposits take up to 200 years
to decompose.When they enter the sea, not only do they cause pollution to the
water but also
harm to water creatures.
5. Oil Spills: Oil is also one of the most dangerous
causes of water pollution. Oil
waste from industries, ships, and machinery
sometimes gains access to water bodies along with other waste products. Oil is
not soluble with water and thus causes a layer that covers the water
underneath. Besides polluting the water and making it harmful to humans, it
also causes death to marine wildlife.
6. Pesticides and chemical fertilizers: These are
products used by farmers to grow crops free of bacteria and insect infestation.
While they may be usefulto plant life, they pose serious hazards to humans and
animals if they gain access to water. This cause of water pollution mostly
occurs when it rains. The chemicals mix with rainwater and flow to water
bodies.
7. Radioactive waste discharge: There are nuclear
power plants all around our
country, and the government allows “permissible
levels” of radioactive water
to be released into the environment every day. And,
while it’s permissible—it
doesn't mean it's safe. Likewise, accidents have
been known to occur,releasing horribly high amounts of harmful radioactive
chemicals to be released into the air, water, and soil.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
PART: A Very Short Answer Type
Questions:
A. MCQs:
1. Which of the following is the most
harmful cause of oceanic water pollution?
(a) Plastic Waste
(b) Industrial Effluents
(c) Oil Spills
(d) Domestic Waste
2. Eutrophication by sewage pollution
refers to the
(a) Nutrient enrichment of freshwater bodies
(b) Nutrient depletion of freshwater bodies
(c) Toxic chemical accumulation in freshwater bodies
(d) Heavy Metals accumulation in freshwater bodies
3. Waste water released from are not the
sources of bacteria
(a) Sanitary
(b) Municipalities
(c) Tanning
(d) Industries
4. The is an important requirement of the
aquatic life.
(a) Dissolved Nitrogen
(b) Dissolved Chlorine
(c) Dissolved Oxygen
(d) Dissolved Methane
5. Which of the following is not the
inorganic water pollutant?
(a) Phenols
(b) Nitrates
(c) Chlorides
(d) Phosphates
B. True / False:
1. Mostly pollution of rivers takes place by
discharge sewage/effluents.
2. Pollution from pesticides is part of surface run
off type of pollution.
3. Radioactive water released in permissible limits
is safe..
C. Fill in the Blanks:
1. Nutrient accelerates growth of algae.
2. Waste from sewers contains which cause deadly
diseases.
ANSWER KEY OF PART-A
A. MCQs:
1. (c) Oil Spills — Oil spill in oceans make
insoluble layer over water causing deaths of marine wildlife and making
hazardous to humans.
2. (a) Nutrient enrichment of freshwater bodies —
Eutrophication is nutrient
enrichment resulting in excessive plant and algae growth.
3. (d) Industries — Waste water released from the
sanitary, municipalities,tanning and slaughtering plants are the sources of
bacteria.
4. (c) Dissolved Oxygen — The dissolved oxygen is an
important requirement of the aquatic life. They take oxygen from water to
survive.
5. (a) Phenols — Phenols are the example of organic
water pollutants
B. True / False:
1. True — River Pollution is majorly caused from
discharge of effluents and sewage.
2. True — The chemicals mix with rainwater and flow
to water bodies.
3. False — Radioactive water released in permissible
limit doesn’t mean it's safe.
C. Fill in the Blanks:
1. Enrichment — Nutrient enrichment accelerates
growth of algae and plants.
2. Pathogens — Pathogens are organisms that can
produce diseases.
PART: B Short Answer Type Questions:
1. What is the difference between point and
non-point sources?
2. How water pollutants are classified?
3. How urbanization is major source of water
pollution?
PART: C Long Answer Type Questions:
1. What is water pollution? Explain different
sources of water pollution.
A188
INTRODUCTION
WATER POLLUTION, to a larger extent, can be
controlled by a variety of methods. Rather than releasing sewage waste into
water bodies, it is better to treat them before discharge. Practicing this can
reduce the initial toxicity and the remaining substances can be degraded and
rendered harmless by the
water body itself. If the secondary treatment of
water has been carried out,then this can be reused in sanitary systems and
agricultural fields.Even chemical processes such as coagulation, ion exchange
method, reverse osmosis, etc. will greatly reduce the level of water pollution.
CONTROL MEASURES OF WATER POLLUTION:
TREATMENT OF WASTE WATER:We
know that large quantities of waste water are generated every day in cities and
towns. A major component of this waste water is human excreta. This
municipal waste-water is also called sewage. It
contains large amounts of organic matter and microbes. Many of which are
pathogenic.
This cannot be discharged into natural water bodies
like rivers and streams directly — you can understand {his treatment is carried
out in two stages:
a) EE These treatment steps basically involve
physical removal of particles — large and small — from the sewage through
filtration and sedimentation. These are removed in stages; initially, floating
debris is
removed by sequential filtration. Then the grit
(soil and small pebbles) are
removed by sedimentation. All solids that settle
form the primary sludge, and
the supernatant forms the effluent. The effluent
from the primary settling tank
is taken for secondary treatment.
b) ee The primary effluent is passed into large
aeration tanks where it is constantly agitated mechanically and air is pumped
into it. This allows vigorous growth of useful aerobic microbes into flocs
(masses of bacteria associated with fungal filaments to
form mesh like structures). While growing, these
microbes consume the major part of the organic matter in the effluent. This
significantly reduces the BOD (biochemical oxygen demand) of the effluent. BOD
refers to the amount of the oxygen that would be consumed if all the organic
matter in one litre of water were oxidised by bacteria. The sewage water is
treated till the BOD is reduced.The BOD test measures the rate of uptake of
oxygen by micro-organisms ina
sample of water and thus, indirectly, BOD is a
measure of the organic matter present in the water. The greater the BOD of
waste water, more is its polluting potential. Once the BOD of sewage or waste water
is reduced significantly, the effluent is then passed into a settling tank
where the bacterial ‘flocs’ are allowed to sediment. This sediment is called
activated sludge. A small part of the activated sludge is pumped back into the
aeration tank to serve as the
inoculum. The remaining major part of the sludge is
pumped into large tanks
called anaerobic sludge digesters. Here, other kinds
of bacteria, which grow
anaerobically, digest the bacteria and the fungi in
the sludge. During this digestion, bacteria produce a mixture of gases such as
methane, hydrogen sulphide and carbon dioxide. These gases form biogas and can
be used as source of energy as it is
inflammable. The effluent from the secondary
treatment plant is generally released into natural
water bodies like rivers and
streams.
Trickling Filter method is another method of
Secondary Treatment. In this,sewage water passes through thick bed of gravel
stones so that bacteria consume most of the organic matter.
es 10 this, salts like nitrates and phosphates are
removed by precipitation technique. It may involve processes like biological
nutrient removal, disinfection and removal of micro pollutants. Water is now
pure enough to drink.
Gobar Gas plant can be used for prevention and
control of water pollution and
to recycle the various kinds of waste products. Some
other recommended
methods are:
a) Compositing kills most of the pathogens and also
ripens the dung into manure.
b) From jute wastes, hardboard can be prepared.
c) Coconut and other agricultural wastes can be used
for the manufacture of paper and board.
CONTROLLED USE OF PESTICIDES AND
FERTILIZERS:
Minimum amounts of pesticides should be applied so
that no surplus remains in the soil. Only less stable compounds should be used
in manufacturing biocides.
REVERSE OSMOSIS:By this technique, brackish water is
demineralized by pumping it through a semipermeable membrane under strong
pressure.Thermal pollution can be checked and controlled by employing heat or
dry
cooling towers.
WATER HYACINTH:Water Hyacinth removes biological and
chemical pollutants. It also removes heavy metals like Cd, Hg, Pb and Ni.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
PART: A Very Short Answer Type
Questions:
A. MCQs:
1. What is the full form of BOD?
(a) Biochemical Oxygen Demand
(b) Biological Oxygen Demand
(c) Biometric Oxygen Deep water
(d) Biological Oxygen Deep water
2. Water Pollution Act was introduced in
which year?
(a) 1973
(b) 1971
(c) 1974
(d) 1984
3. Infiltration, the amount of dissolved
solids passing through the filters
is:
(a) Difference between total solids and suspended
solids
(b) Sum of total solids and suspended solids
(c) Independent of suspended solids
(d) None of the above
4. The Total dissolved solids (TDS) can be
reduced by:
(a) Distillation
(b) Reverse osmosis
(c) lon exchange
(d) All of the above
5. In tertiary treatment nitrates and
phosphates are removed by:
(a) Precipitation
(b) Sedimentation
(c) Sequential filtration
(d) None of the above
B. True / False:
1. Trickling filter method is a primary treatment
method of waste water treatment.
2. Coconut and other agricultural wastes can be used
for the manufacture of paper and board.
3. In primary filtration method, small pebbles are
removed by sequential filtration method.
C. Fill in the Blanks:
1. The the BOD of waste water, more is its polluting
potential.
2. Brackish water is demineralised by pumping it
through a semipermeable membrane under strong pressure, this method is known as
:
ANSWER KEY OF PART -A
A. MCQs:
1. (a) Biochemical Oxygen Demand - BOD is
Biochemical Oxygen Demand which is a measure of the organic matter present in
the water.
2. (c) 1974 — Water Pollution Act was introduced in
1974 for prevention and
control of water pollution, and for the maintaining
and restoring of wholesomeness of water India.
3. (a) Difference between total solids and suspended
solids — In filtration, the
amount of dissolved solids passing through the
filters is Difference between total solids and suspended solids.
4. (d) All of the above — Reverse Osmosis, lon
Exchange and Distillation all are processes for reducing TDS in water.
5. (a) Precipitation — Salts like nitrates and
phosphates are removed by precipitation technique.
B. True / False:
1. False — Trickling Filter method is another method
of Secondary Treatment.In this, sewage water passes through thick bed of gravel
stones so that bacteria consume most of the organic matter.
2. True — Coconut and other agricultural wastes can
be used for the manufacture of paper and board.
3. False — Floating debris is removed by sequential
filtration and then the grit
(soil and small pebbles) are removed by
sedimentation.
C. Fill in the Blanks:
1. greater - The greater the BOD of waste water,
more is it's polluting potential.
2. Reverse osmosis — The brackish water is
demineralized by pumping it through a semipermeable membrane under strong
pressure, this method is known as reverse osmosis.
PART: B Short Answer Type Questions:
1. What is trickling filter method?
2. How waste water can be recycled? Give few examples.
3. How water pollution can be prevented?
PART: C Long Answer Type Questions:
1. Explain all the methods of treatment of water
pollution.
A189
INTRODUCTION
WATER POLLUTION adversely affects the health and
life of man, animals and plants alike. Polluted water is also harmful for
agriculture as it adversely affects the crops and the soil fertility. Pollution
of sea water damages the oceanic life.
As we work with water in our homes in the cities and
towns, we wash everything into drains. Have you ever wondered where the sewage
that comes out of our houses goes? What happens in villages? Is the sewage
treated before being transported to the nearest river and mixed with it? A mere
0.1
per cent impurities make domestic sewage unfit for
human use.
EFFECTS OF WATER POLLUTANTS:The
effect of water pollution depends upon the type of pollutants and its
concentration. Also, the location of water bodies is an important factor to
determine the levels of pollution. Water bodies in the vicinity of urban areas
are extremely polluted. This is the result of
dumping garbage and toxic chemicals by industrial and commercial
establishments.
Following are the adverse effects of various
pollutants:
1. Effect of Organic waste and Domestic
Sewage:Domestic sewage primarily contains biodegradable organic matter, which
readily decomposes — thanks to bacteria and other micro-organisms, which can multiply by using these organic substances as substrates and hence utilize some of the components of sewage. It is possible to estimate the amount of biodegradable organic matter in sewage water by measuring Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD).
Micro-organisms involved in
biodegradation of organic matter in the receiving water body consume a lot of
oxygen, and as a result there is a sharp decline in dissolved oxygen downstream
from the point of sewage discharge. This causes mortality of fisn and other
aquatic creatures. Deoxygenation of water by biodegradation of organic wastes
produces foul smell in water bodies and make it unfit for human consumption.
Pathogen contaminated water causes infectious diseases like cholera, jaundice,
typhoid, dysentery, hepatitis etc. According to Central Water Health
Engineering Institute, about 50-60% Indian population suffers from water borne
diseases and about 30-40% deaths occur due to water pollution. Also these
wastes form scum and sludge in polluted water making it unfit for industrial
use.
2. Effect. of Nutrients on Water
Quality:
Water supports aquatic life because of the presence
of nutrients in it. Here the
primary focus is on fertilizing chemicals such as
nitrates and phosphates.These are contributed by sewage, agricultural run-off
and run-off from un sewered residential areas. Although nutrients are important
for plant growth,too much of nutrients encourage the overabundance of plant
life and can result in environmental damage called ‘Eutrophication’. Due to
this excessive growth of planktonic (free flowing) algae takes places which is
also called “Algal
bloom” which imparts a distinct colour to the water bodies.
Algal blooms cause deterioration of the water quality and fish
mortality. Some
bloom-forming algae are extremely toxic to human
beings and animals.Plants having beautiful mauve-colored flowers which were
introduced into India for their lovely flowers have caused havoc by their
excessive growth by causing blocks in our waterways. They grow faster than our
ability to remove
them. These are plants of water hyacinth (Eichhornia
crassipes), the world’s
most problematic aquatic weed, also called ‘Terror
of Bengal’. They grow abundantly in eutrophic water bodies, and lead to an
imbalance in the ecosystem dynamics of the water body.
3. Effect of High Dissolved Solids
(TDS):
Water is the best solvent and can dissolve a large
variety of substances which
come in its contact. The amount of dissolved solid
is a very important consideration in determining its suitability for drinking,
irrigation and industrial uses. In general, waters with total dissolved solids
of less than 500 mg/Aitre are most suitable for drinking purposes.Higher amount
of dissolved solids may lead to impairment of physiological processes in human
body. Dissolved solid is very important criteria for irrigation. This is due to
the fact dissolved solid accumulates on the ground
resulting in salinization of soil.In this way it
renders the agricultural land non-productive. Dissolved solids are harmful for
industries also because they form scales, cause foaming in boilers,accelerate
corrosion and interfere with the colour and taste of many finished products.
4. Effect of Toxic pollutants:Waste
water from industries like petroleum, paper manufacturing, metal extraction and
processing, chemical manufacturing, etc., often contain toxic substances,
notably, heavy metals (defined as elements with density > 5 g/cm3 such as
mercury, cadmium, copper, lead, etc.) and a variety of organic
compounds.
Minamata disease: Due to consumption of mercury
contaminated fishes of Minamata Bay,
Minamata disease appeared in Japan
in 1962.
Itaiitai disease: Due to consumption of Cadmium
contaminated rice, this disease appeared in Japan which causes liver and lung
cancer.A few toxic substances, often present
in industrial waste waters, can undergo biological
magnification (Biomagnification) in the aquatic food chain. Biomagnification
refers to increase in concentration of the
toxicant at successive trophic levels.
This happens because a_ toxic substance accumulated
by = an organism cannot be metabolised or excreted, and is thus passed on to
the next higher trophic level. This
phenomenon is well known for mercury and DDT.
DDT(Dichloro Diphenyl Trichloroethane) interferes
with the calcium metabolism and egg-shell formation in many birds. The shells
remain thin and undergo premature break by bird's weight during incubation. This
decreases bird population. This was the reason for banning of DDT in the United
States in 1972.
5. Effects of Thermal Discharges on
Water Quality:The discharge of cooling water from
industrial and commercial operations
generally heats up the aquatic environment.
Organisms may become physiologically stress or may even be killed when exposed
to heated water. If water heating is supplemented by the summer heat, the
impact on aquatic
environment can be disastrous.Thermal pollution also
causes a decrease on the driving force or oxygenation which may directly kill
aquatic life through asphyxiation. If toxic pollutants are
present in the aquatic environment, thermal
pollution may increase their toxicity to the aquatic life. Bioavailability of
many pollutants may also increase due to thermal pollution, which may
ultimately adversely affect the aquatic life.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
PART: A Very Short Answer Type
Questions:
MCQs:
1. Which of the following is the major
reason for algal bloom?
(a) Presence of Heavy Metals
(b) Contamination by Pathogens
(c) Eutrophication
(d) Soil Erosion
2. Minamata Disease in Japan was caused due
to?
(a) Cadmium
(b) Mercury
(c) Copper
(d) Lead
3. The disappearance of the plants and
animals is due to____in water?
(a) Nitrogen Depletion
(b) Chlorine Depletion
(c) Oxygen Depletion
(d) Ozone Depletion
4. Which of the following causes
Biomagnification?
(a) SO»
(b) Mercury
(c) DDT
(d) Both (b) & (c)
5. Which of the following is a water borne
disease?
(a) Typhoid
(b) Cholera
(c) Jaundice
(d) All of the above
True / False:
1. Itaidtai disease was caused due to cadmium
contaminated rice.
2. Polluted water creates imbalance in the
ecosystem.
3. DDT is Dichloro Dipheny!Tetrachloroethane.
Fill in the Blanks:
1. Heavy Metals are defined as elements with density
.
2. Total dissolved solids of less than are most
suitable for drinking purposes.
ANSWER KEY OF PART-A
MCQs:
1. (c) Eutrophication — too much of nutrients
encourage the overabundance of plant life which results in algal bloom.
2. (b) Mercury — Due to consumption of mercury
contaminated fishes from Minamata Bay, Minamata disease was caused.
3. (c) Oxygen Depletion — Plants and animals die to
non-availability of oxygen.
4. (d) Both (b) & (c) — Biomagnification is caused
due to inhalation ofmercury and DDT.
5. (d) All of these — Typhoid, Cholera and Jaundice
are all water borne diseases as these are caused from polluted water.
True / False:
1. True — Itai-Itai disease was caused due to
consumption of cadmium contaminated rice in Japan.
2. True — Polluted water disturbs the ecosystem
causing imbalance.
3. False — DDT is Dichloro Diphenyl Tricholorethane.
Fill in the Blanks:
1. 5g/cc — Elements having density higher than
5mg/itre are classified as heavy metals.
2. 500mg/litre - Water having TDS less than
500mg/itre are fit for drinking.
PART: B Short Answer Type Questions:
1. What is Biomagnification and how it effects food
chain?
2. What caused Algal Bloom? Explain briefly.
3. What do you mean by BOD and what is used for?
PART: C Long Answer Type Questions:
1. Explain the various effects of water pollutants.
A190
INTRODUCTION
In the wake of green revolution, use of inorganic
fertilizers and pesticides has
increased manifold for enhancing crop production.
Pesticides, herbicides, fungicides,etc., are being increasingly used. Those
incidentally, are also toxic to non-target organisms that are important
components of the soil ecosystem. Do you think these can be biomagnified in the
terrestrial ecosystems?
We know what the addition of Increasing amounts of
chemical fertilizers can do to aquatic ecosystems via-a-vis eutrophication. The
current problems in agriculture are, therefore, extremely greate.
What are Agrochemicals?
Agrochemicals are pesticides, herbicides or
fertilizers used for the management of
ecosystem in agricultural sectors.
Agrochemical (Crop protector):Pesticides: Pesticide
is a chemical or a substance used to destroy or control some types of plants or
organisms also known as pests, which are harmful to cultivated plants or to
animals.
Insecticide: It is used to destroy insects.
Insecticides can be ovicides that kill eggs,
larvicides to kill larvae.
Pesticides examples: Organochlorines,
organophosphates, carbamates and pyrethroids.
Herbicides: It is used to control or kill weeds and
herbs.
Herbicides examples: Gramoxone and glyphosate.
Agrochemicals:
Fertilizer: These are chemical compounds used for
promoting plant growth.Fertilizers can be categorized into two
categories:Organic fertilizers are naturally existing substances prepared
through natural processes.
Inorganic fertilizer, also referred to as synthetic
fertilizers are manufactured artificial using chemical processes by utilizing
natural deposits, which are altered chemically.
Hormones/Growth Agents :Are of Endogenous origin and
are synthesized by plants.
These are Growth regulators performing function in
overall development of plant.
Liming and acidifying agents: Soils sometimes can be
too acidic or too alkaline for
proper growth of crops. In these cases, liming and
acidifying products are added to
soil to adjust its pH. When the soil is too acidic
calcite on the form of powdered
limestone is added primarily, whereas for more
alkaline soil sulfur compounds are
added to neutralize.
Benefits: -
Agrochemicals are used to improve quality and
quantity of food.
Improve plant nutrition.
Improve economic production.
Improve quality of life.
Effects on Soil:-Soil health is the capacity of soil
to function within ecosystem and land
use boundaries, to sustain productivity maintain
environmental quality, and promote plant and animal health.
Negative Impacts of Agrochemicals on Soil Health:-
Kills beneficial organisms.
Increase in nitrate levels of soil.
Damage natural make up of soil.
Alters the pH.
Decrease soil quality.
Kills soil organisms.
Toxic to microbes.
Toxicity of availability of nutrients.
Kills earthworms.
Growth regulators.
Residual effect.
Toxic to soil organisms.
Effects on Water:-
Water becomes unfit for drinking.
The runoff of agrochemicals into
streams, lakes, and other surface waters
can increase the growth of algae.
Eutrophication — Change in quality and
composition of aquatic ecosystems by
accumulation of excessive chemicals in
water bodies.
Polluted water leading to the death of
fish and other aquatic animals.
Excessive use of agrochemicals has led
to the contamination of groundwater.
Effects on air:-
Pesticides can contribute to air pollution.
Pesticides drift occurs when pesticides suspended in
the air as particles are carried
by wind to other areas.
Weather conditions at the time of application as
well as temperature and relative
humidity change the spread of the pesticide in the
air.
Low relative humidity and high temperature result in
more spray evaporating.
The polluted air is inhaled by humans end up with
different diseases.
Effect on Humans:
It causes variety of health effects from simple skin
and eye irritation.
Effects nervous system, causes cancer and also reproductive
problems.
Can cause nerve damage, hormones disorders and
neurotoxicity.
Pesticides entering human body:-
Pesticides can enter the body through inhalation of
aerosols, dust and
vapors that contain pesticides; through oral
exposure by consuming food/water; and through skin exposure by direct contact.
The effects of pesticides on human health depend on
the toxicity of the chemical and the length and magnitude of exposure.
Farm workers and their family experience the
greatest exposure to agricultural pesticides through direct contact.
Pesticide exposure can cause a variety of adverse
health effects, ranging from
simple irritation of the skin and eyes.
It also affects the nervous system, mimicking
hormones causing reproductive problems, and also causing cancer.
Children are more susceptible and sensitive to
pesticides, because they are still
developing and have a weaker immune system than
adults.
FIFRA:-(FEDERAL INSECTICIDE, FUNGICIDE
& RODENTICIDE ACT)
twas first established in 1947 & revised as
recently as 1996.
It states what must be on a pesticide label &
requires registration of all pesticides>
FFDCA:-(FEDERAL FOOD, DRUG, &
COSMETIC ACT)
Strengthened in 1996
Sets pesticide tolerance levels
“Let Us Know What We Have Learnt”
PART- A VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
a. Multiple choice questions:
1. Which one is an agrochemical waste?
(a) Mobile
(b) Pesticides
(c) Sludge
(d) scrap
2. Which kind of pollution is caused mainly
due to agrochemical waste?
(a) Soil
(b) Sound
(c) Water
(d) Air
3. Which one of the following agrochemical
waste is added in the soil to increase the growth of plants?
(a) Pesticides
(b) Fertilizers
(c) Water
(d) compost
4. FIFRA was established in year:
(a) 1947
(b) 1950
(c)1954
(d) 2000
5. Agrochemicals that control weeds are:
(a) Weedicides
(b) Insecticides
(c) Fertilizer
(d) Compost
b. True/False:
1. Agrochemicals are chemicals which are used in
agriculture.
2. Insecticides are most widely consumed
agrochemical.
3. FFDCA sets pesticide tolerance level.
c. Fill up:
1. Agrochemicals alter the of soil.
2. Change in quality and composition of aquatic
ecosystem due to agrochemicals is
ANSWER KEY: PART -A
a. MCQs:
1. Pesticides (b)Any chemical that harms the
ecosystem are agrochemical wastes.
2. Soil (a)An agrochemical is a chemical used to
help manage agriculture area. When thi
chemical harms the ecosystem it is said to be waste.
This waste leads to pollution of
soil.
3. Fertilizers (b)Fertilizers are the agrochemical
waste is added in the soil to increase the growth of plants.
4. 1947 (a)Federal Insecticide, Fungicide &
Rodenticide Act was first established in 1947
5. Weedicides (a)Weedicides control weeds.
b. True/False:
1. True.
2. True
3. True
c. Fill ups:
1.pH
2. Eutrophication
PART-B SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. Is there any harmful effect of agrochemical rise
on soil micro-organisms?
2. Discuss 2 types of agrochemicals?
3. How does use of agrochemical affect the quality
of ground water in crop farming
areas?
PART-C LONG ANSWER TYPES OF QUESTIONS:
1. What are the effects of agrochemical on human
health?
A191
INTRODUCTION
Solid waste is any material unused or rejected as
worthless or unwanted.
Or Solid waste refers to everything that goes out in
trash.
In this topic we will discuss about how solid waste
can be managed.
Defination:Solid waste management may be defined as
discipline associated with the control Of generation, storage , collection,
transfer, processing and disposal of solid waste.
Basic Principles:
1. Segregation of biodegradable and recyclable waste
at household.
2. Reuse of recyclable & processed end product.
3. Treatment of waste at household and community
systems to be promoted only if space is a constraint.
4. Technology choices to be limited to those that
are simple, easy to maintain & not very
capital and operation intensive.
1.Segregation can be done in two ways :
(i)On-site segregation at the point of generation of
wastes:All the wastes generated at source are required to be segregated in two
different bins.
Blue-coloured bin/receptacle will be for non-biodegradable waste.
(ii) Central processing facility:
Itinvolves separation of different kinds of wastes
by screening,air classifying and magnetic separators.Biodegradable solid wastes
are disposed by composting while non-
biodegradable solid wastes are disposed by
incineration, land filling,pyrolysis, etc.
2. Dumping: Dumping is simple and economical method
to manage the urban solid wastes and reclaim the low-lying areas for better
use.
3. Composting: In this, the biodegradable organic
matter of solid wastes is
digested anaerobically or aerobically by microbial
action and converted into humus
and stable mineral compounds.
4. Incineration : It involves the
aerobic burning of the non-biodegradable but combustible
constituents of solid wastes like
garbage, rubbish and dead animals in the
properly-constructed hearth of furnaces at high temperature (>670°C). It is
ideal for disposal of hospital and e-wastes. The final
products are ashes and clinkers.
But incineration
technique also has certain drawbacks:
(i) Incinerator ash is toxic and contains toxic chemicals like Dioxin and Mercury.
(ii) Its Leachate can pollute ground water.
5. Pyrolysis: It involves anaerobic
destructive distillation of the non-
biodegradable and combustible constituents of the
solid wastes at high temperature (650° to 1000: C)in a pyrolysis chamber so as
to recover the chemical constituents and chemical energy of organic wastes.
6. Recycling of wastes:Paper Waste Paper of old books,
newspapers, answer books, magazines, etc.are recycled to produce newspaper in
the paper mills
2. Agricultural wastes can be recycled to produce
useful products e.g. paper and
hard board from coconut waste, jute waste, cotton
stalks, bagasse of sugarcane
stem of rice, etc., livestock feed from paddy, husk,
etc.
3. Food processing and cannery wastes can be
fermented to produce organic acids.
4. Seeds of Sal (Shorea robusta), Mahua (Medhuca),
Neem (Azadirachtaindica)
can be used to extract oil from them. These oil
cakes may be used both as fodder and manure
5. Composting of organic wastes produces manure.
6. Gobar gas plants use cow dung and other organic
wastes of farm houses to provide manure for fields and biogas for domestic use.
7. Sludge of sewage treatment plants can be burnt to
produce electricity.
Polyblend :- A remedy for plastic waste.
AHMED KHAN developed Polyblend. It is a fine power
of recycled modified plastic.
“LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!”
PART: A Very short Answer Type Questions
:-
(A) Multiple choice questions :
Ques 1 : Which of the following can be
recycled many times?
(a)Plastic
(b)Wood
(c) Organic materials
(d) Aluminum
Ques 2 : What is called for the process of
burning municipal solid waste in properly Designed furnace under suitable
temperature and operating conditions?
(a) Landfill
(b) Recycling
(c) Vermicomposting
(d) Incineration
Ques 3: Why plastics are difficult to
recycle?
(a) Because it is very hard material.
(b) Because it is very adhesive in nature.
(c) Because of different types of polymer resins.
(d) Because of different sizes of plastics.
Ques 4: When the matter present inside the
sanitary landfill breaks down,which gas is generated?
(a) Methane
(b) Nitrogen
(c)Hydrogen
(d) All the above
Ques 5: Municipal solid waste is the term
used to describe which kind of solid waste?
(a) Hazardous
(b) Toxic
(c) Non-Hazardous
(d) Non-Toxic
(B) True/ False:
(1) Managing waste is the responsibility of the
Government.
(2)Waste reduction can be achieved by technology.
(3) Blue colored bin is used for Non-biodegradable
waste.
(C) Fill in the blanks:
1. Polyblend is developed by .
2. of organic wastes produces manure
ANSWER KEY: PART -A
(A) Multiple choice questions:
Answer 1:- (d)
Recycling is reusing some components of waste that
has some economic value.Aluminium can be recycled many times as mining of new
Al is expensive.
Answer 2: (d)
Incineration is a chemical process in which waste is
combined with CO2+ HzO At suitable temperature and operating condition.
Answer 3: (c)
Plastics are made of different types of polymer
resins which cannot be recycled
together. Since each type has a distinct chemical
composition
Answer 4: (a)
Decomposition of waste inside landfill produces
methane gas which is used as fuel.
Answer 5: (a)
MSW is used to describe most of hazardous solid
waste from village, or city that Require daily collection and transport to
disposal site.
(B) True / False:
1. False
2. True
3. True
(C) Fillin the blanks:
1. Ahmed Khan
2. Composting
PART: B_ Short Answer type questions:
Ques 1: What is waste management?
Ques 2: What are the common methods of waste
disposal?
Ques 3: What are the common recyclable materials
that can be recycle from household
Garbage.
PART: C Long Answer type questions:
Ques 1: Explain the process of compositing?
A192
INTRODUCTION
Radioactive pollution is caused by radioactive
wastes. Radioactive
wastes are those wastes which release radioactivity.
(emission of alpha
particles, Beta Particles or gamma rays) from nuclides
of their elements. Traces of radioactive elements occur in a number of products
e.g. polonium in tobacco, radon indoors, several ores.
PROBLEMS RELATED TO USE OF RADIOACTIVE
ELEMENTS & NUCLEAR ENERGY :At one time nuclear
energy was considerd to be quite safe and non-polluting source of electricity
generation. Later on, it was found that
there are a number of inherent problems related to
use of radioactive elements and nuclear energy.
1. ACCIDENTS :-
Nuclear reactors have several inbuilt safety measures.Even then meltdown and
accidental leakages do occur e.g. Three
Mile Island, Chernobyl(1986), Fukushima.
2. RADIOACTIVE WASTES :They
are produced from a number of sources
|. Nuclear testing laboratories.
ll. Minor leakage from nuclear powerplants.
lll. Wastes from Uranium mines.
IV. As natural minor components of ores and coal.
V. Spillage from radioisotopes used in research and
medicine.
VI. Spent fuel of atomic reactors.
Radioactive substances often have a long half-life
e.g. 28 years in case of
Strontium -90 and 30 years for caesium -137. They
persist in the soil for a long period, enter plants and harm human being as
well as animals. P-32 and 1-125 get concentrated in slime sludge and
microorganisms , pass into fish and other aquatic life and from there to
humans.
RADIOACTIVITY LEVELS :- Depending upon the amount of
radioactivity,there are three types of radioactivewastes — low
level,intermediate level and high level.
LOW LEVEL RADIATION :-
i. Extremely small amount of radioactivity enters
coolant water used in atomic reactors and ponds used for quenching heat and
radioactivity of spent fuel. It undergoes biomagnification to some 75,000 times
in birds.
iii Radioactive wastes are produced by testing laboratories,
irradiation centres for induction of mutations, study of metabolic
pathways,radiotherapy and other centres using radioisotopes.
INTERMEDIATE LEVEL RADIATION -
It is radiation which is not accompanied by liberation of heat. There is not
much problem in disposal of wastes emitting intermediate level radiations.
Small amounts of these radioactive wastes occur in all ores. If not dumped
properly, the radioactive wastes can kill vegetation and cause irreparable
injuries to human and animals.
HIGH LEVEL RADIATIONS: -They
are highly destructive radiations which develop
due to:
i. Accidental leakage or meltdown of atomic
reactors.
ii. Spent fuel of atomic reactors.
High level wastes produce a lot of heat and large
amount of radiations. Even short duration exposure to such high level
radiations cause loss of hairs nails,
subcutaneous bleeding and damage to all organs. The
radiations cause tumors,cancers and genetic deformities.
High level wastes require special protective shields
during handling &transport. They need cooling. The wastes are first
concentrated to reduce their bulk, kept in thick leak-proof containers and
dumped for 50-100 years in small ponds in the premises of nuclear plants. Their
Storage dissipates major part of both heat and radioactivity. The weakened
radioactive wastes kept in shielded
containers are then buried 500 m down deep inside
earth. Sea bottom is also used
for it. However, environmentalists are opposing both
the methods of disposal.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
PART —A VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
1. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS;
1. Radiations can cause:
a) Cardiac disease
b) Haemophilia
c) Cancer
d) Bonemarrow disease.
2. You can reduce your exposure to
radiation by doing the following:
a) Increasing your distance from the source.
b) Decreasing the amount of time near the source.
c) Provide shielding between yourself and the
source.
d) All of the above.
3. Radioactive pollution is:
a) Generally man made.
b) Always naturally occurring.
c) Not dangerous.
d) Usually caused by radon gas.
4. When did Chernobyl disaster occured?
a) 1976
b) 1986
c) 1996
d) 2000
5. What is the main purpose of nuclear
energy?
a) To kill the enemy nation.
b) To waste the excessive energy.
c) To use it as an alternate source of energy.
d) To cause mutation for people who are working.
2. TRUE/FALSE:
1. Radioactive wastes are those wastes, which
release UV- radiations.
2. Intermediate level radiations are accompanied by
liberation of lot of heat.
3. Low level radiations are used in irradiation
centres for inducing mutations.
3. FILL IN THE BLANKS:
1) Half — life of strontium 90 is ...............
2) Radioactive wastes emit ............;c:ccceeee
AMG. cece cece eee
particles from the nuclides of their elements.
ANSWER KEY: PART -A
(a) MCQs:
1. (c) The radioactive wastes produce radiations
which cause cancerin human beings.
2. (d) Staying away from the source of radiation
& providing shielding can reduce the exposure to radiation.
3. (a) Radioactive pollution caused by radioactive
wastes are generated by man.
4. (b) On 25 April, 1986 in Chernobyl, an explosion
occurred in nuclear reactor.
5. (c) Nuclear energy is used to produce electric
energy in Nuclear Power Plants.
(b) TRUE/FALSE:
1. False — Radioactive wastes are those wastes which
release Alpha ,Beta or Gamma rays.
2. False — Intermediate level radiations are not
accompanied by liberation of heat.
3. True.
(C) FILL IN THE BLANKS:
1. 28 years.
2. Alpha -particles, Beta -Particles and Gamma
-Particles.
PART-B SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1) Name one incident of accidental leakage from
nuclear reactors.
2) What are radioactive wastes?
3) Describe the methods of handling of radioactive
wastes.
PART-C LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. Discuss the various problems related to use of
radioactive wastes.
A193
INTRODUCTION
Greenhouse effect term is derived from greenhouse
which looks like a small glass house & is used for growing plants during
winters. In a greenhouse the glass panel lets the light in but does not allow
heat to
escape. Therefore the greenhouse warms up. Similar
is naturally occurring in greenhouse effect which is responsible for heating
earth’s surface & atmosphere. Increase in the level of greenhouse gases has
led to
considerable heating of earth leading to global
warming.
GREEN HOUSE EFFECT :-
1. Without greenhouse effect the average temperature
at surface of earth would have been a chilly -18°C, rather than present average
of 15°C.
2.Almost half of incoming solar radiations with
infrared radiation fall on earth’s surface heating it, while a small proportion
is reflected back.
3. Earth’s surface re-emits heat in the form of
infra-red radiation but part of
this is absorbed by gases like CO2 & Methane.
4. The molecules of these gases radiate heat energy.
& major part of which again comes to earth’s surface, thus heating it up
once again.
5. The cycle is repeated many times & surface of
earth is warmed up.
GREEN HOUSE GASES :-
The gases which are transparent to solar radiation but retain & partially
reflect back long wave heat radiations are called greenhouse gases. The various
greenhouse gases are CO2, CH,, CFC’s
& nitrous oxide.
1. €O2:- The rise in COz in the atmosphere is due to
large scale deforestation, change in land use & large scale combustion of
fossil fuels.
2. METHANE :- Methane is produced by incomplete
biomass combustion,incomplete decomposition by anaerobic methanogens. Flooded
paddy fields, marshes, cattle are the major sources of this gas.
3. CFC’s :-They are synthetic gaseous compounds of
carbon & halogen which are odourless, non-toxic, noninflammable, chemically
inert propellants used in aerosol cans & jet fuels, refrigerants in air
conditioner & refrigerators.
4. NITROUS OXIDE :- It is produced by combustion of
nitrogen rich fuels,livestock wastes, breakdown of nitrogen fertilizer in soil,
nitrate contaminated water etc.
Out of these, COz & CH, are the major Greenhouse
gases.
GLOBAL WARMING:Increase in the level of greenhouse
gases has led to considerable heating of earth leading to global warming.
During the past century the temperature of
earth has increased by 0.6°C .
HARMFUL EFFECTS OF GLOBAL WARMING:- Scientiests
believe that this rise in temperature is leading to deleterious changes in
environment & resulting in odd climatic changes (eg. El Nino effect).
It has increased the melting of polar ice-caps. Over
many years, this will result in a rise in sea level that can submerge many
coasts.
Pattern of air-mass movement will change.
Precipitation will increase at higher latitudes both in summer & winter.
Winter precipitation will be reduced at lower latitudes.
Frequency of droughts & floods will increase.
Rise in temperature of 2-5°C Will push temperate
range by some 250- 600 km pole-wards. Many tree species & other organisms
which are sensitive to temperature will die out.
Rise in temperature is detrimental to crop
productivity due to increase in respiration, greater growth of weeds, eruption
of diseases & pests.
Warming of troposphere is accompanied by cooling of
upper strata of atmosphere. Cooling of stratosphere will lead to increase the
size of ozone hole while cooling in thermosphere will disrupt radio
communications.
STRATEGIES TO CONTROL GLOBAL WARMING:-
1. Cutting down use of fossil fuel.
2. Improving efficiency fo energy usage.
3. Reducing deforestation.
4. Planting trees.
5. Slowing down the growth of human population.
6. Complete replacement of CFC’s with substitutes
that have little effect on ozone & Global Warming.
LET US KNOWN WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
PART:A VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
A. MCQs:
1. Greenhouse effect is caused by:
(a) Green Plants
(b) Infrared rays
(c) UV rays
(d) X-rays.
2. Global warming can be controlled by:
a) Increasing deforestation, reducing efficiency of
energy use.
b) Reducing deforestation, cutting down use of
fossil fuels.
c) Reducing deforestation, increasing use of fossil
fuels.
d) Increasing deforestation, slowing down the growth
of human population.
3. Which is not a greenhouse gas?
(a) Methane
(b) CO2
(c) CFC’s
(d) Nitrogen.
4. Greenhouse effect is increasing due to:
(a) Increasing CO2z Concentration.
(b) Increasing SO2 Concentration.
(c) Hole in ozone layer.
(d) Increasing concentration of Nitrogen.
5. The two gases making highest relative
contribution to greenhouse gases:
(a) CHa& N20
(b) CFC’s & N2O
(c) CO2 & N2O
(d) CO2&CH,
B. TRUE/FALSE:
1. UV radiations are responsible for Green House
effect.
2. The average temperature of earth’s surface is
15°C
3. Major greenhouse gases are COz & CHa.
C. FILL IN THE BLANKS:
a. Increase is average temperature of earth’s
surface is called ................
b. Cooling of stratosphere will increase the size of
..............
A. MCQ’s.
1. (b) Earth’s surface re-emits infra-red radiations
after being heated by sunlight. These infra-red radiations are absorbed by
green house gases present in atmosphere.
2. (b) By reducing cutting of forests & limiting
the use of fossil fuels we
can control COz emission which is a major Green
House Gas.
3. (d) Green House gases are CO2 CH,, CFC’s &
Nitrous oxide.
4. (a) increased COz Concentration will lead to more
heat absorbed & hence increased Green House effect.
5. (d) CO.CH, are two major Green House gases which
absorb heat radiations.
B. TRUE/FALSE:
1. False . (Infra-red radiations are responsible for
Green House effect)
2. True.
3. True.
C. FILL IN THE BLANKS:
1. Global warming.
2. Ozone Hole
PART: B SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. What is Green House Effect?
2. What do you mean by Green House Gases?
3. What is Global warming?
PART: C LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. Discuss the effects of Global Warming?
A194
INTRODUCTION
Ozone layer is present in the stratosphere. It is
also called ozonosphere. 90% of atmospheric ozone is present in ozonosphere.
Depletion in the concentration of ozone over a
restricted area as over Antarctica is called ozone hole. There are many
substances that react with ozone present in the stratosphere and destroy the
same. Ozone
layer depletion causes many harmful effects on
animals & environment.
OZONOSPHERE:Ozonosphere
lies at altitude of 23-25 km over equators& slightly lower altitude
elsewhere about 11-16 Km over poles. Thickness of ozone is measured in Dobson
units. Concentration of ozone in the
ozonosphere is above 300 dobsons as compared to 50
dobsons in troposphere. In Stratosphere ozone is being formed & Photo
dissociated. It
dissipates the energy of UV radiations.
Because of it ozonosphere functions as shield
against strong UV radiations. Protection from UV radiations is proportional to
thickness of
ozone layer.
OZONE HOLE:-
Depletion in the concentration of ozone over a restricted area as over
Antarctica is called ozone hole. An ozone hole was discovered over Antarctica.
By Farman et al, 1985 who also coined the term. In the period 1997-2001, the
global average ozone column has declined by 3 %.Thinning of ozone shield will
increase the amount of UV-B radiation reaching the earth.
ODS:- (OZONE DESTRUCTING SUBSTANCES)
They are the substances which read with ozone present in the stratosphere &
destroy the same. The
major ODS are chlorofluorocarbons, nitrogen oxides,
sulphur dioxide,halon, carbon tetrachloride, methyl chloroform, chlorine etc.
Many of these are being released by jets flying in the stratosphere &
rockets being fired into space. Others are persistent in the troposphere &
gradually pass into
stratosphere. Maximum ozone depleting potential is
of CFC due to release
of active chlorine (Cl, ClO) by it. Active chlorine
gets perched over atmospheric ice crystals and remains functional for a long
time.A single chlorine atom converts 1 lakh molecules of ozone into
oxygen.Consequently CFC’s are being replaced by HYDROFLUORO- CARBONS & HYDROCHLOROFLUOROCARBONS. Carbon tetrachloride, halon &
methyl chloroform also deplete ozone by a similar method. Nitric oxide (NO)
& other gases released by jets directly react with ozone to form oxygen.
EFFECTS OF OZONE DEPLETION:
UV radiations are of 3 types —UV-C, UV-B & UV-A . Shorter UV radiations
UV-C are absorbed by the
atmosphere. The longer ones are not much harmful.
The intermediate UV-B are harmful as well as capable of deep penetration.
Thinning of ozone layer increases the amount of UV-B radiations reaching the
earth. These radiations cause many harmful effects as follows.
|. Cornea absorbs UV-B radiations. It becomes
inflamed the disorder is called, “Snow Blindness” or cataract. It loads to
diminishing of eye sight, photo burning & later permanent damage to cornea.
ll. UV-B radiations damage skin cells cause ageing
of skin & skin cancer.
lll. There is increased incidence of herpes &
deficient functioning of immune system.
IV. Alarge no. of animals would become blind.
V. There will be higher mortality of young ones of
animals.
VI. Damage to nucleic acids will increase resulting
in higher number of mutations.
Vil. High energy UV radiations break chemical bonds
of proteins & other biomolecules.
Vill. UV radiations inhibit photosynthesis
IX. Decreased photosynthetic activity will increase
CO2 concentration of the atmosphere resulting in global warming.
X. Both marine & terrestrial food chains will be
disturbed. World ozone day is celebrated on 16 September to spread awareness among
people.
PART—~A VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
A. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
1. Ozone layer occurs in:
A. Troposphere
B. Stratosphere
C.Mesosphere
D. Exosphere.
2. Thickness of ozone layer is measured in:
A. Dobson units
B. Decibel units
C. Pascal
D. Diopter.
3. Ozone hole is caused by:
A. Acetylene
B. Ethylene
C. Chlorofluorocarbons
D. Methane.
4. Result of ozone hole is:
A. Greenhouse effect
B. Global warming
C. Acid rain
D. UV radiations reach the earth.
5. World ozone day is celebrated on:
A. 16" Sept.
B. 21% April
C. 5 June
D. 22"? April.
B. TRUE/FALSE:
1. CH,is the main cause of ozone depletion.
2. Concentration of ozone is ozonosphere is above
300 Dobson's.
3. UV-radiations break chemical bonds of proteins.
C.FILLIN THE BLANKS:
1. The major ODS is
...............cceese
2. Thinning of Ozone layer increases the amount Of
................000 reaching on the surface of earth.
ANSWER KEY: PART - A
(a) MCQs:
1. (b) Most of the ozone is present in Stratosphere.
2. (a) Thickness of ozone layer is measured in
Dobson unit.
3. (c) CFC’s releases active chlorine which gets
perched over ice crystals and remains functional for a long period. A single
chlorine atom converts 1 lakh ozone molecules into oxygen.
4. (d) Thinning of ozone layer increases the amount
of UV- radiations reaching on earth.
5. (a) On16™ September. World Ozone Day is
celebrated.
(b) TRUE/FALSE:
1. False (CFC’s are the main cause of ozone
depletion)
2. True.
3. True.
(c) FILL UPs:
1. Chlorofluorocarbons.
2. UV- radiations.
PART-B SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS:
1. Name two ozone depleting substances.
2. How CFC’s deplete ozone layer?
3. What is Ozone Hole?
PART-C LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS:
1. Discuss the various harmful effects of ozone
depletion
A195
United Nations Environment Program (UNEP) has been made to find solutions for ozone depletion and global warming.(16 September 1987) 27 industrialized countries
1.Montreal protocol: of chlorofluorocarbons to half the level of 1986.
2. May, 1989) Montreal protocol was ratified by 82 nations at Helsinki. They pledged to phase out CFCs by 2000.
3. In June 1990, 93 nations’ anended MONTREAL PROTOCOL and Helsinki Declaration. They agreed to phase out CFCs and other ODS by the end of 20th century.
4. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Changes: (IPCC, 1988) prepared a world climatic program (WCP).
5. Convention on Climate Change: (CCC) Under UN framework in 1991.
6 .Earth summit: United Nations conference on Environment and Development, 1992).
i) It was held in Rio- de-janeiro (Brazil) and adopted recommendations of CCC for reducing greenhouse gases. The recommendations were signed by 154 nations.
ii) At Cancun in COP-16 an agreement was undertaken to limit global warming to below 2°c relative to preinpreindustrial level.
ii) In COP-18 at Doha a second commitment was undertaken to extend the Kyoto protocol for eight years from 2013-2020
iv) In COP-21(2015) held in Paris, it was agreed to limit the globz temperature increase to 1.5°C above the pre-industrial level.
7. Kyoto Protocol (Dec.1997) International conference held in Kyoto, Japan obtained commitments from different countries for reducing overall greenhouse gas emissions at a level 5% below 1990 level by 2008-2012( now
extended to 2020).
8.Beijing protocol (1999): The protocol lays down steps to reduce emissions of CFCs and other ozone depleting substances. It separates the efforts to be made by developing and developed countries.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNTH
A. MCQs:
i) Which association in 1987 agreed to limit production of chlorofluorocarbons to half the level of 1986?
a) Montreal protocol
b) Helsinki protocol
c) Beijing protocol
d) Kyoto protocol
ii) Convention on climate change was done in:
a) 1994
b) 1991
c) 1998
d) 1999
iii) Beijing protocol was laid down in:
a)1976
b)1975
c)1997
d)1901
iv) Japan obtained communities from different countries for reducing overall greenhouse gas emissions under:
a) Beijing protocol
b) Earth summit
c) Montreal protocol
d) Kyoto protocol
V) Helsinki declaration was done in:
a) 1989
b) 1898
c) 1957
d) 1972
B FILLIN THE BLANKS:
i) UNEP is ---------—----- program.
ji) --------------- agreed to limit ozone depleting and global warming in 1987.
C TRUE/FALSE:
1. Beijing protocol in 1999 was laid down to reduce emissions of CFC's and other ozone depleting substances.
2. In COP-3 Kyoto protocol was negotiated
3. Earth protocol was held in Brazil in 1992 adopted the recommendation of CCC for reducing greenhouse gases.
ANSWER KEY: PART -A
A. MCQs:
i) (a)
ii) (b)
iii) (c)
iv) (d)
v) (a)
B. Fill IN THE BLANKS:
i) United Nations Environment Programme (made to find solutions for ozone depletion )
i) Montreal protocol ( to limit production of chlorofluorocarbons)
C. TRUE/FALSE:
i) True
ii) True
ii) True
PART: B SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
i) Name the environment program which has done efforts to find solutions for pollution control?
ii) Describe earth summit?
iii) Write a few lines about Beijing protocol 1999?
i) Make a list of various efforts to find solution for ozone depletion and global warming made by UNEP and describe it.
A196
INTRODUCTION
DEFORESTATION:Deforestation is the removal, decrease or deterioration of forest cover of
an area.
1. Jhuming: It is slash and burn agriculture also known as shifting cultivation act, killing all plants and animals.
2. Hydroelectric projects: Dams, hydroelectric projects submerge forest
tracts killing all plants and animals.
3. EE. Huge forest fire engulfed areas in Indonesia in 1983 and 1997.
4) Human Establishments: To get more food and residential complexes more land is required.
5) Mountain and Forest Roads: Construction of roads and railways in hilly forests area brings a lot of Deforestation.
6) Overgrazing: Livestock grazing in forests causes compaction of soil.
7) Canals: Irrigation projects in 1974 in U.P. to irrigate land destroyed a million Sal trees and put land out of cultivation.
1) Shrinking Fuel wood: Deforestation reduces fuel wood.
2) Change in climate: Deforestation results in reduced rainfall.
3) Soil erosion: Soil is exposed, dries up and gets eroded by wind and water.
4) Siltation: Rainy season rivulets bring eroded soil and deposit the same on bed of reservoir.
5) Drought: There is very little water in rivers during dry season causes draught.
6) Global warming: Deforestation increases co2 content by releasing carbon stored in organic matter and reduced primary productivity.
7) Indigenous people: Tribal living in forests depends upon forests for their survival. Deforestation leads to their uprooting and loss of their livelihoods.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
PART: A VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
A. MCQs:
1) When trees are cut and deterioration of forests take place. It is called
a) Deforestation
b) Afforestation
c) Reforestation
d) None
2) When forest fires engulf huge area inIndonesia?
a) 1983
b) 1987
c) 1985
d) a&b
3) Which project was launched to irrigate 16 lakh hectare of land in U. P.?
a) Sarda sahayak canal
b) Indira Gandhi canal
c) Both
d) None
4) Deforestation increases due to:
a) Global warming
b) Rainfall
c) Floods
d) Soil fertility
5) Siltation means:
a) Rivers bring soil and deposit in reservoir
b) soil collected in rivers
c) Rivers get over flood with soil
d) None
(B) FILL IN THE BLANKS:
1) Cutting of trees is--—--.
2) Van Mahautsav being carried out inIndia since -------.
(C) TRUE/FALSE:
1) Afforestation is growing forest over an area where none existed earlier.
2) Urban forestry is to grow fruits, vegetables and shady trees in urban areas to reduce pollution.
3) Plantation of useful trees and shrubs for commercial requirements is commercial forestry.
ANSWER KEY: PART -A
A. MCQs:
1) (a) Deforestation (Cutting of trees)
2) (d)
3) (a)
4) (a) (increases CO, concentration)
5) (a)
B. FILL IN THE BLANKS:
1) Deforestation
2) 1970
C.TRUE/FALSE:
1) True
2) True
3) True
PART: B SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1) Define Deforestation and Afforestation.
2) What are various causes of Deforestation?
3) List the various effects caused by Deforestation.
PART:C LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1) Define Deforestation? What are its causes and effects on population?
A197
INTRODUCTION
Ecological restoration is one of the most fundamental duties of each and every citizen in this world.
By saving the environment from pollution or other hazardous elements,can leads to sustainability, otherwise our future generations will curse us for not getting pure water, air and other natural products.
There are several communities in our country, who contributed a lot for the safety of our environment.
BISHNO!| MOVEMENT:
1. Bishnoi movement was started by Bishnois in 1731 in Rajasthan to stop the destruction of trees in Kherali village forest region.
Ee Wanted to build a new palace. He sent soldiers to cut the trees.
3. When king's men began to harm the trees, Bishnois protested.
4. AMRITA DEVI a female villager sacrifices her life and become inspiration for others.
5. 363 villagers gave their lives.
6. When king came to know about this activity, he stopped it and apologized.
7. Government of India declared Amrita Devi BISHNOI wildlife protection award for individuals and rural communities who show extraordinary courage and dedication in protecting wildlife.
CHIPKO MOVEMENT:
1. It is a movement initially meant for protecting trees but now for preservation of Environment, including habitat and wildlife.
2. It was born in 1973 in Chamoli district in Uttraknand.
3. Villagers escaped trees by hugging them thatis why this movement was known as CHIPKO movement.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!!
i) Name the award declared by government of India for individuals and communities who show extra courage for protection of wildlife?
a) Amrita Devi BISHNOI
b) Gaura devi
c) Both
d) None
ii) When was Chipko movement started?
a) 1978
b) 1973
c) 1988
d) 1986
iii)When did BISHNO! movement started?
a) 1931
b) 1831
c) 1731
d) 1631
iv) Appiko movement was started in:
a) North India
b) South India
c) East India
d) None
V) Name a valley saved through public agitation:
a) Silicon valley
b) Silent valley
c) Kashmir valley
d) None
i) ------------- movement was started in Rajasthan to save and conserve forests by community participation.
ii) Chipko movement started in----------- district in year-----------------.
¢) TRUE/FALSE:
i) Bishnoi movement was initiated to save and conserve trees.
ii) Appiko movement is not concerned with protection of trees.
iii) Government of India declared Amrita Devi Bishnoi award for conservation of trees in 1731.
A) MCQs:
i) (a) (Amrita Devi Bishnoi Wildfire Conservation Award)
ii) (b) (1973)
iii) (c) (1731)
iv) (b) (South India)
v) (b) (Silent valley in Kerala)
B) FILLIN THE BLANKS:
i) Bishnoi
ii) Chamoli district, 1973
i) True
ii) False
iii) True.
i) When and where was CHIPKO movement started?
ii) Who was AMRITA Bishnoi? Why government of India declared award by het name?
iii) Name the movements initiated by individuals or communities for conservation of forests.
i) Describe the movements started by individuals or communities who played
important role in saving and conservation of trees and forests?
A198
INTRODUCTION
Joint Forest Management (JMF) is the official and popular term in India for partnerships in forest movement involving both the state forest departments and local communities.
Afforestation is GROWING FOREST over an area where none existed earlier.Van Mahotsava is being carried out in India since 1950. Both government and private agencies perform tree plantation during the months of February and July every year.
Reforestation is RESTORING A FOREST COVER over an area where one existed earlier but was removed at some time in the past.
As per recommendation of National Forest Commissions hills should have forest
cover 66% as compared to 33% for plains.
A higher and denser cover shall:-
(i) Increase percolation and absorption of rain water.
(ii) Prevent landslides.
(iii) Decrease runoff and hence flood.
(iv) Moderate climate
Joint Forest Management (JMF) is partnership involving both state forest departments and local communities in natural forest management. The concept was introduced by Government of India through the National
Forest Policy of 1988.
ORIGIN OF THEME:-
Accidentally originated in West Bengal at the Arabari forest range in 1971.
Was to prevent the unprotected grazing and illegal harvesting of major hardwood product (Sal).
Theme was introduced by AJITH KUMAR BANERGIEE (Divisional Forest Officer, Arabari fores t range). Under JFM, village communities are entrusted with the protection of management of nearby forests.
The communities are required to organize forest protection committees,village forest committees, village forest conservative and development societies, etc. Each of these bodies has an executive committee that
manages its day-to-day affairs.
In return of their services to the forests, the communities get the benefit of using minor non - timber forest produce. As a result, the forest can be conserved in sustainable manner. For example:-
Controlled grazing of cattle by the GADDI & GUJJAR tribes in the Himalayan states prevents the widespread growth of wild grass, thus contributing towards conservation of biodiversity.
BISHNOI] COMMUNITY of Rajasthan plays a very significant role in ecological joint conservation effort, with Joint conservation effort with the nomadic tribe of MALDHARIS, living in vicinity of Gir National Park, has contributed to the improvement of lion population.
The potential role of Joint Forest Management in improving the livelihood of the forest dwellers and fringe forest communities are as follows:
For working in coordination with villagers, Forest Committees are constituted which
play an active role to increase the agriculture and forest production and processing their produce. Employment opportunities, such as sustainable tourism are created in villages.
The Chipko movement or chipko andolan , was a forest conservation movement in India. The movement originated in 1973 at the Himalayan region of Uttarakhand However, it was Sunderlal Bahuguna, a Gandhian activist, and Chandi Prasad Bhatt, who gave the movement a proper direction and awareness to eco-groups by helping to slow down the rapid deforestation, increase social awareness and the need to save trees, increase ecological awareness. He used the slogan,
“Ecology is the permanent economy.”
The Panchayat (Extension to Scheduled Areas) Act, 1996 along with the Forest Rights Act plays a significant role towards ensuring entitlement to forest dwellers.
Aspecific woman sub-committee in the Joint Forest Management Committee (JFMC) ensures gender balance.
The JFMC provides training on animal husbandry, poultry farming, dairy
development and managing small forestry enterprises along with implementation of the National Rural Employment Guarantee programme in fringe forest areas.
Non-wood forest products (NWFP) are also important to JFM. NWFP are integral to lifestyle of forest-dependent communities. They fulfill basic requirements, provide gainful employment during lean periods and
supplement incomes from agriculture and wage labor. Medicinal plants collected through JFM have an important role in rural health.
MAJOR ASPECTS OF JFM:-Forest management is a branch of forestry concerned with overall
Administrative, Legal, economic and social aspects, as well as scientific and technical aspects,Such as silviculture, protection and forest regulation
CHALLENGES TO JFM:
The JFM program faces existential crisis.
On the one hand, legislations like the Forest Rights Act (FRA), 2006, and the
Panchayat Extension to Scheduled Areas (PESA) Act, 1996, have come into existence, giving rights to tribal and forest dwellers over forest resources and their management.
Communities demand the huge sums forest departments owe them under the program.
Questions are being raised whether the program should be scrapped.Implementation of JFM programs is expensive. The cost of afforestation,for example, is about Rs. 20,000 per ha.
Lack of legal status and financial and executive powers for FPCs.Forest Department in certain States vested with arbitrary powers to dissolve FPCs.
Faulty design of micro-plans and management plans.Absence of participation by women in spite of their formal representation in
management committees.
Unreasonable controls over the duration of exploitation of admitted resources
leading to low level of exploitation of admitted NTFPs.
Excessive rule and regulations.
Inadequate remuneration for local communities from JFM activities.
Inter and intra-community conflicts that hamper FPC functioning.
Denial of rights on disposal over valuable NTFPs to local communities.
FUNCTIONS OF JFM:
Micro-planning needs to ensure people participation in management of forest.
It should help to access the needs of the participating community and scope for development of the region or resource.
Itneeds to plan, project and regulate the benefit flow to the participant in
consultation with them.
It should identify and highlight the local resources and set priorities for resource development based on site conditions and available funds.
CURRENT STATUS OF JFM:After the initial success in West Bengal and Haryana, the JFM schemes received national importance in legislation of 1988. As per data of 2000, 27 states of the Indian Union had various JFM schemes with over 63000 FPCs
involved in this project over 1400,000 km? of forested land which was increased to 2460,000 by 2010 where 112896 committees with around 1450,000 families getting benefit from JFM program.
MAJOR RESEARCH FINDINGS:Apart from food subsistence collected from the local forests (including protected forest) to meet daily consumption needs of the forest-dwelling households, while as much as one-third (28.3%) of total per household
annual income is derived from sale of NTFPs.This precisely suggests success of protection and conservation measures
undertaken in the VSS assigned areas in the JFM study villages.
Further, while assessing the degree of dependence of the forest dwelling
population on forests (of the JFM sample villages) for their food subsistence
and livelihood, both the imputed value of consumption of NTFPs (by the forest dwelling households) and the sales value of NTFPs constitute as much as one half (49.0%).
Forestry activities are largely performed by female members, and as expected, while per household female person days of employment is 147 days compared to their male counterparts of 91 days, an average person secures only 80 days of employment per annum in forestry activities.
SUMMARY:Of late, the New Forest Policy (NFP) 1988 recognized that active
involvement and participation of communities in the management of local
forest resource is imperative for regeneration, protection, conservation and
development of degraded forests. Accordingly, in a major shift from the
traditional systems of forest management the JFM model emerged in many Indian States in 1990 (including Orissa) consistent with NFP 1988, and is now considered to be a revolutionary program in the forestry sector to make effective involvement of local communities in establishing sustainable Forest Management (SFM). Besides, it is now being looked upon as the only alternative to problems of deforestation and land degradation.
(A) MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE QUESTIONS:
Q1. JFM in forest management stand for?
a) Junior forest management
b) Joint forest management
c) Both a) andb)
d) Neither a) nor b)
Q2. Bishnoi movement improved the count of decreasing:
a) Bear
b) Elephant
c) Tiger
d) Lion
Q3. Chipko movement was born in:
a) 1973
b) 1947
c) 2000
d) 2020
Q4. Chipko Movement was led by-
a) Sunder Lal Bahuguna
b) Chandi Prasad Bhatt
c) Both a) and b)
d) Neither a) nor b)
Q5.Where did the concept of joint forest management originate?
a) Andhra Pradesh
b) Haryana
c) Rajasthan
d) West Bengal
(B) TRUE / FALSE:
Q 1. JFMC ensures gender balance.
Q 2. JFMC does not provide employment.
Q 3. JFM provide empowerment to women.
(C) FILL UP THE BLANK SPACES:-
1) JFM was introduced by -----------—---.
2) Expand SFM---—-------—---—---—-.
a. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. b)
2. d)
3. a)
4. c)
5. d)
b. TRUE/ FALSE:
1. TRUE
2. FALSE
3. TRUE
c. FILL IN THE BLANK SPACES:
1. Ajith Kumar Banergiee (Divisional Forest officer, Arabari forest range)
2. sustainable Forest Management
1) What is the role of women in JFM?
2) Give the various aspects of Joint Forest Management?
3) What do you meant by Jhum cultivation?
1) Write about the challenges facing Joint Forest Management Committee?
A199
INTRODUCTION
ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES:Dear students we have taken all the topics of this chapter in detail.Now we shall go through some questions related to this chapter.
Environmental issues are issues related to human impact on the living environment, habitats, land use and natural resources. The following alphabetical list shows some of the main known environmental issues by
major topic title:
Climate change (encompasses "global warming”, greenhouse effect, loss of
glaciers, climate refugees, climate justice, equity, etc.)
Conservation (nature and animal conservation, etc.)
Deforestation (illegal logging, impact of fires, rapid pace of destruction, etc.)
Desertification
Endangered species (loss of species, impact of chemical use on species,cultural use, species extinction, invasive species, etc.)
Energy (use, conservation, extraction of resources to create energy, efficient
use, renewable energy, etc.)
Environmental degradation
Environmental health (poor environmental quality causing poor health in human beings, bio-accumulation, poisoning)
Environmental impact assessment (one major current form of assessing human impact on the environment)
Food safety (including food justice, impacts of additives, etc.)
Genetically modified organisms and other forms of genetic engineering or modification
Global environmental issues (in recognition that environmental issues cross borders)
Global warming
Habitat loss (destruction, fragmentation, changed
use)
Intensive farming and bio intensive farming
Invasive species (weeds, pests, feral animals, etc.)
Land degradation
Land use / Land use planning (includes urban sprawl)
Natural disasters (linked to climate change,
desertification, deforestation, loss of natural resources such as wetlands,
etc.)
Nuclear energy, waste and pollution
Ocean acidification (includes algal bloom, coral
reef loss, etc.)
Over-exploitation of natural resources (plant and
animal stocks, mineral
resources (mining), etc.)
Overfishing (depletion of ocean fish stocks)
Ozone depletion (CFCs, Montreal Protocol)
Pollution (air, water, land, toxins, light, point
source and non-point source, use of coal/gas/etc., reclaimed land issues)
Population growth and related issues, like
overpopulation, access to reproductive control (reproductive health), etc.
Reduce, reuse, repair and recycle (ways to reduce
impact, minimize footprint, etc.)
Soil conservation (includes soil erosion,
contamination and salination of land,
especially fertile land; see also desertification
and deforestation)
Sustainability (finding ways to live more
sustainably on the planet, lessening
human footprint, increasing human fulfillment with
less impact) (see also
sustainable development and poverty alleviation)
Toxic chemicals (persistent organic pollutants,
prior informed consent,
pesticides, endocrine disruptors, etc.)
Waste (landfills, recycling, incineration, various
types of waste produced from
human endeavors, etc.)
Water pollution (fresh water and ocean pollution,
Great Pacific Garbage Patch, river and lake pollution, riparian issues)
Water scarcity
QUESTIONS FROM NCERT TEXTBOOK :
1. What are the various constituents of
domestic sewage? Discuss the effects of sewage discharge on a river.
Ans: Domestic sewage contains four kind of
impurities:
(i) Suspended solids: They are soil particles such
as sand and silt.
(ii) Colloidal particles: They are inorganic and
organic materials such as
faecal matter, bacteria, paper and cloth
(iii) Dissolved solids: They are nitrates,
phosphates, ammonia sodium,calcium and other nutrients.
(iv) Pathogens: Domestic sewage has pathogens of
various disease such as
typhoid, cholera, dysentery, diarrhoea, etc.Effects
of sewage discharge on river is:
(i) Eutrophication.
(ii) Growth of pathogenic bacteria.
(iii) Ageing of river where slit and decaying
matters start accumulating and
filling river.
(iv) Increase in BOD
(v) Destruction of flora and fauna of that river.
2. List all the wastes that you generate at
home, school or during your trips to other places. Could you very easily reduce
the generation of these wastes? Which would be difficult or rather impossible
to reduce?
Ans: Waste materials generated at home: paper,
disposable cups, cloth,plates, spoons, plastic envelopes, discarded food etc.
Wastes materials generated during trips are: paper, disposable cups, plates,
spoons, plastic envelopes, discarded food etc. No, we cannot reduce the
generation of these wastes easily, but few can be
reduced. The wastes belong to two categories:
biodegradable and non-
biodegradable. It is difficult or rather impossible
to reduce discarded food
like peel of potato, peel of banana etc. We can do
one important thing i.e., to
reduce wastage of food.
3. Discuss the causes and effects of global
warming. What measures need to be taken to control global warming?
Ans: Causes of global warming:
|. Increase in concentration of greenhouse gases.
Il. Increase of automobile and use of fossil fuel.
Ill. Deforestation and change in land use
IV. CFC and aerosol emission from refrigerator and
aero plane.
V. Increased particulate matter in lower atmosphere.
Effects of global warming:Many species of plants,
being sensitive to temperature will die with sudden rise in temperature. Loss
of biodiversity. Rise in sea level.
Possibilities of drought and floods. Change in
rainfall pattern.Methods that can reduce the atmospheric concentration of
greenhouse gases are:Reducing the greenhouse gas emission by limiting the use
of fossil fuels,by developing alternate renewable sources of energy( wind
energy, solar energy) Increasing vegetation cover, Minimizing the use of
nitrogen fertilizers in agriculture. Developing substitutes of
chlorofluorocarbons.
4. Write critical notes on the following:
(a) Eutrophication
(b) Biomagnification
(c) Groundwater depletion and ways for its
replenishment
Ans: (a) Eutrophication: It is excessive growth of
algae, plants and animals
in water-bodies due to nutrient enrichment particularly
with nitrogen and phosphorus. It is both natural and accelerated. It leads to
loss of biodiversity and causes chemical accumulation in food chain and ageing
of water bodies.
b) Biological magnification: Increase in
concentration of persistent chemical
at successive trophic levels is called
eutrophication. This happens because a
toxic substance accumulated by an organism cannot be
metabolized or excreted, and is thus passed onto next trophic level, e.g., DDT.
(c)Ground water depletion and replacement: Ground
water depletion, a term often defined as long term water level declines caused
by sustained ground water pumping, is a key issue associated with ground water
use.Many areas of India experiencing ground water depletion.The most severe consequence
of excessive ground water pumping is that the water table, below which the
ground is saturated — with water, can be lowered. If ground water level
declines too far, then the well owner might have to deepen the well, drill a
new well, or at least attempt to lower the pump.
5.Why ozone hole forms over Antarctica? How
will enhanced ultraviolet radiation affect us?
Ans: Chlorofluorocarbons, mainly released in the
atmosphere by developed countries, slowly enters the stratosphere and the winds
move them towards the poles. Environmental conditions prevailing in Antarctica
during winter months; there is no sunlight in Antarctica and extremely low
temperature (— 85°C) facilitates the formation of ice clouds. During winter,
natural circulation of wind (polar vertex)
completely isolates Antarctic air
from the rest of the world. The ice clouds provide
the catalytic surface for
the reaction of chlorine atoms and then ozone. But
this degradation of ozone occurs with the return of solar radiations to
Antarctica during spring (September and October). This results in the thinning
of ozone layer every year over most of Antarctica. This hole disappears in
summer
due to warming up of air and the mixing up of
Antarctic air with that of the
rest of the world.Enhanced UV radiations on earth
would affect humans and
other animals by causing:
Skin cancer.
Blindness and increased chances of cataract in eyes.
Malfunctioning of immune system.
Higher number of mutations.
6. Discuss the role of women and
communities in protection and conservation of forests.
Ans: Amrita Bishnoi Wildlife protection project The
Bishnoi community is known for
its peaceful coexistence with nature. It was in 1730
AD. Amrita Devi protested
against king's men’s attempt to cut trees as it was
prohibited in Bishnoi religion. It was a party of Maharaja Abhay Singh ji,
ruler of Marwar (Jodhpur) wanted to fell green Khejdali trees. Amrita Devi with
her three daughters and more than 360 of other Bishnois lost their lives in
saving trees and became martyrs. Later Chipko movement was started by Sunder
Lal Bahuguna and
others to prevent cutting trees. The people showed
enormous bravery in
protecting trees from the axe of contractors by
hugging them.
7. What measures, as an individual, would
you take to reduce environment Pollution?
Ans: To reduce environmental pollution we should
take following measures:
Reducing use of CFC.
Disposing off waste safely.
Reducing use of polythene.
Not disposing off waste in water bodies.
Making automobiles pollution free.
Prevention of noise pollution by using fire
crackers/TV/musical instruments at
permissible limits.
Tree plantation in school, around residence.
8. Discuss briefly the following:
(a) Radioactive wastes
(b) Defunct ships and e-wastes
(c) Municipal solid wastes
Ans: (a) Radioactive waste: Radioactive waste
includes materials that are
radioactive & for which there is no further
practical use. These are generated by nuclear reactor, nuclear fallout, manmade
(refining and mining of platinum and thorium), natural radioactive waste and
release of radiation in radiation therapy.Increased risk of cancer, birth
defects & infertility are few harmful
effects caused by nuclear waste. So, nuclear waste
is an extremely potent
pollutant.
(b) Defunct ships & e-wastes — The dismantling
of defunct ship is a technically complex process, which is potentially harmful
to the environment & human health. Defunct i ships contain toxicants like
asbestos, mercury, etc. The
workers breaking the ships are not suitably
protected and are exposed to toxic chemicals.The coastal areas in the vicinity
of the ship- breaking yard also become polluted. At the international level, it
is accepted that there is uncertainty about the relevant controls for the
dismantling of such vessels & there is an urgent need to establish a
specific enforceable control framework.
Electronic waste comprised of irreparable computer
and other electronic goods, generated by developed countries. It is valuable
source of secondary raw materials, if treated properly, however if not treated
properly it is the major source of toxins. Eventually recycling is
the only solution for the treatment of e-wastes
provided it is carried out in an environment friendly manner.
9. What initiatives were taken for reducing
vehicular air pollution
in Delhi? Has air quality improved in
Delhi?
Ans:The initiatives were taken for reducing
vehicular air pollution in Delhi
are:-
(i) Introduction of CNG
(ii)Enforcement of pollution control law
(iii) Introduction of green zones
(iv) Use of unleaded fuels
(v)Replacement of old vehicle with new one. The
result is that the air quality of
Delhi has improved considerably with a substantial
fall in pollutant gases.
(vi) Use of catalytic converters in vehicles.
(vii)Application of Euro Il norms for vehicle.
10. Discuss briefly the following:
(a) Greenhouse gases
(b) Catalytic converter
(c) Ultraviolet B
Ans:(a) Greenhouse gases:Gases that trap the heat of
the sun in the earth's atmosphere increasing atmospheric temperature effect are
called greenhouses gases. COQ2, CHa,N2O and CFC, cause greenhouse. In the
absence of greenhouse gases,the temperature of earth would go down to - 18°C.
The net effect of higher
GHGs will be disastrous, melting of polar ice caps
and mountain snow caps resulting in rising of sea level threatening submergence
of many islands and coastal areas.Odd climate changes like increased floods and
drought.
(b) Catalytic converter:Catalytic converter ‘are
used to reduce emission of poisonous gases like nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide
& un reacted hydrocarbon in automotive emission. It is made of platinum,
palladium and rhodium and is used as catalyst. It converts unburnt hydrocarbons
into COz. The only precaution
required is not to use gasoline having lead as lead
inactivates the catalysts
of the converter.
(c) Ultraviolet B:Ultraviolet B is one of the three
types of invisible light rays given off by the sun. Ultraviolet B penetrates
the ozone layer in attenuated form & reaches earths. This is more over
equator than poles due to thinning of ozone shield over equator. It causes skin
cancer, reduce rate of photosynthesis in
phytoplankton, and reduces diversity of aquatic
ecosystem.
A200
INTRODUCTION
ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES:Environmental
issues are harmful effects caused to environment because of human activities.
It causes degradation in the quality of air, water and soil. These unfavorable
events cause environmental issues that affect the natural state of the
environment.
ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION:Pollution
is an undesirable change caused to the chemical, biological, and physical
composition of air, soil and water. The wastes that cause pollution are called
pollutants.
The various pollution types include air, water,
noise, soil and radioactive
pollution.
GLOBAL WARMING:Global
warming is the gradual increase in the temperature of the Earth. It happens
when there is an increase in the level of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
The greenhouse gases present in the atmosphere prevent heat captured from the
sun from escaping to the outer space. These gases are thus, responsible for
keeping the Earth warm. With the rise in the level of greenhouse gases, the
Earth’s temperature also rises. This is an environmental concern that can cause
problems to nature and, eventually, to humans.Global warming is caused because
of industrialization, deforestation, vehicle emission, and farming in
factories.
Global warming can be controlled by Cutting down use
of fossil fuel, Improving
efficiency of energy usage, reducing deforestation,
planting trees, slowing down the growth of human population.
OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE:
Ozone found in the upper part of the atmosphere
called stratosphere acts as a
shield, absorbing ultraviolet radiations from the
sun. UV rays are highly injurious
to living organisms
SOLID WASTE:
Solid
waste comes from offices, homes, hospitals and schools that are disposed of by
the town municipality. These comprise solid wastes like plastics, paper,
glass,leather, and many more such things. Solid waste is either dumped or burnt
in the sanitary landfill.
DEPLETION OF NATURAL RESOURCES:When
the natural resources get depleted, then this too causes environmental
pollution. The consumption of fossil fuels leads to the emission of greenhouse
gas.This again causes a change in the climate and leads to global warming.
ELECTRONIC WASTES:
Electronic
wastes are basically electronic goods like computers that are unrepaired. These
are called e-wastes, which are either buried in the landfills, or they are
incinerated. The e-wastes that are generated in the developed countries are
sent to the developing nations to recover metals like iron, copper, gold,
nickel etc. Recycling is the only way to treat the e-wastes.
AGRO — CHEMICALS:Inorganic
pesticides and fertilizers have seen a massive increase in use because of the
green revolution. This helps to enhance the production of
crops. The insecticides and pesticides are toxic.
These get biomagnified in the terrestrial ecosystem that causes
eutrophication in the ecosystem of aquatic life.
DEFORESTATION:Another
major environmental concern is deforestation. This happens because of the
destruction of trees that are used to make buildings. Trees are also cut for
obtaining raw materials. Deforestation causes global warming, soil erosion and
also leads to extinction in biodiversity. Main consequences of deforestation
includes-Enhanced carbon dioxide concentration, Loss of biodiversity, Disturbed
hydrologic cycles, Soil erosion and Desertification etc.
AIR POLLUTION:Air
is essential for respiration in all living organisms. Pollutants reduce growth
and production of crops as well as premature death of plants. The harmful
effect of pollution on all the living organisms depends upon-Concentration of
pollutants and
Duration of exposure. Thermal power plants, smelters
and other industries release particulate and gaseous air pollutants. These
pollutants should be filtered out before releasing the harmless gases into the
atmosphere. There are many
methods of removing particulate matter. The most
widely used is the Electrostatic
Precipitator that can remove over 99% of particulate
matter present in the exhaust
from thermal power plant.
A Scrubber can also remove gases like
sulphurdioxide. The exhaust is passed
through spray of water or lime.
NOISE also causes sleeplessness, increased heart
beating, altered breathing
pattern, thus considerably stressing humans.
Reduction of noise in industries can be affected by use of sound absorbent
materials or by muffling noise.
WATER POLLUTION AND ITS CONTROL: Water bodies are lifeline of human beings as well as other animals. Due to disposal of all kinds of waste and other anthropogenic actions the ponds, lakes, stream, river, estuaries and oceans
are becoming polluted in several
parts of world. The Government of India has passed the Water (Prevention and
Control of Pollution) Act, 1974 to protect the water resources.
DOMESTIC SEWAGE AND INDUSTRIAL
EFFLUENTS:The sewage that comes out from house and office
makes the domestic sewage. A mere 0.1% impurities make domestic sewage unfit
for human use. Solid wastes are relatively easy to remove but dissolved salts
as nitrates, phosphates and other nutrients and toxic metal ions and organic
compounds present in domestic wastes are comparatively difficult to remove.
Domestic sewage mainly contains
biodegradable organic matter, which can be easily
decomposed by microbes like
bacteria and fungi. They use organic wastes as
nutrients.
BIOLOGICAL OXYGEN DEMAND (BOD):The
microbes that decompose organic wastes in water bodies consume a lot of oxygen
that result into sharp decline in dissolved oxygen downstream from the point of
sewage discharge. This causes mortality of fish and other aquatic creatures.
BOD refers to the amount of oxygen that would be consumed if all the organic
matter is one liter of water were oxidized by bacteria. The BOD test measures
the rate of uptake of oxygen by micro- organisms in a sample of
water.Indirectly BOD is a measure of the organic matter present in the water.
Thegreater the BOD of waste water more is its polluting potential.
ALGAL BLOOM
is presence of large amount of organic nutrients in water causes excessive
growth of planktonic or free floating algae called algal bloom.Due to this
color of water bodies get changed. This may cause deterioration of the
water quality thus increase in fish mortality. Water
hyacinth (Eichhornia) is the world’s most problematic aquatic weed. They were
introduced into India for their
beautiful flowers that have caused havoc by their
excessive growth by causing
blocks in our water bodies. This weed is commonly
known as ‘Terror of Bengal’.
BIO MAGNIFICATION or BIOLOGICAL
MAGNIFICATION: Toxic wastes present in industrial
wastes and water from farmhouse containing pesticides and weedicides enters the
food chain of aquatic organisms. This
increase in concentration
of toxicant at each successive trophic level is called biological magnification.
The most common toxicant that gets accumulated at successive trophic levels includes DDT and Mercury. High concentrations of DDT disturb calcium metabolism in birds,which causes thinning of eggshell and their premature breaking, eventually causing decline in bird populations.
EUTROPHICATION
It is the natural aging of a lake by biological enrichment of
its water. Due to addition of nutrients such as
nitrogen and phosphorus that
encourage the growth of aquatic organism the
accumulation of organic remains in
course of time leads to shallowing of lake. Over the
centuries the silt and organic debris piles up at the bottom of lake and
encourage the growth of marsh plants.Eventually large masses of floating plants
grows and finally converting into land.The pollutants from man’s activities
such as effluents from the industries and
homes radically accelerate the aging of lake. This
phenomenon is called Cultural
or Accelerated Eutrophication. Main contaminants
include nitrates, phosphates
that act as plant nutrients. They increase the
growth of algae, causing unsightly
scum and unpleasant odors, and depleting the
dissolved oxygen of water which
is important for other aquatic life.
INTEGRATED WASTE WATER TREATMENT
Wastewater including sewage can be treated in an integrated way, by combining
artificial and natural processes. The Government of India has recently started
the Amrita Devi Bishnoi Wildlife Protection Award for individuals or
communities from rural areas that have shown extraordinary courage and
dedication in protecting wildlife.
CHIPKO MOVEMENT -
In 1974, local women of Garhwali Himalayas showed tremendous courage in
protecting trees from the axe of contractors by hugging them. Realizing the
importance of participation by local communities, the Government of India in
1980s has introduced the concept of;
The biologists developed a series of six connected
marshes over 60 hectares of marshland where plants, algae, fungi and
bacteria were seeded which neutralize, absorb and
assimilate the pollutants. As
the water flows through the marshes, it gets
purified naturally. The marshes also
constitute a sanctuary, which is highly diverse in
the form of fishes, animals and
birds that now reside there. Ecological sanitation
is a sustainable system for
managing human excreta, using dry composting
toilets. Human excreta can be
recycled into natural fertilizer. There are working
‘Eco San’ toilets in many areas of Kerala and Sri Lanka.
SUMMARY:With
increase in human population, demands for food, shelter, water,
electricity, Roads and automobiles are increasing
rapidly and exerting
pressure on Environment and altering the natural
health of ecosystem. All
across the world, People are facing a wealth of new
and challenging
environmental problems every day. Some of them are
pollution,greenhouse effect, ozone depletion, deforestation etc. Pollution is
undesirable change in physical, chemical or biological properties of air,land,
water or soil.
The agents which cause undesirable change are called
pollutants.Loss in biodiversity, depletion of the ozone layer, effects on
marine life and
increase in the carbon footprint are other factors
that cause Environmental Issue
ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES SOLUTIONS:Following
are the solutions to environmental issues: Recycling of waste
Conservation of water and electricity
Use reusable items instead of disposable items
Avoid using plastics
Minimize the use of vehicles
LET US NOW ASK YOU SOME QUESTIONS!!
(A) MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE QUESTIONS:
Q1. The natural aging of lake is called:
a) Bio magnification
b) Eutrophication
c) BOD
d) None of these
Q2. The agents that bring undesirable
changes in the environment are called:
a) Pollution
b) Fragments.
c) Pollutants
d) None of the above
Q3.Which metal activates a catalytic
converter?
a) Gold
b) Iron
c) Silver
d) Lead
Q4. E-Waste is referred to as:
a) Radioactive Waste
b) Nuclear waste
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) Electronic Waste
Q5.increased skin cancer and high mutation
rate are due to:
a) Acid rain
b) Ozone depletion
c) Algal bloom
d) CO pollution
B. TRUE/FALSE:
1. The particulate matter can be removed by
convertor.
2. Ozone layer is found in Stratosphere.
3. Use reusable items instead of disposable items
C. FILL UPS:
1. is undesirable high level of sound.
2.The natural aging of a lake is called .
ANSWER KEY: PART-A
A) MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE QUESTIONS:
Q1. (b) Eutrophication
Q2. (c) Pollutants
Q3. (d) Lead
Q4. (d) Electronic Waste
Q5. (b) Ozone depletion
B) TRUE/FALSE:
1. FALSE
2. TRUE
3. TRUE
C) FILL UPS:
1. Noise
2. Eutrophication
1. Why is a scrubber used? Which spray is used on
exhaust gases passing through a scrubber?
2. Precipitator can remove over 99%particculate matter present in exhaust
from a thermal power plant. How?
3. What is relationship between BOD, micro-organisms
and amount of Biodegradable matter?
1. (a) Discuss the role of women and communities in
protection and conservation of forests.
(b) Explain Bio magnification of DDT in an aquatic
food chain. How does it affect the bird population?