CHAPTER NO.8
IMAGE EDITING & FILE CONVERSION TOOLS
8.1
INTRODUCTION
In present time, we capture lots of images using
mobile & digital camera and often we need to edit them by resizing
(increasing or decreasing the dimensions), colour correction,
adjusting the brightness and contrast levels, crop,
rotate, flip to make a better image. This whole process of making changes &
corrections is known as image editing or retouching. To
achieve this, we use special software in computer
known as Image Editing Software. This software enables us to produce images of
Professional Quality.
8.2 POPULAR IMAGE EDITING
TOOLS/SOFTWARE
For image editing, several softwares are available
in market. By using these softwares, we can easily edit images. Some popular
softwares are:
Adobe Photoshop
Corel Draw Graphics Suite
MS Office Picture Manager
GIMP (GNU Image Manipulation Program)
All above mentioned softwares are similar in nature,
if we learn one of these then with little effort we can learn any other image
editing software.
Adobe Photoshop is very popular image editing
software and is widely used as compared to other image editing softwares but
it's not free, we need to purchase it. Adobe Company offers different plans of
monthly or yearly subscription.
8.2.1 GIMP (GNU Image Manipulation
Program)
This is very popular free software for image
editing. We can download it freely from www.gimp.org and then we can install it
on our computer system.
8.2.L.1 ; GIMP Features:
1, It can be used as simple Paint
program.
2. It can be used as professional
software for image editing.
3. A scripting language can be used in
it, te accomplish complex tasks.
4. It can be used as image convertor and format of
image can also be changed.
5. It can open multiple images at one time.
6. It is cross platform (Windows/Linux/Mac) software
means it can be installed and used on different operating systems.
7. It is open source software.
8.2.1.2 : GIMP supports these popular
image formats:
1, _.gif (Graphics Interchange Format)
2. pug (Portable Network Graphics)
3. __ .tif (Tagged Image File Format)
4, jpeg (Joint Photographic Expert Group)
5. .psd (Photoshop Document)
6. .bmp @itmap Picture)
7. _ .xcf ( eXperimental Computing Facility)
8.2.1.3 GIMP Preferences :
In GIMP we can change all settings as per our requirements like System
Resources, Image Import & Export, Tools Options, Interface (Icon, Theme,
Toolbox),
Image Windows & Folders.
8.3 WORKING WITH IMAGE EDITOR - GIMP
8.3.1 Creating a new image
For creating a new image, click File > New or use
shortcut key CTRL+N.
"Create a New Image" dialog box like shown
in Figure 8.4 will open, in which values for width and height can be
entered.For more advanced settings, click on Advanced options.Note ; Canvas is
that important area of Window where new image or open image is displayed and
can be edited.
8.3.2 Opening an image for editing
To open an existing image, click on File > Open or use shortcut key CTRL+O or double click in working area of main interface of GIMP.An open dialog box will appear. Select the image to edit and click open.
It is recommended to create a duplicate copy of the original image before editing to avoid unwanted changes to the original image. For creating duplicate image, click Image > Duplicate or use shortcut CTRL+D key.
8.3.3 Saving an image
After editing an image, it can be saved by clicking
File > Save or use shortcut key CTRL+S.Whenever image is to be saved with
new name, click File > Save As or use shortcut key CTRL+SHIFT+S.
Save Image Dialog box gives us option to choose
location to save our image and also provides us facility to create a new folder
as well.GIMP uses its default file extension .xcf to save an image.
8.3.4 Export As
GIMP provides the facility "Export As” to save
images into different file formats. If image is to be saved in other formats
like jpg, png, gif, tif etc. then use File > Export As or use
shortcut key SHIFT+CTRL+E.To choose different file
formats click on "Select File Type" and GIMP will show us
different file formats. We can select the desired
file format to save image in that particular format.
8.3.5 Image Properties
It is essential that user must be aware of image
properties before editing an image. To view image properties, click on
Image> Properties or use shortcut key ALT+ENTER. Image properties
like size in pixels, print size, resolution, file
name, location, file size, file type etc, are shown in
image properties dialog window (Fig. 8.8).
8.3.6 Auto Correct
Auto correct means, to automatically
correct an image, GIMP will try to change colour
settings of an image automatically. To use this feature on menu bar, click
Colors >Auto. There are few options available further
which can be changed as per need.
Eqnalize : This will make brightness level of every
pixel equal.
White Balance : This command is useful for images in which white or black color is not displayed correctly.
Stretch Contrast : This command further increases the brightness of brighter colors and it makes the darker colors more darker. This will also remove any tint present in an
image.
Note : Tint means to mix white color in any color.
Color Enhance : This command corrects colors by
enhancing color intensity
which leads to better looking image.
8.3.7 Brightness and Contrast
Click Colors> Brightness-Contrast to
adjust the brightness and contrast of the image It
is a simple tool that handles bright and dark colors alike while advanced
versions of this tool are "Levels and Curves" that handle bright and
dark colors separately, which can finely enhance the look of the picture.
On image with holding down left mouse
button and dragging it from top to bottom
(vertically) brightness can be increased and doing the same from left to right
(Horizontal)vertices of the image, can increase contrast.To apply these
settings, press the Enter key on the keyboard.Sliders can also be used to
decrease or increase brightness and contrast. The previously used settings in
the Presets option are automatically saved which we can reuse later.
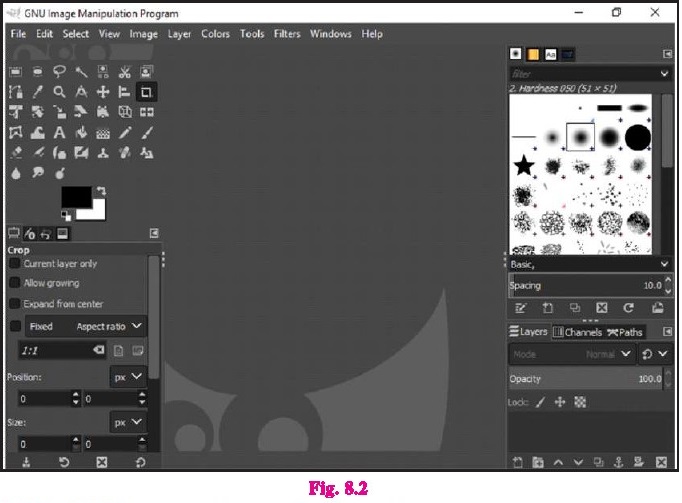
8.3.8 Crop Settings
Cropping a picture means cutting off unnecessary
sections of the image from the corners.To use this tool, click on Tools >
Transform Tools > Crop or click on the crop tool icon from the toolbox or
use shortcut key SHIFT + C.
A box will appear on the picture, its four corners
can be used to reduce or increase the cropping area.
After setting the correct area, press the Enter key
from the keyboard. Image will be cropped.
8.3.9 Rotate and Flip Settings
Rotate tool, is used to rotate a picture at a
certain angle.To use it, click on Tools> Transform Tools > Rotate or
click on the Rotate tool icon in the toolbox to select this tool then click on
the picture or use SHIFT + R.
Use the slider to rotate the image or we can even
enter the angle value directly.
If we want to change the position of the image we
can enter the value in Center X and Center Y. In the end, click the Rotate
button. (see fig 8.14)
Click the Reset button to undo the changes.
8.3.10 Flip
The flip means changing the side of the picture. This tool can flip the image vertically or horizontally, or both. To use it, click on Tools > Transform Tools > Flip or click the icon of flip tool in the toolbox to select this tool then click on the picture to flip.
8.3.11 Resize
Sometimes we need to change the size of the image,
i.e. to increase or decrease the Width or Height of the image. Changing the
image dimensions is called resizing. Click on Image >Scale Image to resize
the image.
Adjust Width and Height of image with any unit such
as px, percentage, centimetres,metres, inches, feet etc.
8.3.12 Aspect Ratio (Resolution)
This means proportional relationships such as 1:1,
4:3, 16:9, etc. of the image's width and height. Generally GIMP resizes the
image as per Aspect Ratio of the image itself, meaning that
if we change the height, the width will
automatically change and if we change the width, the value of the height will
change automatically. Aspect Ratio has to be unlocked if we want to set
both of these values independently. So click on the
chain icon so that it appears in two sections.Clicking on this icon again will
lock the picture's Aspect ratio setting.
Interpolation : GIMP resizes images using pixel
based technique. Let's learn about its types:
Linear : With this resize technique the pixel color
is set to the nearest 4-pixel average color. Sometimes this technique is also
called BiLinear. This technique can be used to quickly resize an image and the
quality does not deteriorate much while
Cubic : With this resizing technique the pixel color
is set to the nearest 8-pixel average color. Sometimes this technique is also
called BiCubic. This technique takes a bit longer to resize the image and
improves the quality of the resized image.Usually this technique is used to
resize the picture.
NoHalo : We can also try this technique if we want
to enlarge the normal picture at higher resolution.
LoHalo : If text or text-like objects are present in
the picture, this technique will produce better results.
8.3.13 Compression Settings
If the image has taken up too much space on the hard
disk, we can compress the picture.
Compressing a picture does not mean changing its dimensions. During resizing the width and
height of the image will be reduced or enlarged while compressing the image will decrease its
size (hard disk space) or altering the quality of an
image.
If we want to use the image for a web site, we
should reduce its size on disk so that web page gets loaded easily duc to its
small size. But it should be taken care that the quality of
image is not destroyed. For this, use Export As and
set the size and quality of the image as needed using Quality Slider.
Click File > Export As to compress the image
Click on the "Select File Type" (Extension) option to compress the
image in a particular format and select the Format / Extension and click on the
Export button. (fig 8.17)
Depending on the selected format, GIMP will display
a separate dialog box such as JPG (fig 8.18) or PNG (fig 8.19):
Use the Quality or Compression level slider to compress the image or enter a
8.4 WORKING WITH IMAGE LAYERS
Layers mean Stack of Slides. Layers are groups of
sheets that look out over one another.The picture can consist of more than one
layer and the number of Maximum Layers depends on the memory available in the
computer. If the computer is powerful and has a lot of memory, there may be as
many layers as we want in one picture. Hach Layer can
be edited separately from the rest of the Layers. Layers are set on top of each other and the bottom layer is the background of the image. Layers can be easily set to be on the foreground or back of the other layers. Layers can also be grouped as needed.
Layers are managed by the Layers Dialog Box. The
Duplicate Layer Tool helps to create duplicate copies of Active layers.
8.4.1 Layer Properties Each layer has
some important properties such as:
Name : Each layer has a name. It can be
customized by double click or right click.
(ii)Presence or absence of alpha channel : The alpha
channel confirms how transparent the layer is to each pixel. White completely
reflects opacity. Black fully demonstrates
transparency. Grey level represents partial
transparencies.
(i) Layer Type : Layer type depends on the presence
or absence of Image Type and alpha channels.RGB e RGBA e Gray
GrayA ° Indexed ° IndexedA
(iv) ‘Filter Menn : The filters in the Filter Menu
only support few layer types. If we want to apply a filter but that filter is
disabled, it means it cannot be selected then the type of the layer needs to be
changed to use that filter.
(v) ‘Visibility : We can tum the layer's visibility
on / off for the image to work properly.Changing this setting means only to
toggle the setting by which the layer is hidden
and not deleted. Visibility settings can be changed
by clicking on the eye icon in the Layers dialog box. If Shift + Click is used,
visibility setting of all the layers except the Active Layer can be turned off.
(vi) Active Layer : The layer that is being worked
on is called Active Layer. Usually the layer is activated by clicking on it. If
there are multiple layers, it becomes difficult for us to know which element
belongs to which layer. So if that part of the
picture is clicked by ALT +
Mouse-Wheel-Button-Pressed, the corresponding layer in the Layers dialog box is
automatically selected.
(vd) Opacity : With this setting we can set the
value of the opacity. It can be set from 0 to 100 scales. 0 means that the
layers below this layer will be fully visible. 100 means that this layer will
not be transparent at all and the layers below it will not be visible at all,
8.4.2 Adding Layer
There are several ways to add a layer.
Right click on the opened image, and then click on
the Layer Menu, We can add a new layer by choose any one of the following
options that appear in the submenu:
New Layer
New from Visible
Duplicate Layer
We can also create a new Layer with paste option
(CTRL + V or Edit Menu > Paste options) after using Cut/Copy a layer.
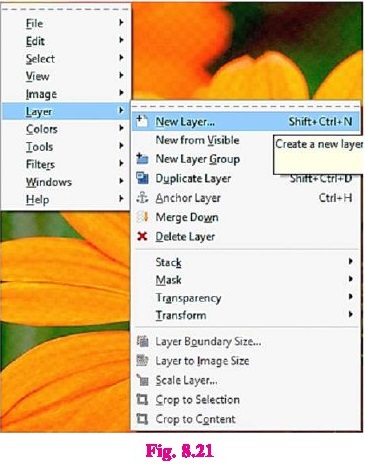
8.4.3 Deleting Layer
Right click on the layer to delete and click on
"Delete Layer", Another way is to drag and drop the layer that we
want to delete in the X icon in Layer Dialog Box (See Figure 8.20), the layer
will be deleted.
8.4.4 Merge Layers
Merge layers means making a single layer from
multiple layers. To do so use the CTRL+M shortcut key or click on the Image
Menu > Merge Visible Layers option.Flatten Image option in Image Menu also
merges all layers after removing Transparency.
Layer Merge Options:
Expanded as necessary : Sometimes a layer may be larger than the size of the picture so this option will increase the size of the image according to the larger layer.
Clipped to image : Sometimes a layer may be larger than the size of the picture so this option will cut the larger layer according to the size of the picture.
Clipped to bottom layer : This option clips and trims the remaining layers according to the size of the Bottom Layer.
8.4.5 Scaling a Layer
Scaling means changing the size of the layer. So use
the Layer Menu > Scale Layer option.Layer can be scaled by entering Width
and Height values as needed.The Cubic (Quality > Interpolation) method is
used to get the best results,
8.5 IMAGE EDITING TOOLS
GIMP provides many tools for working on images that can be used to perform
different tasks on images. If the mouse pointer (arrow) is held over a tool's icon for 2 seconds, the tool name, what the tool is used for, and the shortcut key will be displayed in tooltip. Let's learn some tools:
Selection Tools : These tools are used to select part of the active layer. Each selection tool has its own set of features.They can also be selected from the Tool Box.
Rectangle Select : This tool is used to select the part
of the layer in the rectangular shape.
Ellipse Select : This tool is used to select the
part of the layer in the elliptical shape.
Free Selection : This tool is also known as lasso
tool. This tool allows us to select a drawing note with a free hand. It is used
to select part of the image by drawing a picture with the help of a mouse
pointer,
Fuzzy Select : This tool is also known as the Magic
Wand tool. With this tool, the area is selected on the basis of “Similarity of
color". Usually the selections made with this tool are continuous, i.e.
connected parts.
By Color Select : This tool works similarly to the
Fuzzy (Magic Wand) tool, but any part of the picture that matches the color
similarity is selected.
Intelligent Scissors : This tool is used for
automatic selection where there is a contrast of color which means the two
parts are clearly separated. Clicking the mouse creates the Selection Nodes on
the edges of the area we want to select.
Eraser Tool : This tool is used to
delete the area of the active layer. If the image
has no alpha channel then this tool will erase the area with background color
If the image
has an alpha channel then this tool will erase the
area with transparent color and no color will be used.
Text Tool : This tool is used for
writing text on pictures. Use the Tools > Text
command to access this tool. This tool can also be activated by clicking on the
symbol A in the tool box.
When this tool is activated, a toolbar will appear
which allows us to use Bold, Italic,Underline, Strikethrough options.
To change the font, delete the font in the box and
start typing the name of the font we want to select, GIMP will start showing
the installed fonts in the computer through the Dropdown list from which we can
select the font.
Use CTRL + A to select all the text. The color box
can be used to change the color of the text. By Right clicking on text, we can
change the orientation of the text from given options.
(iv) Move Tool : This tool is used to
move the selections, i.e. textures, layers etc.To
use this tool, use the Tools > TransformTools > Move command or click on
the Move tool icon in the Tool Box.
If a layer is selected and we just want to move that
selection, use CTRL + ALT + Mouse Drag. The selected area will be moved and the
lower layer portion will appear instead,
(v) Align Tool : This tool is used to align layers
with image objects. To access this tool use the Tools > Transform Tools >
Align command or click on the Align tool icon in the Tool Box.For example, open
a picture and make a duplicate layer from the Layer Box (right click of the
layer> Duplicate Layer) and move it slightly and
left click on this duplicate layer. Now select
the Align tool. At the bottom left of the toolbox,
we will see some alignment tool options, click on any one we need and we will
get duplicate layer alignment.
(va) Scale Tool : This tool is used to scale layers
& objects. Use Tools > Transform Tools >Scale command or SHIFT + S to
use this tool.
Use File > Open As Layers, to open another image
as layer and it will open a new image as layer. Activate the Scale tool, we
will see a dialog box. We can scale the layer with the
mouse, to scale in Aspect Ratio hold down the Shift
button.
(vii) Blur / Sharpen Tool : This tool is used to
blur or sharpen any part or object of a picture. This tool uses a brush. This
tool enhances effect when repeatedly used in one place.The CTRL key is used to
toggle between Blur and Sharpen.
Use the Tools > Paint Tools > Blur / Sharpen
command to select this tool.
If any part or object is looking too strong, use
Blur to soften it. If we need to sharpen (increasing contrast) a part or
object, use Sharpen option.
(vidi) Bucket Fill Tool : This tool fills the foreground color in the selected area,if CTRL + Click is used then the tool will fill the background color.Using the ALT key will toggle the
foreground and background colors in this tool. Using
the Shift key will fill in the selected color all at once.
Use the Tools > Paint Tools > Bucket
Fill command to select this tool.
8.6 MASKING
Masking or mask means a new separate layer that is
created for another layer so that the opacity(transparency) of that layer can
be set. By using
layers, Masks hide some part of the main layer that
we want to edit. So the editing that will be done after
applying the mask will be applicable on only that
part of the main layer that is set by the mask.
Layer masks are different from opacity
sliders/settings.They allow us to work on different parts of the picture layer,
i.¢. the optional parts. Using a mask does not damage the main layer, when we
make changes.
8.6.1 Adding Layer Mask
It's very easy to add a layer mask, Right click on
the layer in the Layer box, now click on the option of
Add Layer Mask from the menu.
8.7 IMAGE FILE CONVERSION
There are several formats of pictures such as jpg,
.png, .gif, tif etc. Each format has its own specific properties and we can use
these formats as needed. Different Softwares can be used to convert one image
format to another, or we can convert pictures from one format to another using
specific websites available on the Internet. Generally, we can change the
format using the Save As option. After changing the format, the appearance of
the image does not only vary but its properties also change. Some formats are
good for using pictures on the Intemet,some for painting pictures, some for
viewing on computers or electronic devices or some for printing. In GIMP
software, we can also change the format of the pictures.
Some of the more popular free image
converter softwares are:
1, FastStone Image Viewer
2, FastStone Batch Resizer
3. Irfan View
4. XnConvert
1. Changes and modifications made as needed in an
image are called image editing or retouching.
2. Adobe Photoshop, Corel PaintShop Pro, MS Office
Picture Manager and GIMP are popular softwares for image editing.
3. GIMP's full name is the GNU Image Manipulation
Program.
4. Use CTRL +N or File > New to create a new
picture.
5. Double click with the mouse on the image window
or use CTRL + O or File > Open to open the image.
6. Todo image editing, always create a Duplicate
Image / Copy so that the original image does not change.
7, Cropping an image means eliminating unnecessary
sections at comers.
8. Use CTRL + Z to undo and CTRL + Y shortcut keys
to redo.
9. Exporting a picture means saving the image in
another format, while the Save or Save As option saves the image in a Native
format only.
10. Having a resolution of 300 ppi (pixel per inch)
gives the picture a good quality print.
11. GIMP saves the image in its original xcf format.
12. Usually the .jpeg (Joint Photographic Expert
Group) format is used for an image which is popular and widely used in the
world.
13. The quality of the image decreases when it is
scaled.
Part-A (Questions carrying 1 Mark each)
1. Multiple Choice Questions:
1 tool allows us to select a drawing with a
free hand.
a Fuzzy Selection
b. Lasso
c. Text
d. Bucket Fill
2 SHIFT + C is a shortcut for .
a. To Create Duplicate Image
b. To Delete Layer
c. To Copy of an image
d. To Crop an Image
3. Scale option is used to change the of an
image.
a, Color
b. Size
c. Area
d. All of the above
4. _____ sis: known ass group of sheets
looking at each other.
a. Masking
b. = Tools
c, Layers
d. None of the above
5. helps to make a duplicate copy of the
active layer
a. Smudge Tool
b. Dodge Tool
c. Perspective Tool
d. Duplicate Layer
2. Fill in the blanks:
1. To resize the layer tool is used.
2 To move the layers tool is used.
3. Teo remove objects from Canvas tool is used.
4. The quality of the picture decreases when the
picture is ,
5. An important part of the Image Window is
___.___———ss Where the picture is
shown,
Part-B (Questions carrying 3 marks)
3. Short Answer Type Questions. (Write
the answers in 4-5 lines)
1. What is Image Editing?
2 What are masks?
3. How can a duplicate image be made?
4. How image is opened in GIMP 7?
5. Enter full names: gif, png, tif, jpg, ped, bmp
Part-C (Questions carrying 5 marks)
4, Long Answer Type Questions. (Write
the answers in 10-15 lines)
1. Write down the names of any 4 tools of GIMP and
explain the usage.
2 How to resize a picture in GIMP?
3. What are Layers in GIMP?
4. How to create images for a website in GIMP?
5. What are Image Properties in GIMP?
aby xctwatys
Take a picture and perform the Image Editing
Operations explained in this chapter using any Image Editing Software
direct value and click on the Export Button.
8.4 WORKING WITH IMAGE LAYERS
Layers mean Stack of Slides. Layers are groups of
sheets that look out over one another.The picture can consist of more than one
layer and the number of Maximum Layers depends on the memory available in the
computer. If the computer is powerful and has a lot of memory, there may be as
many layers as we want in one picture. Hach Layer can
be edited separately from the rest of the Layers.
Layers are set on top of each other and the bottom layer is the
background of the image. Layers can be easily set to
be on the foreground or back of the other layers. Layers can
also be grouped as needed.
Layers are managed by the Layers Dialog Box. The
Duplicate Layer Tool helps to create duplicate copies of Active layers.
8.4.1 Layer Properties Each layer has
some important properties such as:
Name : Each layer has a name. It can be
customized by double click or right click.
(ii)Presence or absence of alpha channel : The alpha
channel confirms how transparent the layer is to each pixel. White completely
reflects opacity. Black fully demonstrates
transparency. Grey level represents partial
transparencies.
(i) Layer Type : Layer type depends on the presence
or absence of Image Type and alpha channels.RGB e RGBA e Gray
GrayA ° Indexed ° IndexedA
(iv) ‘Filter Menn : The filters in the Filter Menu
only support few layer types. If we want to apply a filter but that filter is
disabled, it means it cannot be selected then the type of the layer needs to be
changed to use that filter.
(v) ‘Visibility : We can tum the layer's visibility
on / off for the image to work properly.Changing this setting means only to
toggle the setting by which the layer is hidden
and not deleted. Visibility settings can be changed
by clicking on the eye icon in the Layers dialog box. If Shift + Click is used,
visibility setting of all the layers except the Active Layer can be turned off.
(vi) Active Layer : The layer that is being worked
on is called Active Layer. Usually the layer is activated by clicking on it. If
there are multiple layers, it becomes difficult for us to know which element
belongs to which layer. So if that part of the
picture is clicked by ALT +
Mouse-Wheel-Button-Pressed, the corresponding layer in the Layers dialog box is
automatically selected.
(vd) Opacity : With this setting we can set the
value of the opacity. It can be set from 0 to 100 scales. 0 means that the
layers below this layer will be fully visible. 100 means that this layer will
not be transparent at all and the layers below it will not be visible at all,
8.4.2 Adding Layer
There are several ways to add a layer.
Right click on the opened image, and then click on
the Layer Menu, We can add a new layer by choose any one of the following
options that appear in the submenu:
New Layer
New from Visible
Duplicate Layer
We can also create a new Layer with paste option
(CTRL + V or Edit Menu > Paste options) after using Cut/Copy a layer.
8.4.3 Deleting Layer
Right click on the layer to delete and click on
"Delete Layer", Another way is to drag and drop the layer that we
want to delete in the X icon in Layer Dialog Box (See Figure 8.20), the layer
will be deleted.
8.4.4 Merge Layers
Merge layers means making a single layer from
multiple layers. To do so use the CTRL+M shortcut key or click on the Image
Menu > Merge Visible Layers option.Flatten Image option in Image Menu also
merges all layers after removing Transparency.
Layer Merge Options:
Expanded as necessary : Sometimes
a layer may be larger than the size of
the picture so this option will increase the size of
the image according to the larger layer.
Clipped to image : Sometimes a
layer may be larger than the size of
the picture so this option will cut the
larger layer according to the size of
the picture.
Clipped to bottom layer : This
option clips and trims the remaining
layers according to the size of the
Bottom Layer.
8.4.5 Scaling a Layer
Scaling means changing the size of the layer. So use
the Layer Menu > Scale Layer option.Layer can be scaled by entering Width
and Height values as needed.The Cubic (Quality > Interpolation) method is
used to get the best results,
8.5 IMAGE EDITING TOOLS
GIMP provides many tools for working
on images that can be used to perform
different tasks on images. If the mouse
pointer (arrow) is held over a tool's icon for 2
seconds, the tool name, what the tool is used for, and the shortcut key will be
displayed in tooltip. Let's learn some tools:
Selection Tools : These tools are
used to select part of the active layer. Each
selection tool has its own set of features.They can also be selected from the
Tool Box.
Rectangle Select : This tool is used to select the part
of the layer in the rectangular shape.
Ellipse Select : This tool is used to select the
part of the layer in the elliptical shape.
Free Selection : This tool is also known as lasso
tool. This tool allows us to select a drawing note with a free hand. It is used
to select part of the image by drawing a picture with the help of a mouse
pointer,
Fuzzy Select : This tool is also known as the Magic
Wand tool. With this tool, the area is selected on the basis of “Similarity of
color". Usually the selections made with this tool are continuous, i.e.
connected parts.
By Color Select : This tool works similarly to the
Fuzzy (Magic Wand) tool, but any part of the picture that matches the color
similarity is selected.
Intelligent Scissors : This tool is used for
automatic selection where there is a contrast of color which means the two
parts are clearly separated. Clicking the mouse creates the Selection Nodes on
the edges of the area we want to select.
Eraser Tool : This tool is used to
delete the area of the active layer. If the image
has no alpha channel then this tool will erase the area with background color
If the image
has an alpha channel then this tool will erase the
area with transparent color and no color will be used.
Text Tool : This tool is used for
writing text on pictures. Use the Tools > Text
command to access this tool. This tool can also be activated by clicking on the
symbol A in the tool box.
When this tool is activated, a toolbar will appear
which allows us to use Bold, Italic,Underline, Strikethrough options.
To change the font, delete the font in the box and
start typing the name of the font we want to select, GIMP will start showing
the installed fonts in the computer through the Dropdown list from which we can
select the font.
Use CTRL + A to select all the text. The color box
can be used to change the color of the text. By Right clicking on text, we can
change the orientation of the text from given options.
(iv) Move Tool : This tool is used to
move the selections, i.e. textures, layers etc.To
use this tool, use the Tools > TransformTools > Move command or click on
the Move tool icon in the Tool Box.
If a layer is selected and we just want to move that
selection, use CTRL + ALT + Mouse Drag. The selected area will be moved and the
lower layer portion will appear instead,
(v) Align Tool : This tool is used to align layers
with image objects. To access this tool use the Tools > Transform Tools >
Align command or click on the Align tool icon in the Tool Box.For example, open
a picture and make a duplicate layer from the Layer Box (right click of the
layer> Duplicate Layer) and move it slightly and
left click on this duplicate layer. Now select
the Align tool. At the bottom left of the toolbox,
we will see some alignment tool options, click on any one we need and we will
get duplicate layer alignment.
(va) Scale Tool : This tool is used to scale layers
& objects. Use Tools > Transform Tools >Scale command or SHIFT + S to
use this tool.
Use File > Open As Layers, to open another image
as layer and it will open a new image as layer. Activate the Scale tool, we
will see a dialog box. We can scale the layer with the
mouse, to scale in Aspect Ratio hold down the Shift
button.
(vii) Blur / Sharpen Tool : This tool is used to
blur or sharpen any part or object of a picture. This tool uses a brush. This
tool enhances effect when repeatedly used in one place.The CTRL key is used to
toggle between Blur and Sharpen.
Use the Tools > Paint Tools > Blur / Sharpen
command to select this tool.
If any part or object is looking too strong, use
Blur to soften it. If we need to sharpen (increasing contrast) a part or
object, use Sharpen option.