8-HUMAN HEALTH AND DISEASE
CHAPTER NO.8 HUMAN HEALTH AND DISEASE
A83
INTRODUCTION
DEFINITION OF HEALTH: According to Greek and Indian
Ayurveda System. health was considered as a healthy state of body and mind,
which is
free from diseases and infections.
But according to W.H.O.“Health is a state of
complete physical, mental, social and behavioural wellbeing’.
DISEASE: Disease is any condition which impaires
normal functioning of body or some part of the body, associated with specific
symptoms.
Symptoms: Symptoms are evidence of presence of
disease. However symptoms do not give any exact cause of disease
DISEASE AGENTS: Any substance or agent which causes
disease by its excess or deficiency or presence or absence is called disease
agent.
Disease agents can be biological [eg Bacteria,
virus, fungi, protozoans and
worms] or chemical, physical or mechanical.
Etiology: Study of causes of disease is called
etiology.
CLASSIFICATION OF DISEASES: On the
basis of occurrence diseases are of two types:
1. Congenital or Inborn
2. Acquired
Congenital diseases: Congenital diseases can be
defined as structural or functional disorders that are present by birth. These
conditions develop prenatally. Congenital diseases can be caused by gene
mutations or
chromosomal mutations.
Acquired diseases: These diseases develop after
birth and may be caused by pathogens, deficiency of nutrients. allergies or
organ malfunctions.
Acquired diseases may be communicable or non
communicable Communicable or infectious diseases are transmitted from one
person to other and are caused by pathogens like
Viruses, Bacteria, Fungi,Protozoa and Worms etc.
Non communicable or non infectious diseases are not
transmitted from one person to the other. These diseases may be organ
degenerative diseases, diseases due to hypo or hyper secretion of hormones,
allergies,
deficiency diseases or cancer.
Transmission of diseases: Communicable diseases are
transmitted from infected persons to healthy persons either directly or through
intermediate agents.
Direct transmission takes place through contact with
infected persons,droplet infection or through placenta.Indirect transmission
takes place through arthropod vectors, airborne methods or human carriers
etc.Arthropod vectors transmit disease through many ways:
Housefly carries causative organisms of cholera,
typhoid, dysentery and
tuberculosis on the legs and mouth parts from faeces
and sputum.Ants, Cockroaches and House crickets also carry germs to food
articles.
Mosquitoes carry diseases like Filariasis, Malaria,
Chickenguniya, Yellow fever etc.Epidemiology is a branch of medicine which
deals with epidemic disease.
Balanced diet, personal hygiene and regular exercise
are very important to maintain good health. Yoga has been practised since
hundreds of years in India to achieve physical and mental health.For achieving
good health awareness about diseases, vaccination against diseases, maintaining
personal hygiene and proper disposal of waste is
must,
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
(Il) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
1. Which of the following factors affect
human health?
(a) Infections
(b) Lifestyle
(c) Mutations
(d) All of these
2. Which of the following diseases is non
communicable?
(a) Cancer
(b) Diphtheria
(c) Influenza
(d) Malaria
3. Which of the following is a communicable
disease?
(a) Allergy
(b) Cholera
(c) Depression
(d) Diabetes
4. Which of the following disease can be
avoided by washing hands frequently?
(a) Amoebiasis
(b) Kala azar
(c) Cancer
(d) Malaria
5. The organisms which cause disease in
plants and animals are called............
(a) Vectors
(b) Insects
(c) Pathogens
(d) Worms
(Il) TRUE / FALSE:
1. Pathogens result in morphological and functional
damage in our body.
2. Health is just absence of disease or physical
fitness.
3. Infectious diseases are very common and every one
of us suffers from these at some time or other.
(IH) FILL UPS:
1. Study of causes of disease is called.........
2. Among non infectious diseases ........... is
major cause of death.
ANSWER KEY: PART- A
A) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
1. (d) All of these ( Infections, lifestyle,
hygiene, regular exercise and mutations affect human health)
2. (a) cancer (Cancer is caused by carcinogens and
is not communicable)
3. (b) Cholera (House fly carries Vibrio cholerae ,
Which is causative agent of Cholera.)
4 (a) Amoebiasis (Causative agent of this disease is
Entamoeba hitolytica . When we wash our hands frequently, we can check spread
of this disease. )
5. (c) Pathogens (Pathogens are organisms that cause
diseases, like viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoa and worms etc.)
B) TRUE / FALSE:
1. True
2. False (Health is not just absence of disease or
physical fitness, itis a
state of complete physical, mental, social and behavioral
wellbeing.)
3. True
C) FILL UPS:
1. Etiology
2. Cancer
1. What measures would you take to prevent
waterborne diseases?
2. List some diseases transmitted by houseflies.
3. In which way study of biology has helped us to
control infectious diseases?
1. What are various public health measures which you
would suggest to safeguard against infectious diseases?
A84
INTRODUCTION
The diseases, which are caused by pathogens and
readily spread from infected to healthy persons, are called infectious or
communicable diseases.When pathogens infect a person and start multiplying to
produce toxins. Due to toxins some symptoms are produced. The interval between
infection and
first appearance of disease is called the incubation
period. Multiplication of
microorganisms goes on in the body then microbes may
overcome the body's different system and the victim dies or the body defence
system may overpower the pathogens and the patient recovers from the disease.
Some common diseases caused by pathogens are
typhoid. malaria,pneumonia, amoebic dysentery, Dengue chikungunya, ascariasis
and
filariasis etc.In this assignment, we will study
Causing agent, mode of transmission,
symptoms and preventive measures of two diseases,
TYPHOID and MALARIA.
TYPHOID
Causative agent: Typhoid fever is caused by a rod
shaped bacterium,Salmonella typhi.
Mode of transmission: The disease can spread through
contaminated food and water and close contact with infected person. Houseflies
may carry the pathogens, from the faeces to the food, milk and water. The
bacteria enter via
mouth, reach the intestine and cause ulcers in
intestinal wall.
Symptoms of typhoid: Signs and symptoms of typhoid
usually include high fever, headache, dry cough, rashes, stomach pain and
inflammation in intestine,constipation, diarrhoea, loss of appetite and weight
loss.
Typhoid can be confirmed by Widal test.
Preventive measures: Typhoid fever can be prevented
by improved sanitation,
safe drinking water, covered food and personal
hygiene. Frequent hand wash is
best way to control the disease.
Control of Typhoid: Antibiotics can treat the
disease. Typhoid vaccine is also available.
MALARIA
Malaria is a life threatening disease which is very
common in tropical and subtropical regions. In 2019 there were an estimated 229
million cases of malaria worldwide.
Causative agent: Malaria is caused by the malarial
parasite /asimodium sp.There are four species which cause Malaria: Plasmodium
vivax, Plasmodium ovale, Plasmodium malariae, Plasmodium falciparum.Incubation
period of malaria is about 10 to 14 days.
LIFE CYCLE OF PLASMODIUM:Life
cycle of plasmodium completes in two hosts, therefore it is known as digenetic.
Asexual phase of life takes place in human host and sexual phase in female
Anopheles mosquito host. Hence mosquito is primary host, and Man is secondary
host.
ASEXUAL CYCLE OR SCHIZOGONY in HUMAN
HOST: When infected Female Anopheles mosquito bites
humans, it injects sporozoites into the blood of man.
These sporozoites reach liver cells. This phase is
called Exoerythrocytic Schizogony. The sporozoites become large and spherical
and are called cryptozoites, which multiply by multiple fission to form
cryptomerozoites and are released, when host cell ruptures. These
cryptomerozoites attack RBC and
undergo erythrocytic Schizogony. In Erythrocytic
Schizogony, the parasite
enters RBC, becomes spherical and takes food, it is called trophpzoite. It
develops a large food vacuole and becomes amoeboid. The haemoglobin of RBC gets decomposed into a yellowish brown pigment haemozoin.
TROPHOZOITES undergoes multiple fission to form
merozoites. These merozoites arrange themselves around the cytoplasm of RBC to
give rise to rosette stage. The weakened RBC ruptures and symptoms of malaria
appear.
Some merozoites change into sexual forms, male and
female gametocytes. The further development takes place inside the gut to form
sporozoites.
SEXUAL CYCLE IN MOSQUITO HOST:
First step in sexual cycle is gametogenesis, which
takes place inside the stomach of the mosquito. In Gametogenesis micro
gaietccytsas divide to form 4 to 8 daughter nuclei, which ultimately form male
gametes. Female gametocyte matures into a single macro gamete or ovum.
Fertilization Occurs in the stomach of mosquito to
form zygote.This zygote becomes elongated worm like motile structure called
ookinete and pierces the wall of stomach and becomes a spherical structure
surrounded by cyst wall. It is now called oocyst.
Sporogony: The oocyst now undergoes asexual
reproduction. It grows in size and develops a number of vacuoles and nucleus
divides repeatedly to form a large number of daughter nuclei. The resulting
cells are called sporozoites.Ultimately the oocyst ruptures and the sporozoites
are set free in the body of the mosquito. From stomach sporozoites reach the
salivary glands of the mosquito.
When this infected female Anopheles mosquito bites a
person, sporozoites are injected into his or her body with Saliva.Symptoms of
malaria: Symptoms of malaria include fever, chills, headache,nausea abdominal
pain, muscle or joint pain, rapid breathing and cough.
PREVENTIVE MEASURES:
1. Mosquitoes are most active in the moming and
evening. Cover your skin, apply
insect repellent to skin when going outside.
2. Drain off stagnant water, or sprinkle kerosene.
3. Larvicidal fisnes can also be used.
4. Removing unnecessary vegetation around the
houses.
(I) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
1. Widal test is carried out to test:
(a) Malaria
(b) Diabetes
(c) Typhoid
(d) AIDS
2. Trophozoites, schizonts and gametocytes
of all malarial parasites are seen in the peripheral blood smear except:
(a) P. falciparum
(b) P. vivax
(c) P.malanae
(d) P.ovale
3. Haemozoin is:
(a) A precursor of haemoglobin
(b) A toxin from streptococcus
(c) A toxin from plasmodium species
(d) A toxin from haemophilus species
4. Where will you look for the sporozoites
of the malarial parasite?
(a) Saliva of the infected female Anopheles mosquito
(b) Red blood corpuscles of human suffering from
malaria
(c) Spleen of infected humans
(d) Liver of infected human
5. Typhoid is also known as:
(a) Pneumonic fever
(b) Enteric fever
(c) Hepatic fever
(d) Vesical fever
(Il) TRUE / FALSE:
1. Malarial parasite plasmodium reproduces sexually
in human host.
2. Salmonella typhi bacterium is spherical in shape.
3. Microgametocyte and macrogametocyte produce male
and female gametes in Plasmodium.
(Ill) FILL UPS:
1. Female Anopheles mosquito takes up
................ With blood
meal.
2. Causative agent of Typhoid is..............
ANSWER KEY: PART-A
(I) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
1. (c) Typhoid (Widal test is named after its
inventor, Georges Fernand Widal is
confirmatory test for typhoid)
2.(a) Plasmodium falciparum ( Schizogony occurs
inside the capillaries of the
internal organs like spleen, liver and bone marrow,
only Signet ring form is found in
the peripheral blood smear.)
3. (c) A toxin from Plasmodium sp. ( Haemozoin is a
disposal product formed by
digestion of blood by pathogens like plasmodium. )
4. (a) Saliva of the infected female Anopheles
mosquito ( Mature sporozoites
leave the intestine and migrate to salivary glands
of female Anopheles mosquito)
5. (b) Enteric fever ( because Enteric fever is a
systemic disease characterized by
fever and abdominal pain.)
(Il) TRUE / FALSE:
1. False; in mosquito host
2. False; rod shaped.
3. True
(Ill) FILL UPS:
1. Male and female gametocytes
2. Salmonella typhi
1. Which organisms are primary and secondary hosts
of malaria and why?
2. List some symptoms of typhoid fever.
3. How is Plasmodium falciparum most fatal?
4. How can Typhoid be prevented?
1. Describe the life cycle of Plasmodium vivax.
A85
INTRODUCTION
Respiratory diseases are those diseases which affect
any part of respiratory system, nasal chamber, larynx, pharynx, bronchi,
bronchioles, alveoli and the respiratory muscles of chest cage.Some common
respiratory diseases are pneumonia, common cold, influenza,asthma, bronchitis
and lung cancer etc. There are two types of respiratory
diseases and disorders: Infectious and chronic.
Pulmonary infections are most
commonly bacterial or viral.
PNEUMONIA
Pneumonia is a respiratory infection that affects
the lungs.
Pneumonia is the single largest infectious cause of death in children.In lungs, small sacs like air filled structures called alveoli are present at the ends of bronchioles. In healthy person, these alveoli help in exchange of
gases in respiration. But when individual has pneumonia, the
alveoli filled with pus and fluid which makes breathing painful and oxygen
intake
comes down. Anyone can get this lung infection but
children younger than
14 years of age and people above 65 years of age are
at higher risk. People with health cause weakened immune system are also
susceptible to pneumonia.
CAUSATIVE AGENT OF PNEUMONIA:
There are several types of infectious agents that can cause pneumonia.
Bacterial Pneumonia: The most common cause of
bacterial pneumonia is Streptococcus pneumoniae. Other causes include
Mycoplasma
pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae.
Viral pneumonia: Common causes of viral pneumonia
are:
CAUSATIVE AGENTS OF PNEUMONIA
Influenza virus, SARS- CoV-2.
TRANSMISSION OF PNEUMONIA: Pneumonia is spread when droplets of fluid containing the pneumonia bacteria or virus spread in air when someone
coughs or sneezes and then inhaled by others. Transfer of
germs can also take place by touching the things contaminated with Pneumonia
causing virus or
bacteria and then touching your mouth or nose.
SYMPTOMS OF PNEUMONIA:
Pneumonia symptoms can be mild to life threatening. They include:
Cough with phlegm
Fever and chills (Fever 102 F or higher)
Shortness of breath and chest pain
Feeling of tiredness or fatigue
Nausea, vomiting
Loss of appetite
Wheezing
In severe cases lips and fingernails turn grey to
bluish in colour.
PREVENTIVE MEASURES AND CONTROL: Risk of
bacterial Pneumonia can be lowered by:
Washing hands frequently
Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables
Staying away from persons suffering from Pneumonia
Reducing away from Pollution
TREATMENT: Bacterial Pneumonia
can be treated with antibiotics.Immunization against Hib, pneumococcus, measles
and whooping
cough is the most effective way to prevent
Pneumonia.
COMMON COLD
Common cold is a viral infection of upper
respiratory tract (Nose and throat)
It is usually harmless. Healthy adults are expected
to have 2 to 3 colds each
year. Infants and children can have even more
frequent colds. Symptoms usually last for 3-7 days.
CAUSE OF COMMON COLD: Common cold is
caused by more than 200 types of viruses, but the most common one is
Rhinovirus. Cold begins
when virus attached to the lining of the nose or
throat. Inflammation occurs in nose and throat, a lot of mucus is produced.The
viruses which cause common cold are:
Human Rhinovirus, Parainfuenza virus, Adeno virus
etc.
SYMPTOMS OF COMMON COLD:
Signs and symptoms of common cold can
Runny or stuffy nose
sore throat
cough and congestion
mild headache and tiredness
Sneezing and low grade fever.
Hoarseness
PREVENTION OF COMMON COLD:There
is no vaccine for common cold but with using some precautions you can slow down
the spread of cold. These are:
Wash your hands frequently.
Disinfect and clean the high touch surfaces.
Sneeze and cough into tissues and throw the used
tissues in closed dustbins.
Don’t share your utensils with other members of the
family when you have cold.
PART: A VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
(I) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
1. What are signs and symptoms of common
cold?
(a) Runny nose and sore throat
(b) Ear pain
(c) Chills
(d) All of the above
2. Which of these microbes causes walking
pneumonia?
(a) Klebsiella pneumoniae
(b) Streptococcus pneumoniae
(c) Mycoplasma pneumoniae
(d) Chlamydophila pneumoniae
3. What are symptoms of Pneumonia?
(a) Rash, painful joints and itching skin
(b) Jaundice and peeling skin
(c) Cough, fever and chills
(d) All of the above
4. Which disease is known as viral upper
respiratory tract infection?
(a) Pneumonia
(b) Shingles
(c) Typhoid
(d) Common cold
5. The primary preventive strategies for
community acquired
pneumonia is:
(a) Antibiotic therapy
(b) Immunization with pneumococcal and influenza
vaccines
(c) Good hand hygiene
(d) Adherence to healthy lifestyle behaviours
(Il) TRUE/ FALSE:
1. You should expect your doctor to prescribe
antibiotics for standard cold symptoms.
2. In common cold, the lips and fingernails may turn
grey to bluish in colour.
3. As a result of pneumonia the alveoli get filled
with fluid leading to severe problems in respiration.
(III) FILL UPS:
1. Hib vaccine is used against.........
2. Causative agent of common cold is
.................
ANSWER KEY: PART-A
(I) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
1. (a) Runny nose and sore throat
2. (c) Mycoplasma pneumoniae (|In walking pneumonia
symptoms are generally so mild that no hospitalization is required.)
3. (c ) Cough, fever and chills
4. (d) Common cold ( Common cold is a contagious
upper respiratory infection that affects nose throat and sinuses)
5. (b) immunization with pneumococcal and influenza
vaccines
(II) TRUE/ FALSE:
1. FALSE: There is no vaccine or antibiotics for
common cold.
2. FALSE: In severe cases of Pneumonia lips and
fingernails turn grey to bluish in colour.
3. TRUE
(III) FILL UPS:
1. Haemophilus influenzae type b
2. Rhinovirus
PART: B SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. What are the symptoms of walking pneumonia?
2. How common cold differs from pneumonia?
3. Why it is hard to cure common cold?
PART: C LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. Describe cause, symptoms and prevention of
Pneumonia.
2. Name Causative agent of common cold; write its
symptoms and prevention.
A86
INTRODUCTION
GEE is an infectious tropical disease caused by any
one of several thread-like parasitic round worms. The two species of worms most
often associated with this disease are Wuchereria bancrofti and Brugia malayi.
The larval form of the parasite transmits the disease to humans by the bite of
a mosquito.
BE is a type of roundworm infection. These worms are
parasites that use your body as a host to mature from larvae or eggs to adult
worms. Adult worms, which reproduce, can be more than a foot (30 centimeters)
long.
CAUSES OF ELEPHANTIASIS / FILARIASIS
Elephantiasis is caused by three types of parasitic
worms:
Wuchereria bancrofti
Brugia timori
Brugia malayi
These worms affect the lymphatic system that is
responsible for removing the toxins
and wastes from the body. When the lymphatic system
is blocked, it is unable to
remove toxins from the body. This results in the
accumulation of lymphatic fluid that
causes swelling.When the infected Anopheles
mosquitoes bite a healthy person, the larvae called microfilariae moves into
the lymph nodes and develop into adult worms and persist for years.
TRANSMISSION: -Adult worms nest in the lymphatic vessels and disrupt the normal function of the lymphatic system. The worms can live for approximately 6—8 years and, during their lifetime, produce millions of microfilariae (immature larvae) that circulate in the blood.
Mosquitoes are infected with microfilariae by ingesting
blood when biting an infected host. Microfilariae mature into infective larvae
within the mosquito. When infected
mosquitoes bite people, mature parasite larvae are
deposited on the skin from where
they can enter the body. The larvae then migrate to
the lymphatic vessels where they
develop into adult worms, thus continuing a cycle of
transmission.
Lymphatic filariasis is transmitted by different
types of mosquitoes for example by
the Culex mosquito, widespread across urban and
semi-urban areas, Anopheles,mainly found in rural areas, and Aedes, mainly in
endemic islands in the Pacific.
SYMPTOMS
The filariasis elephantiasis symptoms include:
Swelling in:
legs
Arms
Genitals
Breasts
Damaged lymph system resulting in an impaired
immune system.
Repeated bacterial infections of the skin.
Fevers
Chills
Initial symptoms are vague including high-fever,
rashes and chills. At first, most of those afflicted believe they have caught
the Flu. Gradually, the lower torso- legs, sex
organs,abdomen- start to swell out of
control. This swelling is so severe that most physicians have a tough time
controlling it. The skin around these swollen parts starts to itch and pain, besides becoming rough. Lumpy outgrowth on the skin on these parts is also common.
Since the Filariodidea parasites affect the
lymphatic system first, there may also be
gradual swelling of lymph nodes of an affected
individual's body. On occasions,
secondary bacterial infections have been noted on
these regions of our bodies.
Elephantiasis is determined when blood samples are
tested under high-powered
microscopes. The last stage- chronic lymphoedema- is
usually when the disease
starts to develop rapidly.
PREVENTIVE MEASURES AND CONTROL
The disease can be cured by drugs like Hetrazoan,
MSE and Di Ethyl Carbamazine (DEC)
Reconstruction of affected body parts through
surgery.
The disease can be prevented by taking precautions
against mosquito bites.Ascaris has several species but they are all almost a
type of parasitic nematode worm. The giant roundworm that infects the human
intestine by entering through the route of fecal-oral has the scientific name
of Ascaris lumbricoides.
These can grow up to a length of 14 inches or around
35cm long and 2-6 mm wide (depending on the gender of the parasite) inside the
host body and causes the disease of roundworms]EEEE in humans. People are more
affected by Ascariasis in areas with poor sanitation conditions, and it is a
common infection occurring worldwide, which is more prevalent in tropical and
subtropical countries. It is estimated that almost one-sixth of the human
population gets infected
by HM disease.
You can become infected with ascariasis after
accidentally ingesting the eggs of the A. fumbricoides roundworm. The eggs can
be found in soil contaminated by human feces or uncooked food contaminated by
soil that contains roundworm eggs.Children often become infected when they put
their hands in their mouths after playing in contaminated soil, according to
WHO. Ascariasis can also be passed directly from person to person.
One of the characteristics of Ascaris is that the
adult female organism releases the
eggs, and at a time their uteri contain 27 million
eggs, with almost 2 lakh eggs being
laid by them every day for 12-18 months. The
roundworm life cycle also has the step
where the eggs are shed by the feces of an infected
person and flies might carry the
eggs of the parasite to a healthy person.
Fertilized eggs depend on the changes of the
environmental conditions to an embryo
and become infective in almost 18 days and they can
persist in the optimum, moist,
and shaded soil for ten years almost or more.
The eggs of the parasite enter the human body from
the mouth and are ingested through contaminated food or water. These eggs when
it enters the body, then develops into a Rhabditiform larva and hatches and
penetrates the gastrointestinal tract walls and enters into the
bloodstream.These larvae move through the bloodstream and enter the lungs and
break into the alveoli, after maturing the roundworms in a human move up the
trachea where they are coughed up to be swallowed again, and this is how the
eggs reach the small intestine. And after passing three weeks in the stomach,
the roundworms in
humans develop into adult female or male worms, and
in the small intestine, they
mate to lay more eggs.People with ascariasis often
have no symptoms. Symptoms become more noticeable when the roundworm
infestation grows.Roundworms in your lungs can cause:
coughing or gagging
wheezing or shortness of breath
aspiration pneumonia (rarely)
blood in mucus
chest discomfort
fever Roundworms in your intestines can cause:
nausea
vomiting
irregular stools or diarrhea
intestinal blockage, which causes severe pain and
vomiting
loss of appetite
visible worms in the stool
abdominal discomfort or pain
weightloss
growth impairment in children due to malabsorption
Some people with a large infestation may have other
symptoms,such as fatigue and fever. A major infestation can cause extreme
discomfort. You may have all or many of the above symptoms if you don’t receive
prompt treatment.
Always wash your hands with soap and water before
eating
Boil or filter your water Avoid unclean common areas
for bathing
Peel or cook unwashed vegetables and fruits in
regions that use human faeces for fertilizers
LET US KNOW WHAT YOU HAVE LEARNT!
PART: A VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
MCQs:.
1. The causative of filariasis is:
a) Schistosome
b) Trichinella
c) Culex
d) Wuchereria
2. Which is helminthic disease:
a) Polio
b) Filariasis
c) Lepeosy
d) Amoebiasis
3. Infection of ascariasis usually occur
by:
a) Mosquito bite
b) Drinking water containing eggs of ascariasis
c) Injection of dead pathogens
d) IfB & Tlymphocytes damage
4. Filarial larva can be collected from
man’s:
a) Peripheral blood at midnight
b) Smear of spleen
c) Smear of intenstinal contents
d) Biopsy of liver
5. Which drug is used to treat lymphatic
filariasis caused by Wuchereria
bancrofti?
a) Albendazole
b) DEC
c) Lavermectin
d) Doxycycline
Fill ups:
1. Ascariasis is caused by .
2. Filariasis is also called ;
3. Filariasis can be controlled by taking
precautions against .
True/False:
Ascariasis is caused by contaminated soil water,
vegetables etc.
Elephanteases in caused by filarial worm Wichereria
boncrofli
ANSWER KEY: PART-A
MCQs:
1. (d) Wuchereria most cases the filariases is
caused by the parasite known as
Wuchereria bancrofli
2. (b) filariasis. Filaria is a helminthic disease
3. (c) Drinking of water containing eggs of ascaris
4. (a) Peripheral blood at night . Adult parasite
produce microfilariae which
circulate in the peripheral blood usually at night.
5. (b) DEC
Fill ups:
1. Ascarids (common round worms)
2. Elephantiasis
3. Mosquito bites
True/False:
1. True. Eggs of the parasite are present in
contaminated soil
2. True One can say that the lymphatic filariasis
which is also called as
elephantiasis is a type of parasite disease.
1. List some symptoms of ascariasis.
2. How is filariasis transmitted?
3. Give the scientific name of organism that causes
filariasis.
1. Name the causative agents, symptoms and cure for
the following
diseases;
(i) Filaria (Elephantiasis) (ii) Ascariasis
A87
INTRODUCTION
Amoebiasis is also known as amoebic dysentery. It is
caused by a protozoan
parasite of the human large intestine, Entamoeba
histolytica. They are
cosmopolitan, they live in the large intestines and
produce eggs or cysts,
which are passed out of the body with the stool. It
results in diarrhoea and
colitis.
Dermophytoses are Ringworm or round red and silvery
type of superficial FUNGAL infections of the skin. Heat and moisture promote
the growth of these fungi.
AMOEBIASIS
CAUSES OF AMOEBIASIS:
AMOEBIASIS is caused by the following ways:
1. Living in areas with poor sanitary conditions.
2. Ingesting water or food, contaminated by faeces
of infected people.
3. By swallowing cysts of the parasite.
4. It can also occur by oral-anal sexual contact with an infected person.
Inside the intestine the parasite secretes an enzyme
Cytolysin that dissolves the wall of large intestine. The feeding stage of
parasite is called Trophozoite.
SYMPTOMS OF AMOEBIASIS:
An individual infected with E. histolytica may have
mild to severe symptoms.
Sometimes a person may show no symptoms of the
disease:
Fever
Chills
Nausea
Weight loss
Abdominal discomfort
Diarrhoea that may include blood or mucus with
periods of constipation.
TREATMENT OF AMOEBIASIS:Symptomatic
amoebiasis can be treated with administration of metronidazole,followed by
eliminating any organisms present in the colon by a luminal amoebicide.Asymptomatic
carriers are treated by giving a luminal amoebicide.
This reduces the risk of transmission.
RINGWORM
Ringworm, also known as dermatophytosis, is a fungal
infection of the skin. It
can affect both humans and animals. The infection
initially appears as red
patches on the affected areas that later spreads to
different areas of the body.
It majorly affects the scalp, nails, feet, groin and
beard.The ringworm fungus grows well in moist environment such as showers,
bathroom floors and walls, swimming pools and also
in between the skin folds. The vectors for this disease include pets such as
cats and dogs. There are multiple forms of ringworm fungi, which affect
different body parts.Tryptophyton rubrum, T. mentagrophytes, T.tonsurans,
Microsporum andoninni, Epidermophyton floccosum etc.
CAUSES OF RINGWORM:
Ringworm can be caused by the following ways:
It spreads by skin contact with an infected person.
It spreads from pets and cows.
The fungus causing ringworm might be found lingering
on clothes,comb, towels and brushes.
These fungi are mainly present in the spores of
soil. Coming into contact with such soil will result in an infection.
SYMPTOMS OF RINGWORM:Ringworm
symptoms vary depending upon the site of infection.The following are the common
characteristic symptoms of rinqworm:
1. The skin of the feet becomes swollen and itchy
between the toes. The soles and heels of the feet may also be affected.
2. Itchy, scaly red spots appear on the groin area.
3. Ringworm appears like an itchy, scaly, inflamed
bald spot on the scalp.
4. Ringworm on nails appear to be thick and abnormal
in colour and shape.
5. In the beard, itchy, red spots appear on the
chin, cheeks, and the upper neck.
RINGWORM TREATMENT:A
variety of products to treat ringworm infections are available in the market,
such as antifungal cream, lotion, and powder. Sometimes, even home remedies are
very effective.
1. The best antifungal creams used for this
infection are Miconazole or Terbinafine, which should be applied twice in a day
on the infected region until the symptoms withdraw.
2. Amphotericin B is a very powerful fungicide that
is used in the most serious cases of fungal infections.
3. There are many home remedies which help to
prevent and control the infections. Using talcum powder is recommended as it
helps to control sweating
4. Home remedies include Neem, which is a
particularly effective antimicrobial and antifungal agent
RINGWORM PREVENTION:Following
precautions is one of the best methods to avoid ringworms.
And more than often, lifestyle choices and decisions
affect how the disease is spread. For instance, obesity increases the risk of
ringworm.
1. Maintain cleanliness and hygiene.
2. Wash hands with sanitizers.
3. Wear clean ironed clothes.
4. Avoid using communal pools.
5. Wear loose-fitting cotton clothes to avoid the
accumulation of sweat
6. The skin folds have to be kept clean regularly to
avoid the accumulation
of sweat and dirt between the creases.
7. Having a shower twice a day is also recommended.
8. Not touching or scratching the itchy red patches
would help to prevent it
from spreading.
MCQs:
1. Amoebiasis is known to cause:
(a) Headache
(b) Convulsions
(c) Dysentery
(d) None of the above
2. Causative organism of Amoebiasis is:
(a) Ascaris lumbricoides
(b) Toxoplasma gondii
(c) Entamoeba histolytica
(d) None of the above
3. The feeding stage of Entamoba
histolytica is:
(a) Minuta form
(b) Magna form or Trophozoite
(c) Sporozoite
(d) None of the above
4. Which of the following is not the
species of ring worm?
(a) Trichophyton
(b) Microsporum
(c) Plasmodium
(d) Epidermophyton
5. The most common site for amoebiasis is:
(a) Caecum
(b) Sigmoid colon
(c) Transverse colon
(d) Hepatic flexure
FILL Ups:
1. Entamoeba histolytica cysts have nuclei.
2. Ring worm is also known as .
TRUE/ FALSE:
1. Ringworm is caused by a fungus.
2. Animals can transmit ringworm to people.
ANSWER KEY: PART-A
MCQs:
1. (c) Dysentery
2. (c) Entamoeba histolytica
3. (b) Magna form or Trophozoite
4. (c) Plasmodium
5. (a) Caecum; the first part of large intestine.
FILL Ups:
1. 1-4
2. Dermatophytoses
TRUE/FALSE:
1. TRUE. Ringworm, despite the name, is not caused
by a worm. Rather, it is
a skin infection caused by a fungus.
2. TRUE Different kinds of animals can transmit
ringworm infection to people,
particularly kittens and puppies.
1. Give the causative agent of ringworm.
2. How transmission of Amoebiasis and Ringworm takes
place?
3. Write the scientific name of the causal organism
of Ringworm in human.
1. Name the causative agents, symptoms and cure for
the following diseases
(i) Amoebiasis (ii) Ringworm
A88
INTRODUCTION
The overall ability of the body to fight against
disease causing microorganisms with
the help of immune system is called IMMUNITY.
Immunity is of two types-
1. Innate immunity.
2. Acquired immunity.
The system that includes specialized cells, tissues
and organs involved in
protecting our body against invading pathogens is
called the IMMUNE SYSTEM.
INNATE IMMUNITY:The
immunity which occurs by birth is called innate immunity.Innate immunity is
non-specific type of defense.
Innate immunity consists of various barriers which
prevent the entry of microorganisms into the body.
Innate immunity consists of four types of barriers:
PHYSICAL BARRIERS-Skin
on our body is the main barrier which prevents entry of the micro-organisms and
mucus coating of the epithelium lining the respiratory, gastrointestinal and
urogenital tracts also help in trapping microbes entering our body.
PHYSIOLOGICAL BARRIERS- Acid in the
stomach, saliva in the mouth,tears from eyes—all prevent microbial growth.
CYTOKINE BARRIERS-
Virus-infected cells secrete proteins called interferons which protect
non-infected cells from further viral infection
CELLULAR BARRIERS -
Certain types of leukocytes (WBC) of our body like polymorpho-nuclear
leukocytes (PMNL-
neutrophils), monocytes and natural killer (type of
lymphocytes) in the blood as well as macrophages in tissues can phagocytose and
destroy microbes.
ACQUIRED IMMUNITY
The immunity which develops during lifetime by
exposure to suitable foreign agents like microorganisms is called acquired
immunity.Acquired immunity is pathogen specific and it is characterized by
memory.
When the body first encounters a pathogen it
produces a response which takes long time to develop and of low intensity
called as primary immune response and if the body encounters the same pathogen
again it produces highly intensified and
quick response called as secondary immune
response.After responding to the foreign microorganisms and elimination of the
pathogen,the immune system keeps the memory of the that encounter (primary
response)
and during its second encounter with the same
pathogen produces a highly intensified immune response (secondary response).
The primary and secondary immune responses are
carried out with the help of
two special types of lymphocytes present in our
blood-
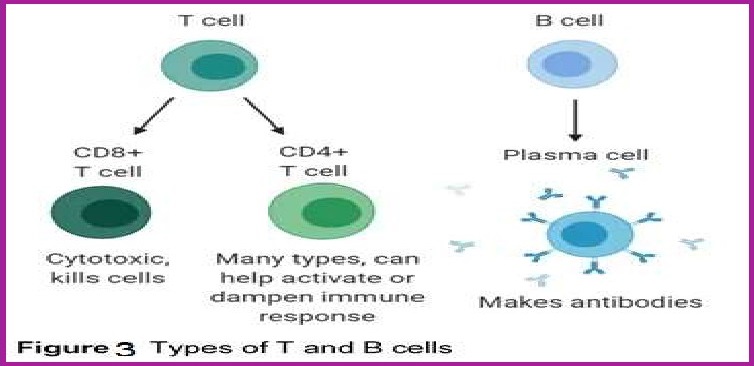
B-lymphocytes :The B-lymphocytes produce an army of
proteins in response to pathogens into our blood to fight with them called as
antibodies.
T-lymphocytes: The T-cells themselves do not produce
antibodies but help B- cells to produce them.
LET US KNOW WHAT YOU HAVE LEARNT!
MCQs:
1. Which of the following systems protects
our body against disease-causing microbes?
(a) Immune system
(b) Digestive system
(c) Excretory system
(d) Respiratory system
2. Which of the following immunity is
present from our birth?
(a) Innate Immunity
(b) Active immunity
(c) Passive immunity
(d) Acquired immunity
3. B-cells and T-cells are two types of
cells involved in .
(a) Innate Immunity
(b) Active immunity
(c) Passive immunity
(d) Acquired immunity
4. Which of the following immunity is
obtained during a lifetime?
(a) Innate immunity
(b) Active immunity
(c) Passive immunity
(d) Both (b) and (c)
5. Which of the following immunity is
called the first line of defence?
(a) Innate Immunity
(b) Active immunity
(c) Passive immunity
(d) Acquired immunity
Fill ups:
1. The branch of biology involved in the study of
immune systems in all organisms is called .
2. The common disorders caused by a poor immune
system include
3. Vaccination leads to the production of B and T
cells.
True/False:
1. T- Cells are involved in self mediated immunity.
2. Only invertebrates have specific immune responses.
MCQs:
1. (a) Immune System
2. (a) Innate Immunity
3. (d) Acquired Immunity
4. (d) Both (b) and (c)
5. (a) Innate Immunity
Fill ups:
1. Immunology
2. Epidemic diseases
3. Memory. Vaccination works to stimulate a specific
immune response that will
create memory B and T cells specific to a certain
pathogen.
True/False:
1. True.
2. False
1. What do you mean by passive immunity?
2. Name various types of barriers of Innate
Immunity?
3. Distinguish between B- cells and T- cells?
1. What is Immune System? Mention 2 types of Immune
system and explain.
A89
INTRODUCTION
Have you ever wondered that why the widely prevalent
covid 19 infection can infect
an individual after inhaling the virus and not
through the skin????
Just by touching the virus contaminated secretions,
one cannot get the infection,
unless the individual touches his nose or mouth or
eyes with his contaminated
hands.
Well dear students, the answer lies in the fact that
skin is a part of “innate immunity”
and forms a barrier for entry of organisms.
We will now study more about INNATE IMMUNITY.
INNATE IMMUNITY:This
type of immunity is present right at the time of birth, and includes different
barriers. These barriers include:
1) Physical barriers: This includes epithelium lining
of skin, respiratory tract,
urogenital system and gastrointestinal system. This
is the reason that COVID-
19 cannot enter the body by just touching virus
contaminated secretions.However, this is not a fool proof method as you very
well know that certain viruses like coronavirus and influenza can enter through
respiratory lining.
2) Physiological barriers: This includes things like
tear film, saliva and acid in
stomach. The food we eat contains many bacteria, but
we seldom fall ill by
eating food. The acid in stomach kills many of the
micro-organisms in the food. In fact, people who eat antacid tablets are more
likely to fall sick to organisms like salmonella typhoid (the causative
organism of typhoid).
3) Cellular barriers: These include the WBCs of the
body like Granulocytes, NK
(Natural Killer) cells and Macrophages.
They patrol the body looking for any micro-organisms
and kill them.Patients (like cancer patients) often have low level of WBCs and
have more chances of falling ill than healthy population.It is important to
note that B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes don't form
part of innate immunity. They are a part of acquired
immunity and will be discussed in a later module.
It is also important to know that cells of innate
immunity lack the property of “memory”. That is each time the neutrophils
encounter a pathogen, they will react in same way.
This is unlike the cells of acquired immunity which
learn from previous infections (memory) and react in more robust way in any
subsequent infections.
4) Cytokine barriers: Cytokines are non-antibody
proteins, released by the cells
in response to contact with an antigen.
Whenever a virus infects a cell, it produces
chemicals like interferons; the lycoproteins, which guard the neighbouring
cells that a virus has entered the field and the cells then prepare for a
potential future infection.
Inflammatory Barrier is formed in response to tissue
injury or at the site of infection, which is manifested as redness, swelling,
pain and heat. The damaged Mast cells of connective tissue and Basophils of
blood produce chemical alarm signals in the form of Histamine and
Prostaglandins. Both
plasma and phagocytes come out of the blood. Serum
proteins in plasma has antibacterial properties. Phagocytes destroy the
invading microorganisms.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
(i) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
1) Skin covering the body is an example of
barrier.
a) Physical
b) Physiological
c) Cellular
d) Cytokine
2) Acid secretion of stomach is an example
of barrier.
a) Physical
b) Physiological
c) Cellular
d) Cytokine
3) Neutrophils are an example of barrier.
a) Physical
b) Physiological
c) Cellular
d) Cytokine
4) Virally infected cells produce chemicals
called as to protect surrounding non-infected cells.
a) Prostaglandins
b) Interferons
c)Leukotrienes
d) Histamine
5) NK cells are a part of immunity.
a) Innate
b) Humoral
c) Acquired
d) Cellular
(ii) TRUE/ FALSE:
1. B-lymphocytes are part of innate immunity.
2. Eosinophils are an example of innate immunity.
3. Innate immunity cells don’t have “memory”
(iii) FILLIN THE BLANKS:
1. The four type of barriers ofinnate immunity are.
=, sand
2. immunity is non-specific and present right at
birth.
(i) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
1) (a) Physical. Skin, epithelium of GI system,
genital system and respiratory system form part of physical barrier.
2) (b) Physiological. Acid in stomach, tears and
saliva are part of physiological barriers
3) (c) Cellular. Cells of innate immunity are
granulocytes (neutrophils,eosinophils, bas1zophils), macrophages, NK cells.
4) (b) Interferons Virally infected cells produce
interferons to protect the
surrounding non-infected cells
5) (d) NK cells. Cells of innate immunity are
granulocytes (neutrophils,eosinophils, basophils), macrophages, NK cells.
(ii) TRUE / FALSE:
1) False. Cells of innate immunity are granulocytes
(neutrophils, eosinophils,
basophils), macrophages, NK cells. B- lymphocytes
and T-lymphocytes are
examples of acquired immunity.
2) True. Cells of innate immunity are granulocytes
(neutrophils, eosinophils,
basophils), macrophages, NK cells
3) True. Memory is a feature of acquired immunity.
(Ill) FILL INTHE BLANKS:
1) The four type of barriers of innate immunity are
physical, physiological,
cellular and cytokine barriers.
2) Innate immunity is non-specific and present right
at birth.
1. What are interferons? How do interferons check
infection of new cells?
2. Write a short note on cellular barriers with
respect to immunity.
1. What are the four types of barriers of innate
immunity? Briefly describe each
of them with relevant examples.
A90
INTRODUCTION
Have you ever wondered; why when someone has second
infection of COVID -19,it is usually milder than the first infection????
It is because the body's immune system learns about
the virus from the first infection, and is well prepared when the body gets
infected second time.In other words, we can say that that body has “acquired”
the immunity from the first infection. We will learn more about acquired immunity
in this module.“Acquired” means something (antigen or antibody) enters the body
from outside and produce immunity.
ACQUIRED IMMUNNITY:
It is the immunity or resistance to a disease which
develops during lifetime of an
individual by obtaining or producing self-antibodies
and cells against the specific
microorganism.It is a pathogen specific immunity.
When the body gets infected by a pathogen for the first time, it generates a
very mild response. This is called primary
response. On subsequent encounter by the same
pathogen, the body generates a much stronger immune response. Our body has
“memory” of the first infection and is better prepared to fight off the
infection the second time, secondary response.
MECHANISM:The primary and secondary immune responses
are carried out with the help of two special type of lymphocytes B and T in our
blood.
1. Humoral or AMIS (Antibody Mediated
Immune System)It is carried out with the help of
activated B — cells and Antibodies.
There are 4 kinds of antibodies in the blood,
namely IgG, IgA, IgM, IgE (remembered by
the acronym GAME). All four antibodies are
produced from the B-lymphocytes.
When the body encounters the pathogen
the first time, the primary response of B-
cells is to generate the IgM antibody.
Helper T-lymphocytes then get activated
and after about 2 weeks, they help B-cells
to produce IgG.So, the initial response is milder as
only IgM is produced but after about 2 weeks,the IgG antibodies are also
produced and the patient gets cured of the illness.
On subsequent exposure to the same pathogen, the
body quickly responds by generating lots of IgG within 1-2 days, and the
pathogen gets killed, thus resulting in a very mild infection the second time.
This is called as secondary or anamnestic response. This type of immune
reaction is called humoral immune
response, or AMIS ( Antibody Mediated Immune System)
as the antibodies are released into the blood. (The word “humor” is Latin for
‘bodily fluids’).
2. CELL- MEDIATED IMMUNE RESPONSE
(CMIS):
There is also a second type of immune response
called as cell-mediated immune
response. Unlike humoral, there is no role of
antibodies.In cell mediated immunity, the T-cells activate certain cells like
macrophages to kill the pathogen infected cells. T- Cells are of four types:
Helper, Killer or Cytotoxic,Supressor and Memory T- cells.
Since in this type of immune response, the pathogen
is killed by cells, so itis
called cell-mediated immune response.
There is also a down side to cell mediated immunity.
Some patients suffer organ failure e.g. kidney or
heart failure. They then require
organ transplant. But it is seen that only the
organs from closely related donors
(e.g. first degree relatives) survive for long
periods. The T-cells can recognize if the transplanted organ is from unrelated
source and generate immune response in an
attempt to kill the organ. Even when the graft is
from a close relative, the patient
needs to take immune system suppressing drugs so
that T-cells are weakened and
don't attack grafted organ. This makes us realize
that the T-cells can distinguish
between “self-proteins” and “nonself-proteins”.It is
the cell-mediated immunity that leads to graft rejection (particularly the
T-cells)
TWO TYPES OF ACQUIRED IMMUNITY:
1. ACQUIRED ACTIVE IMMUNITY:
It is acquired by an individual due to VACCINATION or the PREVIOUS CONTRACTION
OF DISEASE. The
antibodies are produced inside the body. It requires
long time to develop. It
may last for few months to life time.
2. ACQUIRED PASSIVE IMMUNITY:
It is acquired due to obtaining readymade ANTIBODIES from OUT SIDE. Foetus
obtain antibodies from
mother. Antisera are inoculated for avoiding
contraction of disease like antirabies, antitetanus. It develops quickly. It
does not last long.
LET US SEE WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
PART: A VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
(I) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
1) Which of the following play a role in
humoral mediated immunity?
a) B-lymphocytes
b) T-lymphocytes
c) Both AandB
d) None of the above
2) Which of the following play a role in
cell-mediated immunity?
a) B-lymphocytes
b) T-lymphocytes
c) Both A and B
d) None of the above
3) Which of the following are the primary
mediators of humoral immune response?
a) Antibodies
b) Neutrophils
c) T-cells
d) NK cells
4) Which cells are primarily responsible
for graft rejection?
a) T-cells
b) Neutrophils
c) B-cells
d) Antibodies
5) The body gets infected by a pathogen
that stays inside cells and does not in the blood. Which type of immune
response will lead to resolution of the infection?
a) T-cells
b) Neutrophils
c) B-cells
d) Antibodies
(Il) TRUE/ FALSE:
1) Primary response to infection is much stronger
than the delayed response.
2) Both cell-mediated and humoral-mediated immune
system show property of “memory”.
3) Antibodies are produced by the T-cells.
(Ill) FILL IN THE BLANKS:
1) Subsequent encounter with the same pathogen
elicits a highly intensified
secondary or response.
2) are the cells which help B-lymphocytes to produce
antibodies.
ANSWER KEY: PART-A
(I) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
1) (a) c) Both A and B. Humoral immune response is
the one where antibodies are produced. B-lymphocytes produce the antibodies.
However, it is the T-cells which help them to produce the antibodies
2) (b) T-lymphocytes. T-lymphocytes are the key
mediators of cell-
mediated immunity
3) (c) Antibodies. Humoral immune response is the
one where antibodies
are produced. B-lymphocytes produce the antibodies.
4) (a) T-cells Cell-mediated immunity is responsible
for graft rejection. T-
cells mediate cell-mediated immunity
5) (a) T-cells. The pathogens which enter live in
the blood will be targeted by
the humoral immune system (antibodies). However, the
pathogens which live
inside the cells will be killed by the cell-mediated
immunity(T-cells)
(Il) TRUE / FALSE:
1) False. Secondary response or anamnestic response
is much stronger than the primary response.
2) True. Both cell and humoral immunity show memory
as it a property of acquired immune system.
3) False. Antibodies are produced by the B-cells
(humoral immune system)
(ll) FILL UPS:
1) Subsequent encounter with the same pathogen
elicits a highly intensified
secondary or anamnestic response 2) I-lymphocytes
are the cells which help B-lymphocytes to produce antibodies.
PART:B SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1) What does the term ‘memory’ of the Immune system
mean?
2) For an organ transplant, it is an advantage to
have an identical twin. Why?
PART: C LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTION
1) What is the role of B-lymphocytes and
T-lymphocytes in the defence of the body against pathogens?
A91
INTRODUCTION
In the previous module, we learnt about the ACQUIRED
IMMUNITY. We also learnt that B-cells are responsible for production of
antibodies. Antibodies are Glycoproteins called Immunoglobulins, having
specific aminoacid sequence to interact with specific Antigen. Antibodies form
about 20% of the plasma proteins.In this module we will learn about the
structure of the antibody.
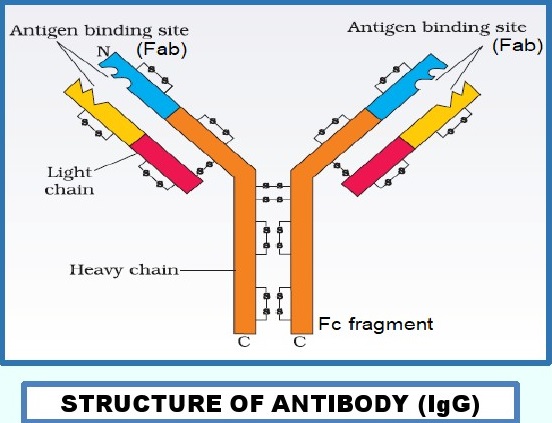
STRUCTURE OF ANTIBODY:There
are FIVE types of antibodies namely IgG, IgA, IgM and IgE (remembered by the
acronym GAME) and Ig D. Each of the 5 antibodies has slightly different
structure. However, for our purpose, we will study only the structure of IgG.
The IgG is a Y-shaped protein. The upper two ends of
the molecule are called
antigen binding sites, and abbreviated as
Fab(antibody binding fragment), and the
lower end is called Fe fragment (crystalline
fragment). Each antibody molecule has
four peptide chains, two small called light chains
and two longer called heavy
chains. The IgG antibody also has abundance of
disulphide bonds.
ANTIGEN — ANTIBODY REACTION:
The antibodies inactivate the antigens through
different processes like;
NEUTRALISATION:
Antibodies cover the toxic sites of antigen and neutralise them by acting as
antitoxins.
AGGLUTINISATION:
The antibodies bring about surface changes in antigens and they get clumped or
agglutinated.
OPSONISATION: Antibodies known
as OPSONINS get adhere to the surface of antigens. This make the antigens
easily visible to the Phagocytes.
PRECIPITATION:
The antibody make the soluble antigen heavier and make them
to setelled down or get precipitated.
LYSIS:
The Lysin antibodies come in contact with the antigen containing cells, and
bring about rupturing of their surface covering.
The
antigen binds to the antigen binding site and is removed from circulation.
(i) Multiple Choice Questions
1) The antibody is made up of how many
peptides?
a) One
b) Two
c) Three
d) Four
2) The antigen binding site of antibody is
made up of:
a) Light chain
b) Heavy Chain
c) Both light and heavy chains
d) None of the above
3) The shape of IgG antibody is:
a) X- shaped
b)V-shaped
c)Y-shaped
d)L- shaped.
(ii) True/ False
1) Antibody is made up of polysaccharides.
2) Antibody molecule contains a lot of disulfide
bonds.
(ii) Fillin the blanks
1) The five antibodies are,__and_.
2) The antibody is made up of a total of __ heavy
and __ light chains.
(i) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
1) (d) Four. The antibody has four peptide chains,
the two small called light
chains and two longer called heavy chains.
2) (c) Both heavy and light chains. The antibody
binding region (Fab) is
made up of two heavy and two light chains.
3) (c) Y-
shaped.
(ii) TRUE / FALSE:
1) False. Antibodies are made of peptides, and not
polysaccharides.
2) True. Both the light chains and heavy chains are
stabilized by disulphide
bonds.
(iii) FILL IN THE BLANKS:
1) The four antibodies are IgG, IgA, IgM, IgE
2) The antibody is made up of a total of two heavy
and two light chains.
PART:B SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1) Draw a labelled structure of antibody.
2) What do you mean by Opsonins?
PART: C LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTION
1) Explain different processes of Antigen — Antibody
interaction.
A92
INTRODUCTION
IMMUNITY is the ability to resist a particular
pathogen.When a host is exposed to antigens, which may be in the form of living
or dead microbes or other proteins, antibodies are produced in the host body;
this type of immunity is called active immunity.Active immunity is slow and
takes time to give its full and active response.
When readymade antibodies are given directly to
protect the body against foreign
agents, it is called passive immunity.
Passive Immunity is fast and gives quick response to fight infection.The yellowish fluid colostrum, the first milk secreted by mother during the initial days of lactation has abundant antibodies IgA to protect the infant.The foetus also receives many antibodies from the mother through the placenta during pregnancy these are examples of passive immunity.
The foundation of IMMUNOLOGY through vaccination and other procedures
were laid by the following scientists:
Edward Jenner found that milkmaids often develop a
milder form of pox called
small pox. He coined the term Vaccine.
Louis Pasteur develops technique of weakening
pathogen by starvation, heat or
cold.Robert Koch is famous for Germ Theory of
disease and method of obtaining pure
cultures of pathogen.Emil Adolf Von Behring proposed
that blood and serum of an immunised
person when injected to other, it brings about
immunisation.Vaccination is a deliberate exposure to a pathogen in order to
bring about immunity.The principal of immunisation or vaccination is based on
property of memory of the immune system.
In vaccination a preparation of antigenic proteins
of pathogen or inactivated
weakened pathogens (vaccine) are introduced in the
body.
The vaccines also generate B and T cells that
recognize the pathogens quickly on
subsequent exposure and counter the invaders with
production of antibodies.
B and T cells are also called memory cells of the
body.
In case of deadly infection like tetanus when a
quick immune response is required
preformed antibodies is injected. This type of
immunisation is called passive
immunization.
Essentially, a vaccine imitates an infection
triggering an immune response,without making a person sick.Recombinant DNA
Technology has allowed the large scale production of
antigenic polypeptides of pathogens in bacteria or
yeast.Vaccines produced using this approach allow large scale production and
hence greater availability for immunization.Before vaccines many children died
that vaccines now prevent whooping cough,measles and polio. Causative germs of
these diseases still exist but because of
effective vaccination these are no longer a danger
now.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE LEARN!
PART: (A) VERYSHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
(1) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
1) Immunity is mainly of:
(a) 2 types
(b) 3 types
(c) 4 types
(d) 5 types
2) The material introduced in the body, in
active immunity:
(a) Particular dead pathogen
(b)antibodies
(c)DNA
(d) Catalyst
3) Introduction of readymade antibodies
into the body is called:
(a) Active immunity
(b) passive immunity
(c) disease
(d) None of these
4) Colostrum, first milk of mother after
parturition is rich in:
(a) Antibodies
(b) antigens
(c) vitamins
(d) pathogens
5) Vaccination is a deliberate attempt to
bring:
(a) Disease
(b) immunity
(c) allergy
(d) none of these
(Il) FILL IN THE BLANKS:
1) Immunity is to diseases.
2) Vaccination also generates and cells which
recognize the pathogens quickly.
3) B and T cells are also called cells of the body.
(II) TRUE/ FALSE:
1) Immunity is resistance of the body to a
particular pathogen or disease.
2) In active immunity readymade antibodies are
introduced in the body.
3) Colostrum is rich in antibodies.
(l) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
1) (a) 2 (Active and Passive immunity. )
2) (a) Particular dead pathogen.( In active immunity
a deliberate exposure to dead pathogen is made)
3) (b) Passive immunity ( Readymade antibodies are
given in passive immunity)
4) (a) Antibodies ( Colostrum is called first milk
of mother after delivery)
5) (c) Immunity ( Vaccination is based on the
property of memory of the immune system)
(Il) FILL IN THE BLANKS:
1) resistance
2) BandT
3) memory
(Il) TRUE/FALSE:
1) True
2) False ( In active immunity dead or inactive
pathogen is introduced in the
body)
3) True
SECTION: B - SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
1) Define immunity.
2) What is vaccination?
3) Name some diseases for which vaccination is
available for newly born babies.
SECTION: C - LONG ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
1) Explain immunity and its types.
2) What is importance of vaccination in providing
immunity?
A93
INTRODUCTION
The human immune system consists of lymphoid organs,
tissues, cells and soluble molecules like antibodies.Lymphoid organs are the
organs where origin and/or maturation and
proliferation of lymphocytes occur.
The primary lymphoid organs are Bone Marrow and
Thymus where lymphocytes differentiate into antigens sensitive lymphocytes.
After mutation lymphocytes migrate to secondary
lymphoid organs like Spleen Lymph Nodes,Tonsils, Peyer's Patches of Small
Intestine and Appendix. The secondary lymphoid organ provides the sites for the
interaction of lymphocytes with the antigen, which
then proliferate to become effector cells.
The bone marrow is the main lymphoid organ where all
blood cells including lymphocytes are produced.
The THYMUS is a lobed organ located near the heart.
Both bone marrow and thymus provide micro environment for the development and
mutation of T lymphocytes.
The spleen is a large bean shaped organ. It acts as
a filter of the blood by
trapping blood borne micro-organisms. The lymph
nodes are small solid structures located at different points along the
lymphatic system. Lymph nodes serve to trap the micro-organisms or other
antigens which enters into lymph and tissue fluid.
There are lymphoid tissues which are located within
the lining of major tracts (respiratory, digestive and urine genital tracts)
called Mucosa Associated Lymphoid Tissues (MALT). It constitutes about 50 % of
lymphoid tissues in human body.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
PART: A- VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
(A) MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE QUESTIONS:
1) The human immune system consist of:
(a) Lymphoid organs
(b) Tissue cells
(c) Antibodies
(d) All of these
2) Bone marrow is a:
(a) Primary lymphoid organ
(b) Secondary lymphoid organ
(c) Tertiary lymphoid organ
(d) None of these
3) Spleen is a:
(a) Primary lymphoid organ
(b) Secondary lymphoid organ
(c) Tertiary lymphoid organ
(d) None of these
4) The site of interaction for lymphocytes
and antigens are:
(a) Primary lymphoid organ
(b) Secondary lymphoid organ
(c) Stomach
(d)None of these
5) All blood cells are produced in:
(a)Bone marrow
(b) Spleen
(c) Thymus
(d) Tonsils
(B) FILL IN THE BLANKS:
(a) Bone marrow and thymus are ............ lymphoid
organ.
(b) Spleen and tonsils are ............... lymphoid
organs.
(c) Spleen is a large .............. shaped organ.
(C) TRUE/FALSE:
(a) Bone marrow is the site for production of
lymphocytes.
(b) Spleen is a primary lymphoid organ.
(c) Peyer's patches are present in the small intestine.
ANSWERS KEY: PART-A
(A) MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE QUESTIONS:
1) (d) All of these(Lymphoid organs, tissue cells,
antibodies all constitutes make immune system)
2) (a) Primary lymphoid organ( Bone marrow is a
primary lymphoid organ)
3) (b) Secondary lymphoid organ(Spleen is a
secondary lymphoid organ)
4) (b) Secondary lymphoid organ(These organs are
interaction sites for lymphocytes and antigens)
5) (a) Bone marrow( All blood cells are produced in
bone marrow)
(B) FILL IN THE BLANKS:
a) Primary lymphoid organs
b) Secondary lymphoid organs
c) Bean shaped
(C) TRUE/FALSE:
a) True
b) False(Spleen is a secondary lymphoid organ)
c) True
SECTION: B - SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
l) Name two primary lymphoid organs.
ll) Name two secondary lymphoid organs.
Il) Write full form of MALT.
SECTION: C- LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
l) Write about primary lymphoid organs and their
functions.
ll) Explain the function of secondary lymphoid
organs.
A94
INTRODUCTION
Immune system is a body’s defence against infection and
other harmful invaders.
Without it the body would constantly get sick from
germs such as bacteria or virus.
Immune system is made up of special cells tissues,
organs that work together to
protect the body.When immune system does not work
the way it should, it is called an immune system disorder.
IMMUNE SYSTEM DISORDER:
Some common examples of immune system disorder are:
1) Severe combined immune deficiency. ( SCID)
2) Temporary acquired immune deficiencies.
3) Auto immune disorder
4) AIDS
1) Severe Combined Immune deficiency (SCID): This is
an example of immune deficiency that is present at the time of birth. Children
are in constant danger of infections from bacteria, viruses and fungi. This
disorder is sometimes called “Bubble boy disease”.
2) Temporary acquired immune deficiency: Immune
system can be weekend by certain medicines for example this can happen to
people on chemotherapy or other medicines used to treat cancer.
3) Auto immune disorder: In response to an unknown
trigger, the immune system may begin producing antibodies that instead of
fighting infections attack the body’s own tissues. Treatment for auto immune
diseases generally
focuses on reducing immune system activities.
Examples of auto immune diseases include:
Rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, multiple sclerosis.
4) AIDS: HIV which causes AIDS is an acquired viral
infection that destroys important white blood cells and weakens the immune
system.
AIDS
The word AIDS stands for Acquired Immune Deficiency
Syndrome.Syndrome means a group of symptoms. AIDS was first reported in 1981.
CAUSES OF AIDS
AIDS is caused by the Human Immune deficiency Virus
(HIV), a member of a group of viruses called RETRO VIRUS, which have an
envelope enclosing RNA genome.Transmission of HIV infection generally occurs
by:
a) Sexual contacts with infected person.
b) By transfusion of contaminating blood.
c) By sharing infected needles.
d) From infected mothers to her child.
It is important to note that HIV /AIDS is not spread
by mere touch or physical contacts, it spreads only through body fluid, so
HIV/AIDS patients should not be isolated from family and society.
MECHANISM OF INFECTION:There
is always a time lag between the infection and appearance of AIDS symptoms.
This period may vary from a few months to many years (5 to 10 years).
After getting into the body of the host, the virus
enters into macrophages where
RNA genome of the virus replicates to form viral DNA
with the help of enzyme
Reverse Transcriptase.This viral DNA incorporates
into host cell's DNA and directs the infected cells to produce virus particles.
The microphages continued to produce virus and in this way acts like an HIV
factory. HIV enters helper T- lymphocytes leading to decrease in their numbers
which cause lot of infections to the host body.
TEST FOR AIDS:
A widely used diagnostic test for AIDS is Enzyme
Linked Immune Sorbent Assay
(ELISA). Treatment of AIDS with anti-retroviral
drugs is only partially effective.
They can only prolong the life of patient but cannot
prevent death which is
inevitable.
Prevention is the best option for AIDS. HIV
infection spreads due to conscious
behaviour pattern and is not something that happens
in advertently like pneumonia
or typhoid.
PREVENTIVE MEASURES OF AIDS:
Use a condom during sexual intercourse.
Avoid sharing syringes.
When getting a tattoo or piercing, make sure the
material is new and disposable or sterilized.
Use
disposable gloves when at risk of direct contact with blood.
For HIV positive women, consider giving birth by
caesarean section.In our country the National AIDS Control Organisation (NACO)
and other Non- Government Organisations (NGO'S) are doing a lot to educate
people about AIDS.
WHO has started a number of programmes for
preventing AIDS such as making blood (from blood banks) safe from HIV, ensuring
the use of only disposable needies and syringes, free distribution of condoms,
controlling drug abuse and promoting regular check-up’s in HIV susceptible
populations.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
PART: A VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
A) MCQs:
1) The human immune system consist of:
(a)Lymphoid organs
(b) Tissue cells
(c) Antibodies
(d) All of these
2) SCID is a:
(a)Deficiency disease
(b) Immune disorder
(c) Allergy
(d) Infection
3) AIDS Infection is caused by:
(a)Bacterial
(b)Fungal
(c)Viral
(d) protozoan
C) TRUE/FALSE:
a) False( Auto immuno disorder is an immunity
disorder caused by over activity
of immunity system)
b) True
c) True
PART: B SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
l) Write full form of ELISA.
li) | NACO stands for which organisation.
lil) What is auto immune disorder?
PART: C LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
I) Give a short account of immune disorder.
lI) Write in detail about AIDS and preventive
measures for the disease.
A95
CANCER is one of the most dreaded diseases of human
beings and is a major cause of death in all over the world. More than a million
Indians suffer from cancer and a large number of them die from it annually.
Caner is the
uncontrolled divisions of cells that have lost the
regulatory mechanism. In our
body, cell growth and differentiation are highly
controlled and regulated. In
cancer cells, there is breakdown of these regulatory
mechanisms. Normal cells
show a property called contact inhibition by virtue
of which contact with other
cells inhibits their uncontrolled growth. Cancer
cells appear to have lost this
property. As a result of this, cancerous cells just
continue to divide giving rise to
masses of cells called TUMOR.
CHARACTERISTICS:
1. Cancers show uncontrolled mitotic divisions of
cells causing unorganised
growth of cells.
2. These ceils grow much more than the normal cells.
3. Due to uncontrolled growth and division of cells,
a tumor is generally formed. However, all tumors are not cancerous. No tumor is
formed in Leukaemia.
4. These cells have less survival capability.
5. Cancer cells are far less adhesive than normal
cells, so these generally wander through the tissues to cause cancerous growth
in different parts of body.
6. Cancer cells do not undergo differentiation and
do not show contact
inhibition.
TYPES OF CANCERS:
On the basis of their original tissue from where
they arise, tumors are of THREE
types:
1. CARCINOMAS: These are located in epithelial tissues and glands, for
example, breast cancer, stomach cancer, skin cancer, lung cancer etc.
2. SARCOMAS: These are located in connective and
muscular tissues, for example, bone cancer, cancer of lymph nodes and muscles.
3. LEUKAEMIA: Also called blood cancer, caused by
increased number of WBC's in blood.
TYPES OF TUMORS:
tumors are of 2 types:
1. Benign Tumor
2. Malignant Tumor
1.BENIGN TUMOR:
Such types of tumors normally remain confined to theiroriginal location and do
not spread to other parts of body and cause little damage.
2.MALIGNANT TUMOR
§These tumors are a mass of proliferating cells.These cells grow very rapidly,
invading and damaging the surrounding normal tissues. Cells from such tumors
reach distant sites through blood and start forming a new tumor there. This
property in called ae and is the
most feared property of malignant tumors.
CAUSES OF CANCER:
1. lonising radiations like X-rays, Gamma rays and
particulate radiations from radioactive substances which rupture DNA strands
and induce mutations to cause cancer.
2. Excessive exposure to sunlight may stimulate the
development of skin cancer.
3. Chemical agents like polycyclic hydrocarbons,
caffein, heavy metallic ions
etc. are also carcinogenic.
4. Hormones like testosterone and estrogen are known
to cause prostate and breast cancer respectively.
5. Tobacco smoking causes lip, mouth and lung cancer
due to presence of carcinogenic agents benzpyrene and N-nitroso-dimethylene.
6. Oncoviruses have viral oncogenes which cause
Cervix cancer.
DANGER SIGNALS OF CANCER:
1. Presence of a persistent tumor.
2. Any wound with continuous bleeding.
3. Any wound not healing for long period.
4. Persistent indigestion.
5. Rapid change in appearance, form and growth on
some parts of body.
6. Persistent changes in the bowel movements.
7. Persistent hoarseness in voice, or persistent
coughing, or persistent
difficulty in swallowing indicate chances of throat
cancer.
8. Unexpected loss of weight.
9. Excessive bleeding in the menses.
CANCER DETECTION AND DIAGNOSIS:
Cancer detection is based on BIOPSY and
HISTOPATHOLOGICAL studies of the tissues, blood and bone marrow.IN BIOPSY a
piece of the suspected tissue cut into thin sections is stained and examined
under microscope by a pathologist.Techniques like radiography (use of x-rays),
CT (computed tomography)
and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) are very useful
to detect cancers of internal organs.
Antibodies against cancer specific antigens are also
used for detection of certain cancers.Techniques of molecular biology can be
applied to detect genes in individuals
with inherited susceptibility to certain cancers.
TREATMENT OF CANCER:
Most cancers are treated by surgery, radiotherapy
and chemotherapy.In radiotherapy tumor cells are irradiated lethally, taking
proper care of the normal tissue surrounding the tumor.In chemotherapy,
chemotherapeutic drugs are used to kill cancerous cells.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
MCQs:
1. Most of the cancers are treated by:
(a)Surgery
(b)Radiotherapy
(c) Chemotherapy
(d)AIl of the above
2. Antiviral proteins are known as:
(a)Interferons
(b)Antigens
(c)AH factors
(d)Vaccines
3. Which of the following is correct for
benign tumor?
(a)It extends into neighbouring tissues
(b)It grows first slowly, then rapidly
(c)It remains confined to the site of its origin
(d)It is cancerous
4. Which of the following is a form of
cancer?
(a)Carcinoma
(b)Leukaemia
(c)Lymphoma
(d)AIl of the above
5. An abnormal rise in the WBC’s count is:
(a)Diapedesis
(b)Leukaemia
(c) Haemopoiesis
(d)Polycythemia
TRUE / FALSE:
1. Malignant tumor is highly cancerous as it invades
surrounding
tissues.
2. Cancerous cells show property of contact
inhibitions.
3. Biopsy is a method of detection of cancer.
FILL IN THE BLANKS:
1. The agents which cause cancer are called .
2. An outgrown which is developed due to
uncontrolled division of cells is known as .
ANSWER KEY: PART -A
Multiple Choice Questions:
1. (d) All of the above (Cancers can be treated by
surgery, radiotherapy and
chemotherapy. )
2. (a) Interferons (Interferons are antiviral
proteins released by cells in response to a viral infection.)
3. (c)lt remains confined to the site of its origin
(Benign tumor remains confined to the site of origin.)
4. (d) All of the above (All carcinoma, leukaemia
and lymphoma are forms of
cancer.)
5. (b) Leukaemia (Leukaemia is an abnormal rise in
count of WBC’s.)
True or False:
1. True
2. False: Cancerous cells do not show property of
contact inhibitions, they
become pushy to spread.
3. True
1. Carcinogens
2. Tumor
1. Name type of the cancer in which no tumor is
formed.
2. Explain what is Metastasis?
3. Write differences between benign and malignant
tumor.
4. Write various danger signals of cancer.
1. What are the causes of cancer? Explain different
therapies for the treatment of cancer.
A96
INTRODUCTION
The physical and mental dependency on smoking, drugs
and alcohol, is
called Addiction.The person who has become dependent
upon these chemicals is called an
“Addict”.Addiction is a psychological attachment to
certain effects, like euphoria and a temporary feeling of normalcy, of smoking,
alcohol and drugs. But with
repeated use of these, the tolerance level of their
receptors increases and respond only to higher dose of these chemicals.This
finally results in addiction or dependency.
An addict is so dependent on drugs that, he cannot
live without Daily Dose of drugs. The amount required to produce the required
effects increases with regular use. Addiction has been reported on the rise
especially in the adolescents. This is a serious concern because abuse of
tobacco, alcohol
or drugs produces many ill-effects of individual's
health, his/ner family and
even on the society.The various sources of drugs
are:
TOBACCO:
Tobacco is derived from the dried and cured leaves
of young branches of
two species of tobacco plant: Nicotiana tobaccum (a
native plant of tropical America) and N. rustica (family Solanaceae).
HISTORY:
Tobacco is being used by human beings for more than
400 years. It was first used by the RED INDIANS in America. It spread to
European countries in early 17 century. Today it is smoked all over the world.
Tobacco is
mainly taken in the form of cigarette or
bidies(smoking), chewing and sniffing.
TOXIC SUBSTANCES IN TOBACCO:
Tobacco is a harmful intoxicant. Tobacco contains a highly
poisonous alkaloid called Nicotine. It is so toxic that the amount of nicotine
present in one cigarette is proven fatal, if it is injected intravenously into
a person.Continuous use of nicotine leads to addiction. Besides nicotine,
tobacco
smoke also contains carbon monoxide, N —
Nitrosodimethyne,polycyclic hydro-carbons like benzpyrene and tar.
ILL EFFECTS OF TOBACCO ADDICTION:
Though tobacco smoking may provide some temporary
relief to the strained nerves (a sense of tranquility or peace) but the regular
use of tobacco causes number of ill effects on various organs of the body. As
while smoking, only 10% of the smoke is inhaled and
the absorption rate of
tobacco smoke is very slow, its ill effects become
evident only after prolonged use.
EFFECTS OF NICOTINE:
1. It stimulates conduction of nerve impulses.
2. Stimulates adrenal medulla to secrete adrenalin
and nor-adrenalin
hormones.
3. Increased constriction of blood vessels.
4. Increased rate of heart beat, blood pressure and
cardiac output.
5. Relaxes the muscles.
6. High concentration of tobacco paralyses neurons.
7. Regular use causes addiction.
TOBACCO SMOKING AND DISEASES:Tobacco
smoking is associated with several diseases:
1. Cancer: Benzpyrene of tobacco is carcinogenic in
nature. About 95% of
victims of lung cancers are associated with smoking.
Reverse smoking causes Oral cancer. Lip cancer is also associated with smoking.
About 33% of all cancers are caused by tobacco. About 50% of all cancers
among men and 25% among women are tobacco related.
It is more common in person smoking cigarettes than those smoking cigar or pipe
because cigarette smokers inhale smoke with
polycyclic hydrocarbons.Tobacco chewing generally causes mouth cancer.
2. Tobacco smoke causes irritation and inflammation
of mucosa of throat
and bronchi which causes coughing and bronchitis.
The chemicals in cigarette smoke in-activates cilia of respiratory tract so the
phlegm accumulates.
3. Nicotine of tobacco causes increased secretion of
adrenalin and non-adrenalin which increases blood pressure and rate of heart
beat which may cause cardiovascular diseases.
4. Emphysema: tobacco smoke is known to cause
inflammation of lung alveoli which decreases surface area for gaseous exchange
and
causes emphysema.
5. It causes increased secretion of gastric juices
which causes gastric and duodenal ulcers.
6. Smoking is known to aggravate pulmonary
tuberculosis.
7. Carbon monoxide of tobacco smoke rapidly binds
haemoglobin of RBC and forms carboxyl-haemogiobin and causes CO-poisoning which
decreases O2 — carrying capacity of haemoglobin of
RBC’s which causes hypoxia in the body tissues.
8. Nicotine of tobacco smoke retards the foetal
growth in the mother's womb.
9. Smokers have a greater tendency of byssinosis, a
lung disease, caused
by prolonged inhalation of textile dust.
10. Smoking and lifespan: There are many evidences
which show that smoking shortens lifespan.Smoking only one cigarette shortens
your lifespan by 11 minutes,while smoking a carton of cigarettes takes about
1.5 days off your lifespan.
NO TOBACCO DAY:
May 31* is observed as “NO TOBACCO DAY’, all over
the world. It is aimed to counter the alarming health; economic and human costs
being extracted by the killer weed.
STEPS RECENTLY TAKEN TO DISCOURAGE PEOPLE
FROM TOBACCO CONSUMPTION:
1. Tobacco smoking has been prohibited in hospitals,
dispensaries and other health care establishments, educational institutions,
conference rooms, domestic air fights, air-conditioned chair cars, sleeper
coaches and buses etc.
2. Smoking has also been prohibited in public places
all over in India.
3. Ithas been mandatory to print a warning — Ee (ES
On chewing tobacco products.
4. Direct advertisements relating to tobacco or
tobacco related products are prohibited on Doordarshan and All India Radio.
5. Anti-Tobacco Act passed on May 1, 2004 states:
Ban on sale of tobacco products within 100 meters of
educational institutions from Dec 1, 2004.
Mandatory depiction pf statutory warning including
pictorial symbols on packets of tobacco products.
6. By 2030, tobacco is expected to be single biggest
cause of death worldwide accounting for 10 million deaths per year.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
A)Multiple Choice Questions:
1. Which of the following is associated
with smoking?
(a)Bronchitis
(b)Lung Cancer
(c)Emphysema
(d)AIl of the above
2. World No Tobacco Day is celebrated on:
(a)May 31st
(b)June 6th
(c)April 22nd
(d)October 2nd
3. The component in tobacco that stimulates
secretion adrenalin and non-adrenalin is:
(a)Tannic acid
(b)Nicotine
(c)Catechin
(d)Curcumin
4. Nicotine in tobacco is synthesised in:
(a)Stem
(b)Flowers
(c)Leaves
(d)Roots
5. Tobacco smoking causes:
(a)Lung cancer
(b)Coronary disease
(c) Infertility in males
(d)AIl of these
B)True or False:
1. Benzpyrene in tobacco is carcinogenic in nature.
2. Tobacco smoking causes inflammation of lung
alveoli and decreases surface area for gaseous exchange and causes Emphysema.
3. Chewing of tobacco does not cause mouth cancer.
C) Fill in the blanks:
1. Tobacco contains highly poisonous alkaloid called
.
2. Tobacco smoke causes irritation and inflammation
of mucosa of the throat and bronchi which causes and .
ANSWER KEY: PART-A
A) Multiple Choice Questions:
1. (d) All of the above (Bronchitis, Lung cancer and
Emphysema all are associated with smoking).
2. (a) May 31 (World No Tobacco Day is celebrated on
May 31).
3. (b) Nicotine (stimulates secretion of adrenalin
and non-adrenalin).
4. (c) Nicotine (is synthesised in leaves of tobacco
plant).
5. (d) All of the above (Lung cancer, coronary
diseases and infertility in
males is caused by tobacco smoking).
B)True or False:
1. True
2. True
4. False: Chewing of tobacco causes mouth cancer.
C)Fill in the blanks:
1. Nicotine
2. Coughing and Bronchitis
1. Name two toxic chemicals present in tobacco.
2. What is meant by addiction?
3. Name two respiratory diseases associated with
smoking.
1. Name and explain various diseases associated with
tobacco smoking.
A97
INTRODUCTION
The word Alcohol refers to Ethyl Alcohol (C2HsOH).
Alcohol is manufactured by fermentation of sugar. Alcohol is quickly absorbed
in the stomach and upper part of the intestine and transferred to the blood.
Firstly it affects the cerebrum part of the brain. Many people think that alcohol
is
When drinking of excessive alcohol is done that
impairs one’s physiological, physical and psychological function. It
constitutes alcohol addiction.
Addiction means psychological attachment to certain
effects such as euphoria and temporary feeling of well-being with alcohol and
drugs.
STAGES OF ADDICTION:-
Five stages are recognized:
i) Experimental use: - Taking alcohol or drug under
group or peer pressure.
ll) | Recreation use: - use of alcoholic substances
out of wrong notion that is gives pleasure or euphoria.
Ill) Situational use: - Intake of alcohol or drug
more than few time but only in the company of other.
IV) Compulsive use: - With regular use the tolerance
level of receptor increases.
V) Dependence: - After an interval of regular use a
person become dependent and cannot do anything without alcohol.
EFFECTS OF ALCOHOL:
1. Deficiency of nutrients: - Deficiency of
nutrients such as minerals, proteins,
vitamins are found in alcoholic.
2. Effect on immunity:- Chronic alcoholic neglect
their health and soon body loses its resistance against infections.
3. Effect on brain:- Alcohol is depressant to brain.
4. Effect on cardiovascular system: - Drinking leads
to hypertension and
increased size of heart. Heart valves became
inefficient.
5. Effects on liver: - Liver size increases due to
reduction in gluconeogenesis
(formation of glucose from glycogen) and this leads
to liver cirrhosis.
6. Mood disorder: - Alcoholic often develops various
types of mood disorder such as sadness, anxiety.
7. Impotency and infertility: - Alcoholism produces
impotency and infertility Alcohol always delays maturity in adolescent.
8. Cancer risk: - Alcohol increases the risk of
carcinoma by ten times.
9. Life span: - Continued intakes of alcohol shorten
the average life span by 10-
15 year.
10. Social problems: - These include absence from
work, unemployment,marital tension, child abuse, financial difficulties etc.
WITHDRAWAL SYMPTOMS OF ALCOHAL:-When
an alcohol addict tries to stop regular dose of alcohol then these following
symptoms appears:-
1. Anxiety.
2. Nervousness.
3. Depressed mood.
4. Restlessness.
5. Insomnia (sleeplessness).
6. Impaired concentration.
7. Excessive sweating, nausea, vomiting.
PREVENTION AND CONTROL OF ALCOHOL
ADDICTION:
Prevention is better than cure is also true
here.This habit generally picked up during young age so following measures
should be taken in adolescent period:-
1. Avoid undue peer pressure.
2. Education and counseling are very important to
face problems.
3. Seeking help from parents and peers if there is
any problem.
4. Parents and teachers should always careful to
look for and identify danger
sign.
5. Take professional and medical help if it is
required.
PART: A VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
all Multiple cheice questions:.
1. Cirrhosis of liver caused by:
a) Cocaine
b) LSD
c) ALCHOL
d) MMORPHINE
2. In the liver, alcohol is converted into
toxic substance:
a) Formic acid
b) Acetaldehyde
c) Nicotine
d) Urea
3. In drunk person, parts of brain to
affected first in:
a) Cerebellum
b) Pons varolli
c) Medulla
d) Cerebrum
4. In alcoholic liver damaged as it:
a) Accumulates excess of fats
b) Store glycogen
c) Secrete bile
d) Detoxify alcohol
5. Effect of alcohol in body. Choose the
wrong one
a) Alcohol increases the size of liver
b) Alcohol increases chance of cancer
c) Alcohol improves your immunity
d) Alcohol create impotency
1. Addiction is psychological attachment to certain
affects.
2. Alcoholism increases the life span.
3. Alcohol addiction causes impotency.
1. The word alcohol refers to ...........alcohol.
2. Anxiety, restlessness, insomnia are withdrawal
symptoms of
ANSWER KEY: PART-A
(a) Multiple choice questions:
1. (c) Alcohol causes liver damage called cirrhosis.
2. (b) Acetaldehyde-:- it is a toxic for cell.
3. (c) Cerebrum:-it is a part of brain which is
affected first.
4. (a) Excess of fats accumulate which cause fatty
liver condition.
5. (c) Alcohol deteriorate the health does not
improve it.
(b) True/ False:
1. True
2. False: Alcoholism decreases the life span by 10
to 15 years.
3. True
(c) Fill-Ups:
1. C2HsOH (ethyl alcohol)
2. Alcohol
PART: B SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. List the four harmful effects of alcohol?
2. Why is that once a person start taking alcohol it
is difficult to get rid of this
habit?
3. Do you think that friend can influence one to
take alcohol?
PART: C LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Explain the preventive measure to control alcohol
addiction?
A98
Drugs are technically medicines or substances used
internally or externally for the
purpose of diagnosis, prevention or cure of
diseases.Drugs are normally used as medicines to help the patients but when
drugs are
taken for purpose other than their normal clinical
use in an amount that impairs one’s physical, physiological and psychological
functions it constitutes DRUG ABUSE.A person who takes a drug for non-medical
use is called DRUG ABUSER and drugs are called ADDICTIVE DRUGS.
Based on the effect on the body, drugs
are mainly of two types:-
1. PSYCHOTROPIC DRUGS
2. PSYCHEDELIC DRUGS or HALLUCINOGENS
1.PSYCHOTROPIC DRUGS:
These are mood altering drugs which selectively affect behavior, perception and
mental activity of a person. These include Sedatives or antidepressents,
Tranquillisers or antidepressents with soothing or calming effects, Opioids or
narcotics and Stimulants or exciters.
Most common among these are:
These drugs derived from OPIUM plant. These drugs relieve pains, acting on Central Nervous System. Opioids bind to specific opioid receptors present in our central nervous system and gastrointestinal tracts. They are also called pain killer.
Opium is latex obtained from unripe fruits of poppy plant (Papaver somniferum). It
is reddish brown in color having bitter taste. It is
eaten or smoked.Opium has many derivatives as following:
1. Morphine: -It is active alkaloid of opium. It is
strong analgesic. It has sedative
and calming effect. It causes addiction. It is used
in patient who has undergone surgery.
2. Heroin: -it is semi-synthetic crystalline powdery
substance obtained by acetylation of morphine. Chemically it is known as Di
Acetyl Morphine having formula, Ci7Hi7(OC2H30)-ON. It is highly addictive and
dangerous. Heroin is taken, orally, inhaled or injected. Heroin is depressant
and slow down body functions.
3. Smack:-It is crude by- product of heroin
synthesis and is commonly called “brown
sugar’. Being cheap, it is considered “poor man’s
heroin”. Smack is stronger analgesic than morphine.
B) RG | is natural coca alkaloid. Obtained from
leaves of coca.A South American plant, growing on the foot hill. Cocaine is
commonly called coke or crack. It is bitter, white crystalline powder. Cocaine
has vaso constriction properties and therefore is a good anesthetic. It is
powerful CNS stimulant.Excessive dosage of cocaine causes Hallucination.
C) RT hey are synthetic drugs. They are commonly
called PEP pills, Anti-Sleep drugs or Superman Drugs. They are CNS stimulant.
They bring about increased activity and alertness
real.
2. PSYCHEDELIC DRUGS or HALLUCINOGENS:
Psychedelic drugs change one’s behavior, thoughts,
feelings and perceptions without actual sensory stimulus.Hallucinations are
sensory experiences that appear real but are created byyour mind. They can
affect all five of your senses. For example, you might
hear a voice that no one else in the room can hear
or see an image that isn't.
Common HALLUCINIGENS are as under:-
I) LSD (LYSERGIC ACID DIETHYLAMIDE):-
It is most powerful psychedelic drug. It is in
crystalline form obtained from
ERGOT, an extract got from fruiting body of fungus
Claviceps purpurea.It is always smoked. LSD cause horrible dream emotional
outburst,hallucination.
ll) CANNABINOIDS (PRODUCTS OF HEMP
PLANTS)
Hallucinogenic chemicals obtained from leaves, resin
and inflorescence of
hemp plants, cannabis sativa are called
cannabinoids, and these are generally
four types:
a) BHANG :- Itis fresh/dried leaves of both male and
female plant of Cannabis sativa.
b) GANJA: - It is dried unfertilized female
inflorescence.
c) CHARAS/HASHISH: - It is dried resinous extract
from flowering top of plant.
d) MARIJUANA: - This is obtained from dried flowers
and top leaves of female
plant.
lll) DATURA & BELLADONA:- Seeds of Daturas
tramonium and aerial parts of Atropa belladonna are misused for their
hallucinogenic properties due to
presence of anticholinergic alkaloids.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
PART:A_ VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
i) Multiple choice questions: -
1. Opium is obtained from
a) Theasinensis
b) Coffeaarebica
c) Oryza sativa
d) Papaversomnefera
2. Marijuana, ganja and LSD are
a) Narcotics
b) Hallucinogens
c) Stimulants
d) Medicine.
3. LSD is obtained from:
a) Cannabis
b) Claviceps
c) Fusarium
d) Nostoc
4. Hemp yields:
a) Bhang
b) Charas
c) Ganja
d) All of above
5. Cocaine is derived from
a) Eythroxylon coca
b) Coffeaorbica
c) Theasinesis
d) Connabis sativa
(ii) True/ False
1. Cocaine is most powerful stimulant.
2. Nicotine is narcotic.
3. LSD is hallucinogen.
(iii) Fill in the blanks
1 Morphine is obtained from ................. Plant.
2 Marijuana obtained from dried flower of
.................. plant.
ANSWER KEY: PART-A
(a) Multiple choice questions:
1 (d) Papaver somniferum a plant which produce a
latex called opium.
2 (b) Hallucinogens this chemical produces effect
when a person consumes these drugs.
3 (b) Claviceps is an ergot fungus from which LSD
obtained.
4(d) All products like bhang, charas, ganja are
obtained from hemp plant.
5 (a) Erythroxylum coca a native plant of South
America produces cocaine.
(b) True/ False:
1. True
2. False; Opioids are narcotics. Nicotine is habit
forming constituent of
Tobacco.
3. True
(c) Fill-Ups:
1. Opium Poppy Plant
2. Female Hemp Plant
PART: B SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. Name the plant source of drug popularly called
heroin. How does it affect body?
2. What is cocaine? What is the adverse effect?
3. what are cannabinoids? Name different types of c
cannabinoids?
PART: C LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. Explain opioids and the derivatives how they act
on the body of drug
abuser?
A99
INTRODUCTION
ADDICTION AND DEPENDENCE
ADDICTION is a psychological attachment to certain
effects . such as euphoria
and a temporary feeling of well-being associated with
drugs and alcohol.
With repeated use of drugs, the tolerance level of
the receptors present in our body
increases and consequently the receptors respond
only to higher doses of drugs or
alcohol leading to greater intake and
addiction.DEPENDENCE is the tendency of the body to manifest a characteristic
and
unpleasant withdrawal syndrome if regular dose of
drugs/alcohol is abruptly
discontinued. Withdrawal syndrome is characterized
by anxiety, shakiness, nausea
and sweating.
ADOLESCENCE AND DRUG/ALCOHOL ABUSE:
Adolescence means both ‘a period’ and ‘a process’
during which a child becomes
mature in terms of his/her attitudes and beliefs for
effective participation in society.12-18 years of age may be thought of as
adolescence period.
Adolescence is accompanied by several biological and
behavioral changes.Curiosity, need for adventure and excitement, and
experimentation, constitute common causes, which motivate youngsters towards
drug and alcohol use.
EFFECTS, PREVENTION AND CONTROL OF
DRUG/ALCOHOL ABUSE:IMMEDIATE EFFECTS are:
Reckless behavior, vandalism and violence.
Excessive doses of drugs may lead to coma and death
due to respiratory failure, heart failure or cerebral hemorrhage.
Those who take drugs intravenously can get infected
with AIDS, hepatitis B.
The chronic use of drugs and alcohol damages nervous
system and cause liver cirrhosis.
The use of drugs and alcohol during pregnancy is
also known to adversely affect the fetus.
Use of anabolic steroids in females can cause
masculinization, increased aggressiveness, mood swings, depression, abnormal
menstrual cycles.excessive hair growth on the face and body. enlargement of
clitoris.deepening of voice.
In males anabolic steroids can cause acne, increased
aggressiveness, mood swings, depression, reduction of size of the testicles,
decreased sperm production, potential for kidney and liver dysfunction, breast
enlargement,premature baldness, enlargement of the prostate gland.
PREVENTION AND CONTROL:
The measures useful for prevention and control of
alcohol and drugs abuse
among adolescents:
Avoid undue peer pressure on children.
Children should be educated and counseled to bear
problems and stress in life.
The child should seek help from parents and elders.
Affected individuals should seek medical help of
qualified psychologists,psychiatrists, and deaddiction and rehabilitation
programs.
LET US KNOW WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT!
PART: A VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
QUESTIONS:
l. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
1. With repeated use of drugs, the
tolerance level of the receptors present in our body:
a. Increases
b. Remains same
c. Decreases
d. None of the above
2. Excessive doses of drugs may lead to
coma and death due to:
a. Respiratory failure
b. Heart failure
c. Cerebral hemorrhage
d. All of the above
3. Which factor is responsible for liver
cirrhosis?
a. Sugar
b. Alcoholism
c. Fats and oil
d. Vitamins
4. Withdrawal syndrome is characterized by:
a. Shakiness
b. Sweating
c. Anxiety
d. All of the above
5. Drug addiction is psychological
attachment to certain effects such as:
a. Euphoria
b. Temporary feeling
c. Both A and B
d. None of the above
ll. FILL IN THE BLANKS:
1. Excessive use of alcohol causes
2. Persons taking drugs intravenously can be
infected with
lll. TRUE/FALSE:
1. The use of drugs and alcohol during pregnancy
affects the fetus.
2. Avoid undue peer pressure on children.
3. Withdrawal syndrome develops if regular dose of
drugs is continued.
ANSWER KEY: PART-A
I. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
1. a. increases- With repeated use of drugs, the
tolerance level of drugs increases
2. d. All of the above- Excessive doses of drugs
leads to failure of all the vital
organs.
3. b. Alcoholism- Excessive intake of alcohol causes
fatty liver which is called liver cirrhosis.
4. d. All of the above- Withdrawal syndrome is
characterized by anxiety,sweating and shakiness.
5. c. Both A and B- Drug addiction causes euphoria
(feeling of extreme happiness) and temporary feeling.
ll. FILL IN THE BLANKS:
1. Liver cirrhosis- Excessive use of alcohol causes
fatty liver which is called
liver cirrhosis.
2. AIDS & Hepatitis B- Sharing of injection,
needles between two individuals
can cause AIDS and Hepatitis B.
lil. TRUE/FALSE:
1. True
2. True
3. False- Withdrawal syndrome develops if regular
dose of drugs is discontinued.
PART B- SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. What is withdrawal syndrome?
2. What are the side effects of anabolic steroids in
males?
PART C- LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
1. What motivates the youngsters to take alcohol or
drugs and how can this is avoided?
A100
INTRODUCTION
Dear students we have completed the chapter 08-
Human Health & Disease very thoroughly in the Daily Dose assignments from
83 to 99.
Now Let Us Solve NCERT Questions of this chapter.
1. What are the various public health measures,
which you would suggest as safeguard against infectious diseases?
Answer:Public health measures which should be taken
to safeguard against infectious
diseases are:
(i) Maintenance of personal and public hygiene: It
is one of the most important methods for prevention of various infectious
diseases. This measure consists of maintaining a hygienic body, taking of
healthy and nutritious food,drinking clean water, etc. In public hygiene there
is proper disposal of garbage, excreta, periodic cleaning of society, and
cleaning of water reservoirs.
(ii) isolation: To prevent the spread of air-borne
infectious diseases like
pneumonia, chicken pox, tuberculosis, etc., it is an
essential measure to keep the
infected person in isolation with others to reduce
the chances of spreading these
infectious diseases.
(iii) Vaccination: Vaccination is the protection of
the body from communicable
diseases by injecting some agent that makes copy of
the microbe inside the body. It
helps in providing passive immunity to the body.
Several vaccines are available
against many diseases such as tetanus, polio,
measles, mumps, etc.
(iv) Vector Eradication: Various diseases such as
malaria, filariasis, dengue, and
chikungunya spread through vectors. Thus, these
diseases can be prevented by
providing a clean environment and by the prevention
of breeding of mosquitoes. This
can be achieved by not allowing water to stagnate
around public areas. Also,
measures like periodic cleaning of coolers, use of
mosquito nets and spreading of
insecticides in drains, ponds, etc. can be
undertaken to ensure a healthy
environment. Introducing fish such as Gambusia in
ponds also controls the breeding
of mosquito larvae in still water against diseases.
2. In which way has the study of biology
helped us to control infectious
diseases?
Answer:Various advancements that have occurred in
the field of biology have helped us gain a better understanding to fight
against various infectious diseases.
Biology has developed as we have come to know about
the life cycle of various parasites, pathogens, and vectors along with the
modes of transmission of various diseases and the measures for controlling
them.
Vaccination programmes against several infectious
diseases such as small pox,
chicken pox, tuberculosis, etc. have helps us to
eradicate these diseases.
Biotechnology has helped in the preparation of
developed and safe drugs and vaccines.
Antibiotics have also played a major role in the
treatment of various infectious
diseases.
3. How does the transmission of each of the
following diseases take place?
(a) Amoebiasis (b) Malaria (c) Ascariasis
(d) Pneumonia
Answer:(a) Amoebiasis: It is a vector transmitted
disease that spreads by the means of contaminated food and water. The vector
involved in the transmission of this disease
is the housefly. Its mode of transmission is
Entamoeba histolytica.
(b) Malaria: It is a vector transmitted disease that
spreads by the biting of the
female Anopheles mosquito. Its mode of transmission
is Plasmodium protozoan.
(c) Ascariasis: It spreads through contaminated food
and water. Its mode of
transmission is Ascaris lumbricoides.
(d) Pneumonia: It spreads by the sputum of a
diseased person. Its mode of
transmission is Streptococcus pneumonia.
4. What measure would you take to prevent
water-borne diseases?
Answer:Water-borne diseases such as cholera,
typhoid, hepatitis B, etc. spread by drinking
contaminated water.
These water-borme diseases can be prevented by
proper disposal of garbage,excreta, regular cleaning.
Spraying insecticide in community water reservoirs,
boiling drinking water, etc.
5. Discuss with your teacher, what does ‘a
suitable gene’ means, in the context of DNA vaccines.
Answer:A suitable gene of specific DNA segment when
inserted in the body of host to
produce specific type of protein which gives passive
immunity to the organism and
helps to fight with foreign organism.
6. Name the primary and secondary lymphoid
organs.
Answer:(i) Primary lymphoid organs include the
Thymus and Bone Marrow.
(ii) Secondary lymphoid organs are the Spleen, lymph
nodes, Tonsils, Peyer's
patches of small intestine, and Appendix.
7. The following are some well-known
abbreviations, which have been used in this chapter. Expand each one to its
full form:
(a)MALT (b)CMI (c)AIDS (d)NACO = (e) HIV
Answer:
(a) MALT- Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue
(b) CMI- Cell-Mediated Immunity
(c) AIDS- Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome
(d) NACO- National AIDS Control Organization
(e) HIV- Human Immune Deficiency virus
8. Differentiate the following and give
examples of each:
(a) Innate and acquired immunity (b) Active
and passive immunity
Answer:(a) INNATE AND ACQUIRED IMMUNITY:
10. What are the various routes by which transmission
of human immuno-deficiency virus takes place?
Answer:AIDS (Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome) is
caused by the Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).This is transmitted by
following modes -
(a) Unprotected sexual contact with a diseased
person.
(b) Transfusion of blood to a healthy from a
diseased person.
(c) Sharing infected needles or syringes.
(d) Infected mother to a child through the placental
connection.
11. What is the mechanism by which the AiDS
virus causes deficiency of
immune system of the infected person?
Answer:AIDS (Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome) is
caused by the Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) via sexual or blood to blood
contact.
After entering the human body, the HIV virus attacks
and enters into the macrophages. Inside the macrophages, the RNA of the virus
replicates with the help of enzyme reverse transcriptase and gives rise to
viral DNA copy.
Then, this viral DNA incorporates into the host DNA
and directs the synthesis of
virus particles. - At the same time, HIV enters
helper T- lymphocytes. It replicates
and produces viral progeny.
These newly formed progeny viruses get released into
the blood, attacking other
healthy helper T-lymphocytes in the body.
As aresult, the number of T-lymphocytes in the body
of an infected person decreases in number, which causes decrease in immunity of
person.
12. How is a cancerous cell different from
a normal cell?
Answer:
13. Explain what is meant by metastasis?
Answer:The property of metastasis is performed by
malignant tumors. These malignant cells move through different part of body by
a pathological process. These cells divide uncontrollably, forming a mass of
cells called tumor. From the tumor, some cells get shed off and enter into the
blood stream. From the blood stream, these cells reach distant parts of the
body and therefore, start the formation of new tumors by dividing actively.
14. List the harmful effects caused by
alcohol/drug abuse.
Answer:HARMFUL EFFECTS CAUSED BY ALCOHOL ABUSE ARE -
(i) Alcohol generates more energy mosily in the form
of heat, but at the same time,
it dilates the blood vessels. Consequently the ‘heat
generated is rapidly lost. Due
to constant dilation, the arterial walls soon become
brittle & rigid. Such a change in
the property of blood vessels & deposition of
alcoholic fat affect the working of heart.
(ii) Alcoholism leads to gastric ulcers &
gastritis.
(iii) In chronic alcoholism, the axon of the nerve
inflames thus causing neuritis.
(iv) Permanent damage to liver cells occur due to
deposition of fats.The liver dries up & harden (CIRRHOSIS).
HARMFUL EFFECTS CAUSED BY DRUG ABUSE
ARE —
(i) Excessive doses of drugs may lead to coma &
death due to respiratory failure,heart failure & cerebral hemorrhage.
(ii) Lack of interest in personal hygiene,
withdrawal, isolation, depression, fatigue
aggressive & rebellious behavior etc.
(iii) Acquire serious infections like AIDS &
HEPATITIS B, who take drugs intravenously.
(iv)The adverse effects of drugs are manifested in
the form of reckless behaviour,
vandalism & violence.
15. Do you think that friends can influence
one to take alcohol/drugs? If yes, how may one protect himself/herself from
such an influence?
Answer:Yes, friends can influence one to take drugs.
Following measures can be taken:
(i) Avoiding undue peer pressure.
(ii)Not taking undue pressure of failures beyond its
threshold.
(iii) Getting counseling from some counselor.
(iv) Seeking help from parents and peers.
(v) Seeking medical help.
16. Why is that once a person starts taking
alcohol or drugs, it is difficult to get rid of this habit? Discuss it with
your teacher.
Answer:Psychological & physiological dependence
of an individual to the intake of certain kinds of drugs and alcohol is called
addiction. Once a person starts taking alcohol & drugs, it is very
difficult to get rid this habit because addiction drive people to take them
even when these are not needed or even when their use becomes self-
destructive. With repeated use of drugs, the
tolerance level of the receptors present
in the body increases, consequently, the receptors
responds only to higher doses of
drugs or alcohol leading to greater intake &
addiction. Thus, the addiction potential of
drugs & alcohol, pull the user into a vicious
circle leading to their regular use (abuse)
from which he/she may not able to get out.
17. In your view what motivates youngsters
to take to alcohol or drugs and how can this be avoided?
Answer:Human have probably been using mind —
affecting drugs since time immemorial. The
root cause of addiction of man to drugs, smoking and
drinking has been due to his
inability to make mental adjustments with stresses
and strains, drudgery and
extreme misery in daily life. As a temporary
measure, to combat these adverse situations and to have a certain degree of
mental relaxation, humans have been making an extensive use of stimulants,
depressants and hallucinogens. Stimulants generally speed up body process, and
depressants slow them. Hallucinogens can alter a person's thoughts, feelings.
and perception.In preventing drug abuse, the role of parents could be:
1. Communicate openly with the children,
2. Listen to their problems patiently and teach them
how to handle the problems.
3. Take interest in children’s activities and their
friends circle.
4. Set an example for children by not taking drugs
or alcohol.
5. Keep track of prescribed drugs in home.
6. Learn as much as possible about drugs.
A101
INTRODUCTION
Dear students we have discussed the whole chapter
no. 08 “HUMAN HEALTH AND DISEASES’ and its NCERT questions in Daily Dose
Assignments from 83 to 100.Now let us revise the common terms and important
concepts:
1. NON-SPECIFIC DEFENSE MECHANISM:
Non-specific defenses are the body's first line of
defense against diseases. They are
not directed against a particular pathogen.
Non-specific defenses guard against all
infections, regardless of their cause. It is also
called as innate immunity. Plants and
many lower animals rely only on innate immunity and
do not possess the second
category of specific defense mechanisms. Nonspecific
defense mechanisms work
against a wide variety of invaders. Innate immunity
consists of various types of
barriers that prevent entry of pathogens into the
body.
2. SPECIFIC DEFENSE MECHANISM
Specific defense mechanism is the ability of the
body to develop immunity against
specific pathogens, toxins, or foreign things. This
is possible by a special immune
system that produces antibodies and/or activated
lymphocytes that attack and
destroy specific invading organisms or toxins.
3. ANTIBODY STRUCTURE
Antibodies are immune system-related proteins called
immunoglobulins. Each
antibody consists of four polypeptides— two heavy
chains and two light chains joined
to form a "Y" shaped molecule.
4. ANTIGEN ANTIBODY REACTION
Antigen-antibody interaction, or antigen-antibody
reaction, is a specific chemical
interaction between antibodies produced by B cells
of the white blood cells and antigens during immune reaction. The antigens and
antibodies combine by a process called aggiutination. It is the fundamental
reaction in the body by which the body is protected from complex foreign
molecules, such as pathogens and their chemical toxins. In the blood, the
antigens are specifically and with high affinity bound by antibodies to form an
antigen-antibody complex. The immune complex is then transported to cellular
systems where it can be destroyed or deactivated.
5. VACCINATION AND IMMUNIZATION
Vaccination is the process of introduction of
vaccines into the body to produce
antibodies against the antigens to neutralize the
effect of pathogens during actual
infection.Vaccines are the dead or weakened pathogens introduced into the body.The dead or weakened pathogen leads to the production of antibodies which neutralizes the pathogenic agents during actual infection with the same pathogen.
Immunization is the process where performed
antibodies against the toxin are introduced into the body.
Example- performed antibody injection against snake
venom.Using recombinant DNA technology antigenic polypeptides of pathogens in
bacteria or yeast.
Example- hepatitis B vaccine produced from yeast.
6. LYMPHOID ORGANS
The organs where origin and/or maturation and
proliferation of lymphocytes occur
are called lymphoid organs.
Lymphoid organs are of two types-
1. Primary lymphoid organs
2. Secondary lymphoid organs.
The primary lymphoid organs are bone marrow and
thymus where immature lymphocytes differentiate into antigen-sensitive
lymphocytes.The bone marrow is the main lymphoid organ where all blood cells
including lymphocytes are produced.
The thymus is a lobed organ located near the heart
and beneath the breastbone.Spleen, tonsil, lymph node, Peyer’s patches of small
intestine and appendix are secondary lymphoid organs where proliferation of
lymphocytes take place.The secondary lymphoid organs provide the sites for
interaction of lymphocytes with the antigen, which then proliferate to become
effector cells.
The spleen is a large bean shaped organ mainly
contains lymphocytes and
phagocytes which acts as a filter of the blood by
trapping blood-bornemicroorganisms and has a large reservoir of erythrocytes.
The lymph nodes are small solid structures located
at different points along the
lymphatic system.Lymph nodes serve to trap the antigens and these antigens trapped are responsible for the activation of lymphocytes and cause the immune response.
Lymphoid tissue is located within the
lining of the respiratory, digestive and urogenital tracts.
Lymphoid tissues are also called mucosalassociated
lymphoid tissue (MALT) which constitutes about 50 per cent ofthe lymphoid
tissue in human body.
7. DISORDERS OF IMMUNITY:
Some of the common disorders caused by a poor immune system include:
Allergic diseases — These are the diseases which
have symptoms which include
hay fever, sinus disease, asthma, hives, dermatitis
and eczema.
Autoimmune diseases — These include multiple
sclerosis, autoimmune thyroid disease, type 1 diabetes, systemic lupus
erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis and systemic vasculitis.
There are immunodeficiencies, which are inherited
from a parent to the child. These
conditions include primary immunodeficiency diseases
such as x-linked severe
combined immunodeficiency (SCID), complement
deficiencies, common variable
immunodeficiency (CVID), etc
8. CANCER:Cancer is the uncontrolled cell division leading to the formation of a mass of cells called as a tumor.
Contact inhibition is the property of normal cells by virtue
of which contact with other cells inhibits their uncontrolled growth.Cancer
cells lost the property of contact inhibition and because of this, cancerous
cells continue to divide giving rise to masses of cells called tumors.
Tumors are of two types: benign and malignant.
Benign tumors normally remain confined to their
original location and do not spread
to other parts of the body.The malignant tumors are
a mass of proliferating cells called neoplastic or tumor cells.Malignant tumors
grow very rapidly and invade and ultimately damage surrounding tissues.
The property by which cancer cells moves to distant
places from their origin by blood and invade the normal cells and make them
cancerous is called as metastasis
9. ADDICTION:
Addiction
is a psychological attachment to certain effects -such as euphoria and a
temporary feeling of well-being — associated with drugs and alcohol.
10. ALCOHOL ADDICTION
A chronic disease characterized by uncontrolled drinking and preoccupation with
alcohol.Alcoholism is the inability to control drinking due to both a physical
and emotional dependence on alcohol.
Symptoms include repeated alcohol consumption
despite related legal and health issues. Those with alcoholism may begin each
day with a drink, feel guilty about their drinking and have the desire to cut
down on the amount of drinking.
11. DRUGS:The
drugs which are commonly abused are opioids, cannabinoids and coca
alkaloids.
OPOIDS-Opioids are the drugs which bind to specific
opioid receptors present in our central nervous system and gastrointestinal
tract.
Heroin commonly called smack is chemically diacetylmorphine
which is a white,odourless, bitter crystalline compound and is obtained by
acetylation of morphine extracted from the latex of poppy plant Papaver
somniferum. Heroin is a
depressant and slows down body functions.
CANNABINOIDS:Cannabinoids interact with cannabinoid
receptors present principally in the brain.Natural cannabinoids are obtained
from the inflorescences of the plant Cannabis
sativa.
The flower tops, leaves and the resin of cannabis
plant are used in various
combinations to produce marijuana, hashish, charas
and ganja effects on cardiovascular system of the body.
COCA ALKALOID:Coca alkaloid or cocaine is obtained
from coca plant Erythroxylum coca.
Coca alkaloid interferes with the transport of the
neuro-transmitterdopamine.Cocaine, commonly called as coke or crack .It has a
potent stimulating action oncentral nervous system, producing a sense of
euphoriaand increased energy.Excessive dosage of cocainecauses hallucinations.
TOBACCO: Tobacco conatins nicotine, an
alkaloid.Nicotine stimulates adrenal gland to release adrenaline and
nor-adrenaline into
blood circulation, both of which raise blood
pressure and increase heart rate.Smoking of tobacco is associated with
increased incidence of cancers of lung,urinary bladder, throat, oral cavity,
bronchitis, emphysema, coronary heart disease, gastric ulcer etc.
12. DRUG ADDICTION:With repeated use of drugs, the
tolerance level of the receptors present in our body increases and consequently
the receptors respond only to higher doses of drugs or alcohol leading to
greater intake and addiction.Dependence is the tendency of the body to manifest
a characteristic and unpleasant withdrawal syndrome if regular dose of
drugs/alcohol is abruptly discontinued.
Withdrawal syndrome is characterised by anxiety,
shakiness, nausea and sweating.
NOW LET US TEST OUR KNOWLEDGE!!!
1. Name the diagnostic test which confirms
typhoid.
Ans. V\idal test
2. Name the two major groups of cells
required to attain specific immunity.
Ans. B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes.
3. You have heard of many incidences of
Chickengunya in our country. Name the vector of the disease.
Ans. Aedes mosquitoes.
4. Breast fed babies are more immune to
diseases than the bottle-fed babies.Why?
Ans. The mother’s milk consists of antibodies (lg A)
such antibodies are not available to bottle fed babies.
5. Name the pathogen which causes malignant
malaria.
Ans. Plasmodium falciparum.
6. Which microorganism is used to produce
hepatitis B Vaccine?
Ans. Yeast.
7. What is the reason of shivering in
malarial patient?
Ans. After sparozoite infection, wnen RBC ruptures,
a toxic substance haemozoin is
released which cause chilling and high fever.
8. When is a tumour refered to as
malignant?
Ans. A tumour is said to be malignant when grows
rapidly, invade & damage the
surrounding normal tissues.
9. Why does an AIDS patient suffer from
many infections?
Ans. Because in AIDS patient, immune system greatly
weakens & cannot fight against any infection.
10. Name two curable sexually transmitted
diseases?
Ans. Gonorhoea & Syphilli
11. Name the type of cells that produce
antibodies?
Ans. B — lymphocytes.
12. Give the scientific name of causative
germ of elephantiasis?
Ans. WuchereriaBancrofti.
13. Name the fish that help in eradication
of mosquito larvae.
Ans. Gambusia
1. Where are B-cells and T-cells formed?
How do they differ from each other?
Ans. B-cells and T-cells are formed in bone marrow.
B-cells produce antibodies but E-cells do not produce antibodies but help
B-cells to produce them.
2. Given below are the pathogens and the
diseases caused by them. Which out of these pairs is not correct matching pair
and why?
(a) Wuchereria- Filariasis
(b) Microsporum- Ringworm
(c) Salmonella - Common Cold
(d) Plasmodium — Malaria
Ans. Salmonella : Common cold is not a matching
pair.
3. What would happen to the immune system,
if thymus gland is removed from the body of a person?
Ans. T-lymphocytes are developed and matured in
thymus gland, Immune system will become weak on removal of thymus gland.
4. Lymph nodes are secondary lymphoid
orgAns. Describe the role of lymph nodes in our immune response.
Ans. Lymph nodes provide the sites for interaction
of lymphocytes with the antigen.
When the microorganisms enter the lymph nodes,
lymphocytes present there are
activated and cause the immune response.
5. What is the role of histamine in
inflammatory response? Name few drugs
which reduce the symptoms of allergy.
Ans. Histamine acts as allergy-mediator which cause
blood vessels to dilate. It is
released by mast cells. Antihistamine steroids and
adrenaline quickly reduce the
symptoms of allergy.
6. What do you mean withdrawal Symptoms?
What are its characteristics?
Ans. Withdrawal symptoms refers to the
characteristic unpleasant symptoms by
body of a drug addict if regular dose of drug is
abruptly discontinued. These include
anxiety, shakiness, sweating, restlessness,
depression, muscular cramps etc.
7. Differentiate between two different
types of tumours?
Ans.
8. Differentiate between active &
passive immunity?
9. Enumerate the two properties of cancer
cells that distinguish them from
normal cell.
Ans. i) uncontrolled proliferation of cells without
any differentiation
ii) Ability of these cells to invade other tissues
called metastasis.
10. What are allergens? How do they cause
inflammatory response inside human body?
Ans. The substance which causes the hypersensitive
reaction of the immune system
is called an allergeneg. dust, pollen grains etc.
These allergens are actually weak
antigens. First exposure to allergen does not cause
allergy but consequent
exposure, allergen combines with Ig E on mast cell.
That causes cells to burst &
release Histamines which cause inflammatory
response.
11. What are autoimmune diseases? Give two
examples?
Ans. Immunity is based on ability to differentiate
foreign organism from self cells.Sometimes immune system may go off the track
& turns against self antigen and
elicit immunity. Such conditions are called auto —
immune diseases eg. Rneumatoid
arthritis, Myasthenia gravis.
12. What are Cannabinoids? From which plant
Cannabinoids are obtained?Which part of the body is affected by consuming these
substances?
Ans. Cannabinoids are a group of chemicals which
interact with Cannabinoid
receptors present
Principally in the brain Cannabinoids are obtained
from the inflorescences of the
plant Cannabis sativa.
The substances affect the cardiovascular system
adversely
13. In the figure, structure of an antibody
molecule is shown. Observe it and Give the answer of the following questions.
(i) Label the parts A, B and C.
(ii) Which cells produce these chemicals?
(iii) State the function of these molecules.
Ans. (a) A-Antigen binding site B-Light chain
(b) B-lymphocytes.
(c) Heavy Chain
(d) Antibodies provide acquired immune response.
14. Mention any three causes of drug abuse.
Suggest some measures for the prevention and control of drug abuse.
Ans. Reasons to attract towards drug abuse:
Curiosity, peer pressure, escape from
frustration and failure, family problems, false
belief of enhanced performance.
Preventive measures:
Avoid undue peer pressure
Education and Counselling
Seeking help from parents and peers.
Looking for danger signs
Seeking professional and medical help
15. A person shows unwelcome immunogenic
reactions while exposed to certain substances.
(a) Name this condition.
(b) What common term is given to the substances
responsible for this
condition?
(c) Name the cells and the chemical substances
released which cause such
reactions.
Ans. (a) Allergy
(b) Allergens
(c) Mast Cells — Histamine, Serotonin
1. A nitrogen fixing microbe associated
with the fern Azolla in rice fields is
(a) Frankia
(b) Rhizobium
(c) Spirulina
(d) Anabaena
Ans: (d) Anabaena
2. Azolla pinnata has been found to be an
important biofertiliser for paddy
crops. This quality is due to the presence
of
(a) N2 fixing bacteria
(b) N2 fixing cyanobacteria
(c) mycorrhizae
(d) all of these
Ans: (b) N2 fixing cyanobacteria
3. Which of the following is widely used as
a successful biofertiliser in
Indian rice field?
(a) Rhizobium
(b) Acacia arabica
(c) Acalypha indica
(d) Azolla pinnata
Ans: (d) Azolla pinnata
4. Which of the following options includes
biofertilizers?
(a) cow dung manure and farmyard waste
(b) A quick growing crop ploughed back into the
field
(c) Nostoc, Oscillatoria
(d) All of these
Ans: (c) Nostoc, Oscillatoria
5. Which of the following is a
non-symbiotic biofertilizer?
(a) VAM
(b) Azotobacter
(c) Anabaena
(d) Rhizobium
Ans: (b) Azotobacter
6. Nitrogen fixation in root nodules of
Alnus is brought about by
(a) Frankia
(b) Azorhizobium
(c) Bradyrhizobium
(d) Clostridium
Ans: (a) Frankia
1. Lactate fermentation does not give off CO2. True
2. High biological oxygen demand in a water body
means Water is not polluted. False
3. The guts of various ruminants contain
Acidophiles. False
4. Aspergillus microbes are used for the commercial
production of citric
acid. True
5. Saccharomyces cerevisiae is used primarily for
Baking. True
Fill in the blanks in the different columns
of the table given below to identify the no. 1 to 6
Ans. (i) Alveoli filled with fluid, reduced
breathing, fever, chills, cough and headache.
(ii) Salmonella typhi
(iii) Common Cold
(iv) Internal bleeding, muscular pain, anaemia,
fever and blockage of the intestinal
passage.
(v) Microsporum species/Trichophyton
species/Epidermophyton Species.
(vi) Amoebiasis/Amoebic dysentery
1. In the given flow diagram, the replication of
retrovirus in a host cell is
shown. Examine it and answer the following questions
(a) Why is virus called reterovirus?
(b) Fill in (1) and (2)
(c) Can infected cell survie while viruses are being
replicated and released by
host cell?
2. What is innate immunity? List the four types of
barriers which protect the body from the entry of the foreign agents.
3. How does humoral immune system works when our
body is infected?
4. It was diagnosed by a specialist that the immune
System of the body of a patient has been suppressed. Describe the infection
& the mechanism of its proliferation in the body.
5.(i) Differentiate between communicable & non —
communicable diseases?
(ii) Name the body part & the host in which
following events takes place in life
cycle of plasmodium.
(a) fertilization
(b) Development of Gametophyte
(c) Release of sporozoites
(d) Asexual Reproduction