Chapter 1st (Office Automation and Typing)
CHAPTER NO.1 OFFICE AUTOMATION &
TYPING
INTRODUCTION
Office automation refers to the integration of
office functions usually related to managing information. Raw data storage,
electronic data transfer and the management of electronic
business information comprise the basic activities
of an office automation system. It involves using computers and software to
digitize, store, process and communicate most routine tasks
and processes in a standard office. Most common and
user friendly software and tools in offices are word processors and electronic
spread sheets.
1.1 WORD PROCESSOR
A word processor is a software that allows users to
create, edit and print documents. It enables us to write text, store it
electronically, display it on a screen, modify it by entering
commands and characters from the keyboard and print
it.
1.1.1 MS Word
In previous classes, we have already studied about
various features of MS Word such as creating, editing and formatting a
document, inserting tables, pictures, used the feature of mail merge, spell-
check and thesaurus etc. and also leamt to create a resume document. Microsoft
Word can be used for the following purposes:
To create business documents having various graphics
including pictures, charts, and diagrams.
To store and reuse readymade content and formatted
elements such as cover pages and sidebars.
To create letterheads for personal and business
purpose.
To design different documents such as resumes or
invitation cards etc.
Microsoft Word allows us to create
professional-quality documents, reports, letters and resumes. Unlike a plain
text editor, Microsoft Word has features including spell check, grammar
check, text and font formatting, HTML support, image
support, advanced page layout and many more settings.
1.2 DOCUMENT WRITING AND EDITING IN MS
WORD
Editing a word file is one of the most basic MS
office word operations. Editing a word file means making changes in the text
contained in the existing document. Everyone needs to edit a word document at
some point or other to incorporate the changes which may arise from time to
time.
Editing a Word Document covers these basic concepts:
Adding new text : To add text in a document, place
the cursor at the required portion and start typing.
Deleting a part of the text : Select the text that
you want to delete and just press the Del/Backspace key from the keyboard.
Copy-Paste a text : Select the text that you want to
copy and then use Copy (Ctrl+C) and Paste (Ctrl+V) commands.
Moving text : Select the text that you want to move
and then use Cut (Ctrl+X) and Paste (Ctrl+V) commands to move the text.
Formatting text : Formatting refers to changing the
font style, size(Ctrl+[ and Ctrl+)), color, bold (Ctrl+B), italic (Ctrl+I),
underline (Ctt+U) and other related parameters. We can also use Format Painter
option available at Home tab to apply existing formats to other text. To clear
the existing formats on the text, we can also
use the Clear Format (Ctrl+Space) option available
at the Home tab ribbon.
Alignment : Alignment determines the appearance and
orientation of the edges of the text of paragraph. There are four types of
paragraph alignment you can set within Word: Left (Ctrl+L), Center (Ctrl+E),
Right (Ctrl+R) and Justify (Ctrl+J).
Lime Spacing : It is the space between each line in
a paragraph. Word allow you to customize the line spacing to be single spaced
(Ctrl+1), double spaced (Ctrl+2), one and half line spaced (Ctrl+5) or any
other amount you want.
Bullets and Numbering : These options are used to
make bulleted (Ctrl+Shift+L) and numbered lists in the documents.
1.3 WORKING WITH FONTS
A font is a graphical representation of text that
may include different typeface, point, size or color. We can change the font of
text in a document using different ways:
1.3.1 Change the Font
Click the Font drop down Menu in Font Group of Home
tab and Select the desired Font.
1.3.2 Change the Default Font Settings
Go to Home, and then select the Font Dialog Box
Launcher or use keyboard shortcut key CtrlsShift+F or Ctrl+D to open the Font
dialog box:
Wecan set the font, font style (normal, bold, italic
etc.) and font size using this dialog box as shown in the figure.
Font Color : We can change the color of the font as
per our requirement.
To change the color of text:
Select the text you want to change.
Click the downward-pointing arrow on the Font Color
button on the Formatting
toolbar. A color palette appears.
Click the color you want to apply.
Word changes the color of your text.
Underline Style : MSWord contain multiple types of
Underline's styles. For changing it, select the text and under Home tab from
Font group, open Underline options and select one.
Underline Color : Click Underline Color to change
its color, you can pick one from a color palette.
Effects ; There are other options as well, like
strikethrough, Double strikethrough,superscript, subscript, shadow, outline,
small caps, All caps and hidden. Thus, this was all about basic editing in a
word file.
After changing settings as per our requirement, we
can also set them as default setting of the document. To do this, clickon set
ss Defaut button. Select one of the following:
This document only.
All documents based on the Normal template.
Now Select OK twice.
1.4 PROOFING
Word can also proofread cur document to highlight
other bage tor: words) «2D
possible problems, such as misplaced commas or
correctly spelled words that may be used incorrectly. To make word — _Freefing
icon proofread our document,
follow these
steps: Fig. 13
Click the Proofing icon at the bottom of the
document window. Word highlights a possible error and displays a pop-up menu
offering options similar to the options displayed and then choose one of the
following:
1.4.1 Auto Correct
To reach the Auto Correct options, click on File, then Options. When the Word Options window pops up, choose Proofing in the sidebar.You can now click the " Auto Correct Options”button. We will now see a list of words that will be identified and replaced with a different term.
Add entry to an Auto Correct list:
1. Go to the AutoCorrect tab.
2. In the Replace box, type a word or
phrase that you often misspell.
3. With in the box, type the correct
spelling of the word.
4. Select Add.
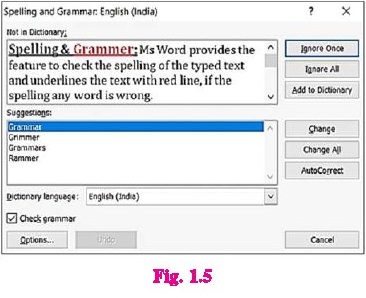
1.4.2 Spelling & Grammar
MS Word provides the feature to check the spelling
& grammatical errors, It shows red wavy underline for spelling errors and
the green wavy underline for grammatical errors.The latest wavy underline
introduced in Word is blue, which shows formatting inconsistencies.
To start a check of the spelling and grammar in our
file just press F7 (Spelling & Grammar checker) or follow these steps:
1, Click the Review tab on the ribbon.
2. Click Spelling or Spelling &
Grammar.
(a) If the program finds spelling
mistakes, a dialog box appears with the first
misspelled word found by the spelling checker.
(b) After you decide how to resolve the misspelling
(ignoring it, adding it to the program's dictionary, or changing it), the
program moves to the next misspelled word,
1.5 FIND AND REPLACE
Find and Replace feature in Ms- Word
helps us to find words or formats in a document and allow us to replace all instances of a word or format. This is particularly handy in long documents. We can use the following steps for this purpose:
1. Click on Replace option in the Editing Group of
Home tab or press Ctrl+H.
2. Enter the word or phrase you want to locate in
the Find box.
3. Enter your new text in the Replace box.
4, Select Find Next until we come to the word we
want to update and then Choose Replace. To update all instances at once, choose
Replace All.
1.6 PAGE SETUP (=,
Page Setup allows us to change the structure and
layout of pages in a document. The "Page Setup" group on the “Page
Layout" tab contains buftons that allows us to make changes in the
page setup of document. We can also open the “Page
Setup" dialog box by clicking on the dialog box launcher (present in the
lower right corner) of the “Page Setup" group of “Page
Layout" tab. This dialog box consists of three
tabs: Margins, Paper and Layout.
1.6.1 Margins
A margin is the space between the text and the edge
of our document. By default, a new document's margins are set to Normal, which
means it has a one-inch space between the text
and each edge. Depending on our requirements,Word
allows us to change our document's margin size.
Steps to change page margins:
1. Click on the Margins tab in the Page
Setup Dialog box.
2. Set the Top, Bottom, Left and Right
margins as per our requirement.
3. Click OK.
1.6.2 Orientation
Page Orientation refers to the direction in which a
document is displayed.Steps to Change Page Orientation:
1. Click on the Margins tab in the Page Setup Dialog
box.
2. Set the page orientation - Portrait or Landscape
as per requirement.
3. Click OK.
1.6.3 Paper Size
We can set the paper size of our document using this
option. Paper size can be of Letter Size, A4 Size, and Legal Size etc. The
default
paper size in Microsoft Word is 8.5 x 11 inches -the
standard size (called Letter size)To change the page size:
1. Click on the Paper tab in the Page
Setup Dialog box.
2. Select the Paper size, For example:
A4é, from the drop down menu.
3. Click OK.
1.7 PAGE BORDERS
MS- Word allows us to put a page border around the
text in our document. We can also adc a border to either all the pages in our
document or certain pages in our document.To add a page border, put the cursor
at the beginning of our document or at the beginning of an existing section in
our document. Then, click the "Design" tab.
In the Page Background group, click the Page Borders
option.
In the Borders and Shading dialog box, click the
Page Border tab.
Select the page border Setting as per requirement.
Select the Style of border we want on the page, which can be solid,dotted, or dashed.
Select the Color and Width of the border. If we want to select art work to use as the border, click the down arrow for the Art drop-down menu.
By default, the borders are applied to the whole document, which means
every page has the same border. By clicking the down arrow on Apply to
gives us the option to select the first page only,
selected page, all pages except the first page, and other options.
After setting the page border options, click on the
OK button.
1.8 PRINT PREVIEW & PRINT
Print preview is a feature that displays on the
screen what a hard copy would look like when printed. Steps to preview our
document are:
1. Click on the File tab.
2. When we click the Print (Ctrl+P) option, it will
automatically show the preview of our document.
3. Now select printing options such as number of
copies, page range, collate etc.
4. Now, click on the Print button to get the
hardcopy of our document.
1.9 MS EXCEL-SPREADSHEET SOFTWARE
Microsoft Excel is a powerful electronic spreadsheet
program used to create results, doing mathematical calculations and
representing data in pictorial view with the help of charts. We can use it to
automate accounting work, organize data, and perform a wide variety of
tasks.Excel is designed to perform calculations, analyse information, and
visualize data in a
spreadsheet. Also, this application includes
database and charting features.
1.10 FORMULA BAR
Formula Bar is one of the most important components in MS Excel. The Formula Bar is the area at the top of the Excel window, just below the ribbon area or the Formatting toolbar.The Formula Bar has two parts: Name Box at the left and right side are the contents of the currently selected cell as shown below
The formula bar gets activated as soon as you type an
equal sign in any cell or click anywhere within the bar. The formula bar
displays formulas located in cells rather than the forroula results. The
formula bar can also be used to edit formulas or other data located in the
active cell by clicking on the data in the formula bar with the cursor. It can
also be used to
modify the ranges for individual data series that
are selected in an Excel chart.
1.11 WORKING WITH FORMULAS
Microsoft Excel is an electronic spread sheet that
automates the calculations involved in School result, Grading & Students
Fee etc. Formula always starts with = sign. Excel can perform the mathematical
calculations for you. You will learn how to create formulas and
functions to perform calculations in a spread
sheet.Example formulas are:
= D15+D18+D21, = B4-B12, = A10/B15, = (B16+C16)*1.07
When creating formulas, we may choose to either type
the cell address or use the mouse to select the cell address.
1.11.1 Mathematical Operators for Formulas We can
create any type of mathematical calculation on our own using the following
mathematical operators:
1.11.2 Basic steps for creating a
formula
1. Click in the empty cell which will contain the
formula.
2. Type an equal sign (=).
3. Type the cell address or click the cell that
contains the first number.
4. Type the math operator (+ - / * 4).
5. Type the cell address or click the cell that
contains the second number.
6. Continue in this manner until the formula is
complete.
7. Use parenthesis for clarification.
8. Press the Enter key.
1.11.3 Manual Formula
We can make manual entries for mathematical formula
by typing
the numbers, cell reference and mathematical
fimction in the spread
sheet cell, as shown in the given figure.
1.12 WORKING WITH FUNCTIONS
A Function provides an automated method for creating
formulas. A function is a predefined formula that performs calculations using
specific values in a particular order. Excel includes
many common functions that can be used to quickly
find the sum, average, count, maximum value, and minimum value for a range of
cells.
1.12.1 Steps for using a function
1. Select an empty cell.
2. Type an equal sign = and then type a function.
For example, =SUM for getting the total
3. Type an opening parenthesis i.e.
4. Select the range of cells, and then type a
closing parenthesis i.e. )
5. Press Enter to get the result.
1.12.2 AutoSum >
Addition is the most common math operation performed
in Excel. The Home ribbonincludes an AutoSum button for adding. This button
provides a shortcut way for typing SUM function in the current cell.
1.12.3 Commonly Used Functions
Now, let's discuss some commonly used functions:
1.12.3.1 SUM : The Excel SUM function returns the
sum of values supplied. The SUM function adds values. You can add individual values,
cell references or ranges or a mix of all three.
Syntax:=SUM (number! , [number2], [number3], ...)
Arguments:
number! - The first value to sum
number2 - [optional] The second value to sum
number3 - [optional] The third value to sum
For example;
It will add the values in cells Al to Cl (A1:C1) and
show 93
1,123.2 COUNT : The COUNT function counts the number
of cells that contain numbers
and counts numbers within the list of arguments. Use
the COUNT function to get the number of entries in a number field that is in a
range or array of numbers.Syntax:
=COUNT (valuel, [value2], ...)
Arguments:
valuel - An item, cell reference, or range
value2 - [optional] An item, cell reference, or
range
For example:
It will count the numbers in the range A1:C1 and
show 3
L12.3.3 MAX :
The Excel MAX function retums the largest numeric value in a range of values.
The MAX function ignores empty cells, the logical values TRUE and FALSE, and
text values.
Syntax:=MAX (number! , [number2}, ...)
Arguments:
number1 - Number, reference to numeric value, or
range that contains numeric
values
gumber?2 - [optional] Number, reference to numeric
value, or range that contains numeric values
For example:
It will display the largest number in the range
Al:C1, Le. 56
L.12.3.4 MIN :
The Excel MIN function returns the smallest numeric value in a range of values.
The MIN function ignores empty cells, the logical values TRUE and FALSE, and
textvalues.
Syntax:
=MIN (numberl, {number2], ...)
Arguments:
gumber!l - Number, reference to numeric value, or
range that contains numeric
values number? - [optional] Number, reference to
numeric value, or range that contains numeric values
For example:
It will display the smallest number in
the range A1:C1, ie. 12
1.12.3.5 AVERAGE :
The Excel AVERAGE function retums the average of values provided.AVERAGE can
handle up to 255 individual arguments, which can include numbers, cell
references, range, atrays and constants.
Syntax:=AVERAGE (number! , [number2],
...)Arguments:number1 - A number or cell reference that refers to numeric
values number2 - [optional] A number or cell reference that refers to numeric
values For example:
It will display the average value of the numbers in
the range Al:C1_ , ic. 31
1.12.3.6 NOW : The Excel NOW function returns the current date and time, updated continuously when a worksheet is changed or opened. The NOW function takes no arguments.You can format the value returned by NOW as a date or as a date with time by applying a number format.
Syntax/Example:
It will display the current date and time.
1,12.3.7 TODAY :
The Excel TODAY function returns the current date, updated continuously when a
worksheet is changed or opened. The TODAY function takes no arguments.
You can format the value returned by TODAY using any
standard date format. If you need current date and time, use the NOW function
It will display the current date only.
1.12.3.8 CONCATENATE : The CONCATENATE
function in Excel is designed to join
different pieces of text together or combine values
from several cells into one cell.
Syntax:
CONCATENATE(textl , [text2], ...)
Arguments:
text - The first text value to join together
text2 - The second text value to join together
For Example:
It will display the text Hello Students after
combining text of cells Al and B1
1.12.3.9 UPPER : The Excel UPPER
function returns a upper-case version of a given text string. Numbers and
punctuation are not affected.
Syntax:=UPPER (text)
Argument:text - The text that to convert to upper
case.
For Example:
It will display the text HELLO in capital letters.
L.12.3.10 PROPER :
The Excel PROPER function capitalizes the first letter of each word in the
given text/string. Numbers and punctuation are not affected.Syntax:=PROPER
(text)
Argument:text - The text that should be converted to
proper case.
For Example:It will display the text Hello Students
in which first letter of each word is written in capital letter,
Relational Operators for Conditional/Logical Functions
When we are constructing a test condition for
conditional functions like IF, SUMIF,COUNTIF etc. we can use any one of the
following relational operators in excel:
1.12,3.11 IF :;
We use an IF statement to ask Excel to test a condition and to return one value
if the condition is true, and another value if condition is false. For
example:=IF(A1>=33,"Pass","Fail"). This function will
show Pass if the value of cell Al is greater than or equals to 33 otherwise it
will show Fail. More than one condition can be tested by nesting IF functions.
The IF function can be combined with logical functions like AND and
OR.Syntax:=IF (criteria, value if true, [value if false])
Arguments:criteria - A value or logical expression
that can be evaluated as TRUE or FALSE.
value if true The value to return when criteria
cvaluates to TRUE
value_if_false - [optional] The value to return when
criteria evaluates to FALSE.
1.12.3.12 SUMIF :
SUMIF is the function used to sum the values according to a single criterion.
Using this function, we can find the sum of numbers that meet certain criteria
within a range. This function comes under Math & Trigonometry
functions.Syntax:
=SUMIF (range, criteria, [sum_range])
Arguments:range - the range of cells to be evaluated
by our criteria, required.
criteria - the condition that must be met,
required.sum_range-[optional] the cells to sum if the condition is met
L12.3.13 COUNTIF :
COUNTIF is another powerful and useful condition function that can be used in
excel. This function is used to count cells that meet certain criteria. COUNTIF
can be used to count cells with dates, numbers, and
text that meet specific criteria.Syntax:=COUNTIF (range,
criteria)Arguments:range - The range of cells to count.criteria - The criteria
that controls which cells should be counted.Following Example shows the usage
of conditional functions IF, SUMIF and COUNTIF:
1.13
BORDER AND SHADING
Border and Shading is used to differentiate various
areas of the spreadsheet. Borders can be applied to one cell or a range of
cells or entire spreadsheet. Use the Borders button, on the Home ribbon to
apply border
styles. Also, the Fill Colour button will add or
remove colour/shading for a cell or range.
1.14 CUSTOM FILTER
If our worksheet contains a lot of content, it can
be difficult to find information quickly. Filters can be used to narrow down
the data in our worksheet, allowing us to view only the information we need.
1. Select the Data tab, then click the Filter
command, A drop-down arrow will appear in the header cell for each column.
2. Click the drop-down arrow for the column we want
to filter, for example: Subject.
3. The Filter menu will appear.
4. The Custom AutoFilter dialog box will appear.
5. Select Filter Criteria and type its value (e.g.
Math).
6. The data will be filtered by the selected text
filter as shown in the following figure.
1.15 CUSTOM SORT
Sorting refers to the operation of arranging sets of
data in some specific order. Sorting of data can be in ascending or descending
order. It may be applied on alphabetic and numeric
values. Following steps can be used to sort data in
Excel:
1. Select the data we want to be sorted.
2. Click the Data tab and then the Sort button.
3. In the Sort box click Custom List under Order.
4. In the List entries box, enter how you want the
data to be sorted. For example, we've sorted Name (Cohumn B) and then by Father
name (Column C) in A-Z sort order,
5. Once completed entering the data into List
entries then click Ok.
1.16 FREEZE PANES
Whenever we are working with a lot of data in Excel,
it can be difficult to compare information in our workbook. Fortunately, Excel
includes several tools that make it easier to view content from different parts
of our workbook at the same time, such as the ability to freeze panes.
To keep an area of a worksheet visible while we scroll to another area of the worksheet, go to the View tab, where we can Freeze Panes to lock specific rows and columns in place, or we can Split panes to create separate windows of the same worksheet.When we freeze panes, Microsoft Excel keeps specific rows or columns visible when we scroll in the worksheet. For example, if the first row in our spreadsheet contains headers, we might freeze that row to make sure that the column headers remain visible as we scroll down in our spreadsheet.
1.17 PAGE SETUP AND PRINTING OPTIONS
When viewing our workbook in Excel, page setup can make a world of difference. Excel gives us lots of options for setting up our page. The Page Setup group of the Page Layout tab contains the following important command buttons in Excel:
Margins : It can be used to select one of three
pre-set margins for the report or to set custom margins on the
Margins tab of the Page Setup dialog box.
Orientation : It is used to switch between Portrait
and Landscape mode for printing.
Size : It is used to select one
of the pre-set paper sizes, set
a custom size or change the printing resolution or
page number on the Page tab of the Page Setup dialog box.
Print Area ; It is used to set and clear the print
area.
Breaks ; It is used to insert or remove page breaks.
Background : It is used to open the Sheet Background
dialog box where we can select a new graphic image or photo to use as a
background for the current worksheet.(This button changes to Delete Background
as soon as we select a background image.)
Print Titles ; It is used to open the Sheet tab of
the Page Setup dialog box where you can define rows of the worksheet to repeat
at the top and columns of the worksheet to repeat at the left as print titles
for the report.
1.18 FILE CONVERSION
File conversion is the process of
converting a file into another type. For example,
transferring a file used in Microsoft Word to PDF or WordPerfect
or PDF to Excel or Word.We can also
convert our .docx or .xls file to PDF here are some
steps to make our file to PDF as below:
How to convert an Excel file to a PDF:
1. Open Microsoft Excel file.
2, Click on File then Save as.
3. Type Desired File name.
4, Change Save As type to PDF.
5. Click on Save.
There are many good websites
available to convert various types of
documents online.
1.19 TYPING TECHNIQUE
Typing is the process of writing or inputting text
by pressing keys on a typewriter,computer keyboard, cell phone, or calculator.
Text can be in the form of letters, numbers and
other symbols. User interface features such as spell
checker and auto complete serve to facilitate and speed up typing and to
prevent or correct errors the typist may make.
1.19.1 Touch Typing
Touch typing is a technique by which we can learn
typing with all fingers, step by step, without having to look down at the
keyboard. It will increase the typing speed. Any typing-tutor software can be
used for learning this technique.
1.19.2 Voice Typing
Voice Typing is a type of speech recognition program
that converts speech to written language. Voice-to-text technique was
originally developed as an assistive technology for the
visually impaired or handicapped persons. The
speech-to-text converter is speech recognition software by which the software
takes user's speech
as input and converts this speech input to text.
1.20 FONT CONVERSION TOOLS
Sometimes we are asked to prepare our document using
a specific font, but we do not know how to type in that particular font. In
such situations, we can use these converters. For
example, we are asked to prepare our document using
Raavi font and we are not familiar with the key-map of Raavi font. But, we are
familiar with Anmol Lipi Key-map. In such a case, font
converter tool, such as G-Lipi-CA, helps us to type
in Raavi font by using key-map of AnmolLipi font. Following are some examples
of such font conversion methods/tools.
AnmolLipi to Raavi (Unicode Conversion)
G-Lipi-CA (http://gurmukhifontconverter.com/)
Punjabi Gurmukhi Keyboard
(https://punjabi-gurmukhi-keyboard-based-on-anmoll.
software.informer.com/download/)
280
1. <A word processor is software that allows
users to create, edit, and print documents.
2. Formatting refers to changing the font style,
size, color, bold, italic, underline and other related parameters.
3. Alignment determines the appearance and
orientation of the edges of the text of paragraph.
4. MS Word provides the feature to check the
spelling of the typed text and underlines the text with red line, if the
spelling of any word is wrong.
5. Page Setup allows us to change the structure and
layout of pages in a Microsoft Word document.
6. Amargin is the space between the text and the
edge of your document.
7. Page Orientation refers to the direction in which
a document is displayed.
8. Print preview is a feature that displays on the
screen what a hard copy would look like when printed.
9. Microsoft Excel is a powerful electronic
spreadsheet program used to create results,doing mathematical calculations and
representing data in pictorial view with help of charts.
10. A function is a predefined formula that performs
calculations using specific values in a particular order.
LL. Filters can be used to narrow down the data in
your worksheet, allowing you to view only the information you need.
12. Touch typing is a technique by which we can
learn typing with all fingers, step by step,without having to look down at the
keyboard.
13. Voice Typing is a type of speech recognition
program that converts speech to written language.
Part-A
1. Multiple Choice Questions:
1 is word processor software.
a. MS Window
b. MS Excel
c. MS PowerPoint
d. MS Word
2. Te check spelling and grammar key is
used.
a. Col+F7
b. Alt+F7
c. F7
d. Shift F7
3. _____ option in MS-word changes the
structure and layout of pages.
a. Format
b. ‘Print and Print Preview
c. Page Setup
d. Proofing
4. _____ is electronic spread sheet
software used for automated calculations.
a. MS Window
b= MS Excel
c. MS PowerPoint
d. MS Word
5. refers to changing the font style, size,
color, bold, italic, underline
and other related parameters.
a. Formatting
b. Alignment
c. Proofing
d. Filtering
2. Fill in the Blanks:
1 __ and functions are used to find the minimum and
maximum value in range.
2. ‘Filter option is available in___ tab of Excel.
3. If the cursor is placed at the end of the file,
then button is
pressed to delete the text.
4. Two options of orientations for page setup are
and
5. ___ Symbol is used to start any formula
(function) in excel calculations.
3. Very Short Answer Type Questions:
1. Write the full form of WYSIWYG.
2. Write the Shortcut keys to move text in Word
Document.
3. Write the name of four types of alignments.
4. Which Excel function is used to combine contents
from different cells into one cell?
5. Write the name of any two fonts that can be used
to type in Punjabi Language.
Part-B
4. Short Auswer Type Questions. (Write
the answers in 4-5 lines)
1. What is Excel?
2. Eaxplain
formatting in details.
3. Explain Print & Print Preview options.
4. What are formulas in MS Excel?
5. What do you know about the formula bar in Excel?
6 What are Margins?
Part-C
5. Long Answer Type Questions. (Write
the answers in 10-15 lines)
1, What are word processors? Explain their uses.
2. Describe the Proofing options in MS Word.
3. Explain the Page Setup and Printing Options
available in Excel.
4, What are functions in Excel? Explain any two
functions with example.
5. Explain the various methods of Typing.
WaDycrn ity om Create Resume in MS Word for job and
also prepare following task.
Correct the mistakes (if shown in document) with the
help of Spelling and Grammar Check.
Set the Page Border.
Save your Resume as PDF file.
Tal Activity.Prepare Result in MS Excel as given
below:Now do as following:
Set Border of cells.
Calculate Total, Percentage and Result with the help
of formulas and functions.
Sort the student data in increasing order according
to "Name of Student’ column.
Filter the data of ‘Section A’ students using Filter
option.
Save the file in PDF format.